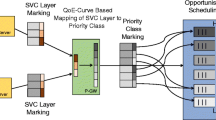
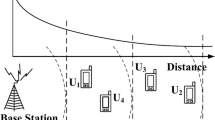
Abstract
In an adaptive multimedia environment, each of the multimedia substreams (i.e. video, audio and data) has its own distinct quality of service (QoS) requirements (e.g. cell loss rate, delay, jitter, etc.). These requirements constitute a certain QoS level. In contrast to the static approach, each substream declares a preset range of acceptable QoS levels (e.g., high, medium, low) instead of just a single one. This range of QoS levels is defined in a user-defined profile (UDP). In this paper, we suggest a channel borrowing algorithm based on an adaptive QoS platform. In a channel borrowing algorithm, an acceptor cell that has used all its nominal channels can borrow free channels from its neighboring cells (candidate donors) to accommodate new calls. In our suggested algorithm, an acceptor cell can borrow from any neighboring (donor) cell as long as this donor cell has some channels available after satisfying a minimum QoS (minQ) level defined in the UDP. A donor cell assigning QoS levels (to calls under its coverage) higher than the minQ levels defined in the UDP will declare those channels as available for borrowing by other acceptor cells. When a channel is borrowed, several other cells are prohibited from using it due to channel locking. The proposed channel borrowing algorithm differs in the way a free channel is selected from a donor cell to be borrowed by an acceptor cell. The criteria for choosing the free channel include not only the number of free channels but also the QoS levels in the donor cell. The criteria is also extended to include the effect of channel locking on the number of free channels and the QoS levels on the locked cells.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
References
Sherif, M.R., Habib, I.W., Naghshineh, M., Kermani, P.: Adaptive Allocation of Resources and Call Admission Control in Wireless ATM Using Genetic Algorithms. IEEE Journal Select. Areas Comm. February, 2000.
Michalewicz, Z.: Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures = Evolution Programs. 3rd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York (1996).
Farouque, S.: Cellular Mobile Systems Engineering. Artech House, Boston, 1996.
Holtzman, J., Goodman, D.: Wireless Communications, Future Directions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1993.
Rappaport, F.: Wireless Personal Communications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1993.
Anderson, L.: A Simulation Study of Sonle Dynamic Channel Assignment Algorithms in High Capacity Mobile Telecommunications System. IEEE Trans. On Vehicular Tech. Vol VT-22, 1973, p.210.
Garret, M., Fernandez, A.: Variable Bit Rate Video Bandwidth Trace Using MPEG Code. Bellcore, ftp://ftp.bellcore.com/pub/vbr.video.trace/, 1992.
Garret, M.: Contributions Towards Real-Time Services on Packet Networks. Ph.D. Dissertation. Columbia University. May 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sherif, M., Habib, I., Naghshineh, M., Kermani, P. (2000). Adaptive QoS Platform in Multimedia Networks. In: Pujolle, G., Perros, H., Fdida, S., Körner, U., Stavrakakis, I. (eds) Networking 2000 Broadband Communications, High Performance Networking, and Performance of Communication Networks. NETWORKING 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1815. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45551-5_73
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45551-5_73
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67506-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45551-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive