Abstract
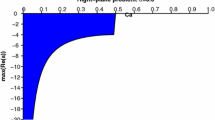
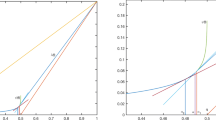
We consider a finite difference scheme, called Quickest, introduced by Leonard in 1979, for the convection-diffusion equation. Quickest uses an explicit, Leith-type differencing and third-order upwinding on the convective derivatives yielding a four-point scheme. For that reason the method requires careful treatment on the inflow boundary considering the fact that we need to introduce numerical boundary conditions and that they could lead us to instability phenomena. The stability region is found with the help of one of the most powerful methods for local analysis of the influence of boundary conditions - the Godunov-Ryabenkii theory.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum, H. R., Ciment, M., Davis, R. W. and Moore, E. F.: (1981), Numerical solutions for a moving shear layer in a swirling axisymmetric flow. Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Numerical Methods in Fluid Dyn. (ed. W. C. Reynolds & R. W. MacCormack). Lect. Notes in Physics 141 (1981) 74–79.
Davis, R. W. and Moore, E. F.: A numerical study of vortex shedding from rectangles. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 116 (1982) 475–506.
Godunov, S. K., Ryabenkii: Spectral criteria for the stability of boundary problems for non-self-adjoint difference equations. Uspekhi Mat. Nauk., 18, 3( 1963) (In Russian).
Gustafsson, B., Kreiss, H.-O. and Sundstrom, A.: Stability theory of difference approximations for mixed initial boundary value problems, II. Mathematics of Computation 26 (1972) 649–686.
Gustafsson, B., Kreiss, H.-O. and Oliger, J.: Time-dependent problems and difference methods, Wiley-Interscience (1995)
Johnson, R.W. and MacKinnon, R. J.: Equivalent versions of the Quick scheme for finite-difference and finite-volume numerical methods. Communications in applied numerical methods 8 (1992) 841–847.
Kreiss, H.-O.: Stability theory for difference approximations of mixed initial boundary value problems I. Mathematics of Computation 22 (1968) 703–714.
Leonard, B. P.: A stable and accurate convective modelling procedure based on quadratic upstream interpolation. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 19 (1979) 59–98.
Leonard, B. P. and Mokhtari, S.: Beyond first-order upwinding the ultra-sharp alternative for non-oscillatory steady-state simulation of convection. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 30 (1990) 729–766.
Morton, K. W. and Sobey, I. J.: Discretisation of a convection-diffusion equation. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis 13 (1993) 141–160.
Osher, S.: Stability of difference approximations of dissipative type for mixed initial-boundary value problems. Mathematics of computation 23 (1969) 335–340.
Richtmyer, R. D. and Morton, K.W.: Difference methods for initial-value problems,2nd edn, Wiley-Interscience, New York (1967)
Sod, G. A.: Numerical methods in fluid dynamics: initial and initial boundary-value problems, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1988)
Strikwerda, J.: Finite difference schemes and partial differential equations,Wadsworth & Brooks, California, (1989)
Trefethen, L. N.: Group velocity interpretation of the stability theory of Gustafsson, Kreiss and Sundstrom. Journal of Computational Physics 49 (1983) 199–217.
Trefethen, L. N.: Instability of difference models for hyperbolic initial boundary value problems. Comm. Pure and applied Mathematics 37 (1984) 329–367.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sousa, E. (2001). A Godunov-Ryabenkii Instability for a Quickest Scheme. In: Vulkov, L., Yalamov, P., Waśniewski, J. (eds) Numerical Analysis and Its Applications. NAA 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1988. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45262-1_86
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45262-1_86
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-41814-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45262-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive