Abstract
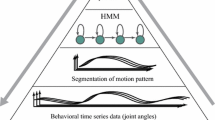
In this paper we claim that meaningful representations can be learned by programs, although today they are almost always designed by skilled engineers. We discuss several kinds of meaning that representations might have, and focus on a functional notion of meaning as appropriate for programs to learn. Specifically, a representation is meaningful if it incorporates an indicator of external conditions and if the indicator relation informs action. We survey methods for inducing kinds of representations we call structural abstractions. Prototypes of sensory time series are one kind of structural abstraction, and though they are not denoting or compositional, they do support planning. Deictic representations of objects and prototype representations of words enable a program to learn the denotational meanings of words. Finally, we discuss two algorithms designed to find the macroscopic structure of episodes in a domain-independent way.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philip E. Agre and David Chapman. Pengi: An implementation of a theory of activity. In Proceedings of the Sixth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 268–272, Seattle, Washington, 1987. American Association for Artificial Intelligence.
James F. Allen. An interval based representation of temporal knowledge. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 221–226, San Mateo, CA, 1981. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc.
Dana H. Ballard, Mary M. Hayhoe, and Polly K. Pook. Deictic codes for the embodiment of cognition. Computer Science Department, University of Rochester.
D.H. Ballard. Reference frames for animate vision. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligenc. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Inc., 1989.
Paul Bloom. How Children Learn the Meanings of Words. MIT Press, 2000.
Paul Cohen. Fluent learning: Elucidating the structure of episodes. In Proceedings of Fourth Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis. Springer, 2001.
Paul Cohen and Niall Adams. An algorithm for segmenting categorical time series into meaningful episodes. In Proceedings of Fourth Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis. Springer, 2001.
Paul R. Cohen and Mary Litch. What are contentful mental states? dretske’s theory of mental content viewed in the light of robot learning and planning algorithms. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1999.
Bénédicte de Boysson-Bardies. How Language Comes to Children. MIT Press, 2001.
Daniel Dennett. Do it yourself understanding. In Daniel Dennett, editor, Brainchildren, Essays on Designing Minds. MIT Press and Penguin, 1998.
Fred Dretske. Knowledge and the Flow of Information. Cambridge University Press, 1981. Reprinted by CSLI Publications, Stanford University.
Fred Dretske. Explaining Behavior: Reasons in a World of Causes. MIT Press, 1988.
Joseph B. Kruskall and Mark Liberman. The symmetric time warping problem: From continuous to discrete. In Time Warps, String Edits and Macromolecules: The Theory and Practice of Sequence Comparison. Addison-Wesley, 1983.
B. Kuipers. The spatial semantic hierarchy. Artificial Intelligence, 119:191–233, 2000.
George Lako.. Women, Fire, and Dangerous Things. University of Chicago Press, 1984.
D. B. Lenat. Cyc: Towards programs with common sense. Communications of the ACM, 33(8), 1990.
D. B. Lenat and R. V. Guha. Building large knowledge-based systems: Representation and inference in the Cyc project. Addison Wesley, 1990.
Paola Sebastiani, Marco Ramoni and Paul Cohen. Bayesian clustering by dynamics. Machine Learning, to appear(to appear):to appear, 2001.
John McCarthy. Situations, actions and causal laws. Stanford Artificial Intelligence Project: Memo 2, also, http://www.formal.stanford.edu/jmc/mcchay69/ mcchay69. htm, 1963.
J. T. Oates. Grounding Knowledge in Sensors: Unsupervised Learning for Language and Planning. PhD thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of Massachusetts, 2001.
Tim Oates, Paul R. Cohen, Marc S. Atkin and Carole R. Beal. NEO: Learning conceptual knowledge by sensorimotor interaction with an environment. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Autonomous Agents, pages 170–177, 1997.
David Pierce and Benjamin Kuipers. Map learning with uninterpreted sensors and effectors. Artificial Intelligence Journal, 92:169–229, 1997.
Marco Ramoni, Paola Sebastiani, and Paul Cohen. Multivariate clustering by dynamics. In Proceedings of the Seventeenth National Conference on AI, pages 633–638. AAAI Press/The MIT Press, 2000.
E. Rosch and C. B. Mervis. Family resemblances: Studies in the internal structure of categories. Cognitive Psychology, 7:573–605, 1975.
Robert St. Amant and Paul R. Cohen. Intelligent Support for Exploratory Data Analysis. The Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 1998.
Robert St. Amant and Paul R. Cohen. Interaction With a Mixed-Initiative System for Exploratory Data Analysis. Knowledge-Based Systems, 10(5):265–273, 1998.
Luc Steels. The Talking Heads Experiment: Volume I. Words and Meanings. Laboratorium, Antwerpen, 1999. This is a museum catalog but is in preparation as a book.
Paul Cohen, Tim Oates, Matthew Schmill. Identifying qualitatively different outcomes of actions: Gaining autonomy through learning. In Proceedings Fourth International Conference on Autonomous Agents, pp 110–111. ACM, 2000.
Paul Cohen, Tim Oates, Matthew Schmill. A method for clustering the experience of a mobile robot that accords with human judgments. In Proceedings of Seventeenth National Conference, pp. 846–851. AAAI Press/The MIT Press, 2000.
Paul Utgo. and Paul R. Cohen. Applicability of reinforcement learning. In The Methodology of Applying Machine leraning Problem Definition, Task Decompostion and Technique Selection Workshop, ICML-98, pages 37–43, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cohen, P.R., Oates, T., Adams, N., Beal, C.R. (2001). Robot Baby 2001. In: Abe, N., Khardon, R., Zeugmann, T. (eds) Algorithmic Learning Theory. ALT 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 2225. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45583-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45583-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42875-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45583-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive