Abstract
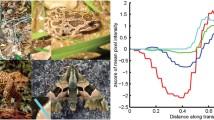
Some animals use counter-shadingin order to prevent their detection by predators. Counter-shading means that the albedo of the animal is such that its image has a flat intensity function rather than a convex intensity function. This implies that there might exist predators who can detect 3D objects based on the convexity of the intensity function. In this paper, we suggest a mathematical model which describes a possible explanation of this detection ability. We demonstrate the effectiveness of convexity based camouflage breaking using an operator (“D arg ”) for detection of 3D convex or concave graylevels. Its high robustness and the biological motivation make D arg particularly suitable for camouflage breaking. As will be demonstrated, the operator is able to break very strong camouflage, which might delude even human viewers. Beingnon-edg e-based, the performance of the operator is juxtaposed with that of a representative edge-based operator in the task of camouflage breaking. Better performance is achieved by D arg for both animal and military camouflage breaking.
Supported by the Minerva Minkowski center for geometry, and by grant from the Israel Academy of Science for Geometric Computing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. Copeland and M. M. Trivedi. Models and metrics for signature strength evaluation of camouflaged targets. Proceedings of the SPIE, 3070:194–199, 1997.
F. M. Gretzmacher, G. S. Ruppert, and S. Nyberg. Camouflage assessment considering human perception data. Proceedings of the SPIE, 3375:58–67, 1998.
Song Guilan and Tang Shunqing. Method for spectral pattern recognition of color camouflage. Optical Engineering, 36(6):1779–1781, June 1997.
Lu Huimin, Wang Xiuchun, Liu Shouzhong, Shi Meide, and Guo Aike. The possible mechanisms underlying visual anti-camouflage: a model and its real-time simulation. IEEE Trans. on Systems, Man & Cybernetics, Part A (Systems & Humans), 29(3):314–318, May 1999.
S. Marouani, A. Huertas, and G. Medioni. Model-based aircraft recognition in perspective aerial imagery. In Proc. of the Intl. Symposium on Comp. Vision, pages 371–376, USA, 1995.
S. P. McKee, S. N. J. Watamaniuk, J. M. Harris, H. S. Smallman, and D. G. Taylor. Is stereopsis effective in breaking camouflage? Vision Research, 37:2047–2055, 1997.
D. Osorio and M. V. Srinivasan. Camouflage by edge enhancement in animal coloraion patterns and its implications for visual mechanisms. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B, 244:81–85, 1991.
Adolf Portmann. Animal Camouflage, pages 30–35. The University of Michigan Press, 1959.
Daniel Reisfeld, Haim Wolfson, and Yehezkel Yeshurun. Context free attentional operators: the generalized symmetry transform. Intl. Journal of Computer Vision, pages 119–130, 1995.
Ariel Tankus, Yehezkel Yeshurun, and Nathan Intrator. Face detection by direct convexity estimation. Pattern Recognition Letters, 18:913–922, 1997.
I. V. Ternovskiy and T. Jannson. Mapping-singularities-based motion estimation. Proceedings of the SPIE, 3173:317–321, 1997.
Abbott H. Thayer. An arraignment of the theories of mimicry and warning colours. Popular Science Monthly, N.Y., pages 550–570, 1909.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tankus, A., Yeshurun, Y. (2000). A Model for Visual Camouflage Breaking. In: Lee, SW., Bülthoff, H.H., Poggio, T. (eds) Biologically Motivated Computer Vision. BMCV 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1811. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45482-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45482-9_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67560-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45482-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive