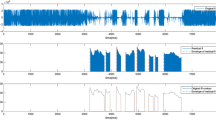
Abstract
This article suggests a based spectral normalization method, which purpose is to alleviate both the changing on peaks structure and on the flat zones of the speech spectrum, caused by additive noise. The proposed spectral normalization can be viewed as a noise estimate done in a frame by frame basis by assuming the clean database as lightly corrupted. This noise estimate is then used to restore both the peaked and the flat spectral zones of the speech spectrum. This algorithm was implemented over a baseline spectral normalisation method, which purpose is to emphasize the robustness in the regions of less energy of the speech spectrum, since in these regions the noise is more dominant.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lima, C., Almeida, Luís B. and Monteiro, João L.: Improving the Role of Unvoiced Speech Segments by Spectral Normalisation in Robust Speech Recognition. 7th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP’2002).
Raj, Biksha: Reconstruction of Incomplete Spectrograms for Robust Speech Recognition. Ph. D. Thesis, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lima, C., Tavares, A., Silva, C. (2003). Pitch Restoration for Robust Speech Recognition. In: Mamede, N.J., Trancoso, I., Baptista, J., das Graças Volpe Nunes, M. (eds) Computational Processing of the Portuguese Language. PROPOR 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 2721. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45011-4_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45011-4_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-40436-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45011-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive