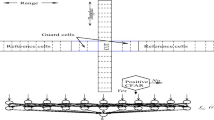
Abstract
In this paper the application of neural networks to Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) using a High Range Resolution radar is studied. Both Multi-layer Perceptrons (MLP) and Radial Basis Function Networks (RBFN) have been used. RBFNs can achieve very good results with a considerably small size of the training set, but they require a high number of radial basis functions to implement the classifier rule. MLPs need a high number of training patterns to achieve good results but when the training set size is higher enough, the performance of the MLP-based classifier approaches the results obtained with RBFNs, but with lower computational complexity. Taking into consideration the complexity of the HRR radar data, the choice between these two kind of neural networks is not easy. The computational capability and the available data set size should be considered in order to choose the best architecture. MLPs must be considered when a low computational complexity is required, and when a large training set is available; RBFNs must be used when the computational complexity is not constrained, or when only few data patterns are available.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. P. Jacobs, J. A. O’sullivan, “Automatic Target Recognition Using Sequences of High Resolution Radar Range-Profiles”, IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 36, no. 2, April, 2000.
C.R. Smith, P.M. Coggans, “Radar Target Identification”, IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 27–37, April 1993.
M. W. Roth, “Survey of Neural Network Technology for Automatic Target Recognition”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 1, no. 1, March, 1990.
K. Fukunaga, Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition, Boston, Academic Press, 1990.
R.A. Mitchell, et al., “Robust Statistical Feature Based Aircraft Identification”, IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 35, no. 3, 1077–1094, 1999.
D.E. Nelson, J.A. Starzyk, “Advance Feature Selection Methodology for Automatic Target Recognition”, Proceedings of the 29 th Southeastern Symposium on System Theory, 1997, pp. 24–28.
D.E. Nelson, J.A. Starzyk, “High Range Resolution Radar Signal Classification. A Partitioned Rough Set Approach.” Proceedings of the 33 rd Southeastern Symposium on System Theory, 2001, pp. 21–24.
E.A. Wan, “Neural Network Classification: A Bayesian Interpretation”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 303–305, December 1990.
S.K. Rogers et al., “Neural Networks for Automatic Target Recognition”, Neural Networks, vol. 8, no. 7/8, pp. 1153–1184, April 2000.
J.K. Aggarwal et al. “A Comparative Study of Three Paradigms for Object Recognition — Bayesian Statistics, Neural Networks and Expert Systems”, Advances in Image Understanding: A Festschrift for A. R., Computer Society Press, 1996.
J. W. Watterson, “An Optimun Multilayer Perceptron Neural Receiver for Signal Detection”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 1, no. 4, December, 1990.
D.W. Ruck, et al., “The Multilayer Perceptron as an Aproximation to a Bayes Optimal Discriminant Function”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 296–298, April 1990.
A. A. Kisienski, et al., “Low-frequency approach to target identification”, Proceedings of the IEEE, 63, pp. 1651–1659, 1975.
F. Rosenblatt, Principles of Neurodynamics, Spartan books, New York, 1962.
G. Cybenko, “Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function”, Mathematics of Control, Signals and Systems, vol. 2, pp. 303–314, 1989.
M.T. Hagan, M.B. Menhaj, “Training Feedforward Networks with the Marquardt Algorithm”, IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 989–993, November 1994.
S. Haykin, Neural networks. A comprehensive foundation (second edition), Prentice-Hall Inc., 1999.
C.M. Bishop, Neural networks for pattern recognition, Oxford University Press Inc., 1995.
F. Schwenker, H.A. Kestler, G. Palm, “Three learning phases for radial-basisfunction networks”, Neural Networks, Vol. 14, Issue 4–5, 2001, pp. 439–458.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gil-Pita, R., Jarabo-Amores, P., Vicen-Bueno, R., Rosa-Zurera, M. (2003). Neural Solutions for High Range Resolution Radar Classification. In: Mira, J., Álvarez, J.R. (eds) Artificial Neural Nets Problem Solving Methods. IWANN 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2687. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44869-1_71
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44869-1_71
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-40211-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-44869-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive