Abstract
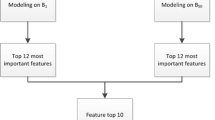
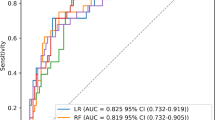
Diagnosis of community acquired legionella pneumonia (CALP) is currently performed by means of laboratory techniques which may delay diagnosis several hours. To determine whether ANN can categorize CALP and non-legionella community-acquired pneumonia (NLCAP) and be standard for use by clinicians, we prospectively studied 203 patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) diagnosed by laboratory tests. Twenty one clinical and analytical variables were recorded to train a neural net with two classes (LCAP or NLCAP class). In this paper we deal with the problem of diagnosis, feature selection, and ranking of the features as a function of their classification importance, and the design of a classifier the criteria of maximizing the ROC (Receiving operating characteristics) area, which gives a good trade-off between true positives and false negatives. In order to guarantee the validity of the statistics; the train-validation-test databases were rotated by the jackknife technique, and a multistarting procedure was done in order to make the system insensitive to local maxima.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Woodhead. Community-acquired pneumonia guidelines. An international comparison. A view from Europe. Chest 1998.
R Blanquer, R Borrás, D Auffal, P Morales, R Menendez, I Subias, L Herrero, J Redon, J Pascual. Aetiology of community acquired pneumonia in Valencia, Spain: a multicentre prospective study. Thorax 1991.
J Aubertin, F Dabis, J Fleurette, N Bornstein, R Salomon, E Brottier, J Brune, P Vincent, J Migueres, A Jover, C Boutin. Prevalence of legionellosis among adults: A study of communityacquired pneumonia in France. Infection 1987.
N Sopena, M Sabria, ML Pedro-Botet, JM Montero, L Matas, J Dominguez, JM Modol, P Tudela, V Ausina, M Foz. Prospective study of Community-Acquired Pneumonia of Bacterial Etiology in Adults Eur J Microbiol Inf Dis (in press).
M.E. Aguero-Rosenfeld, P.H. Edelstein, Retrospective evaluation of the Du Pont radionimmunoassay kit for detection of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigenuria in humans. Journal of clinical microbiology. 1988.
JA Dominguez, JM Manterolas, R Blavia, N Sopena, FJ Belda, E Padilla, M Gimenez, M Sabrià, J Morera, V Ausina. Detection of Legionella pneumophila Serogroup 1 Antigen Antigen in Nonconcentrated Urine and Urine Concentrated by Selective Ultrafiltration. Journal Clinical Microbiology 1996
A.E. F iore, J.P. Nuorti, O.S. Levine, A Marx, A.C. Weltman, S. Yeager, R.F. Benson, J Prucker, P.H. Edelstein, P Green, Sh R. Zaki, B.S. Fields, J.C. Butler. Epidemic Legionnaires’ Disease two decades later: Old Sources, new diagnostic methods. Clinical infectious diseases. 1998.
M. Woodhead. Management of pneumonia in the outpatient setting. Seminars in respiratory infections. 1998.
M.S. Niederman. Community-acquired pneumonia. A North American perspective. Chest 1998.
N Asada, K. Doi, H. MacMahon, S.M. Montner, M.L. Giger, Ch. Abe, Y. Wu. Potential usefulness of an artificial neural network for differential diagnosis of interstitial lung diseases. Pilot study. Radiology 1990.
J. Baker, P. Kornguth, J. Lo, M. Williford, C. Floyd, Breast Cancer: prediction with artificail neural networks based on BI-RADS standadized lexicon. Radiology 1995.
J.A. Scott. Neural network analysis of ventilation-perfusion lung scans. Radiology 1993.
El-Solh AA, MJ Mador,, E. Ten-Brock, DW Shucard, M Abul-Khoudoud, BJ Grant. Validity of neural network in sleep apnea. Sleep 1999.
N Sopena. M Sabrià-Leal, M.L Pedro-Botet, E padilla, J Dominguez, J Morera, P Tudela. Comparative study of the clinical presentation of legionella pneumonia and other commnunityacquired pneumonias. Chest 1998
CH.M. Bishop. Neural Networks for pattern recognition. Clarendon press. Oxford. 1995.
B. Parmanto, P. Munro, Diagnosis of hepatoma by committee. NIPS 94 Post Conference workshop: Neural Network Applications in Medicine, December 1994.
Lippman, L Kukolich, D. Shahian. Predicting the risk of complications in coronary arthery bypass operations using neural networks, in G. Tesauro, D. Touretzky and T. Leen (editors) Advances in Neural Infomation Processing Systems 7, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
G.D. Fang, M Fine, J Orloff. New and emerging etiology for community acquired pneumonia with applications for therapy: prospective multicenter study of 359 cases. Medicine 1990.
H. Burke, D. Rosen, P. Goodman, Comparing the prediction accuracy of artificial neural networks and other statistical models for breast cancer survival. NIPS*94 Post-Conference Workshop: Neural Network Applications in Medicine, Vail, Colorado, USA (2-3 December 1994).
W. Baxt, J Skora. Prospective validation of artificial neural network trained to identify acute myocardial infarction. The Lancet 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Monte, E., Soléi Casals, J., Antonio Fiz, J., Sopena, N. (2001). Feature Selection, Ranking of Each Feature and Classification for the Diagnosis of Community Acquired Legionella Pneumonia. In: Mira, J., Prieto, A. (eds) Bio-Inspired Applications of Connectionism. IWANN 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2085. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45723-2_43
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45723-2_43
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42237-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45723-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive