Abstract
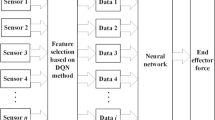
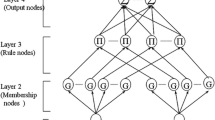
This paper deals with the methodological approach for the development and implementation of force-position control for robotized systems. We propose a first approach based on neural network to treat globally the problem of the adaptation of robot behavior to various classes of tasks and to actual conditions of the task where its parameters may vary. The obtained results are presented and analyzed in order to prove the efficiency of the proposed approach
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.Y. Amirat. Contribution à la commande de haut niveau de processus robotisés et à l’utilisation des concepts de l’IA dans l’interaction robot-environnement. PHD thesis University Paris XII, Janvier 1996.
A.G. Barto and P. Anandan. Pattern recognizing stochastic learning automata. In IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 360–375, 1985.
N. Chatenet and H. Bersini. Economical reinforcement learning for non stationary problems. In Lecture notes in Computer Science 1327, Artificial Neural Network ICANN’97, 7th International Conference Lausanne, Switzerland Proceeding, pp. 283–288, October 1997.
G. Cybenco. Approximations by superposition of sigmoidal function. In Advanced Robotics, Intelligent Automation and Active Systems, pp 373–378, Bremen, September 15-17, 1997.
E. Dafaoui and Y. Amirat and J. Pontnau and C. François. Analysis and Design of a six DOF Parallel Manipulator. Modelling, Singular Configurations and Workspace. In IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, vol. 14, pp. 78–92, Février 1998.
J.C. Doyle and K. Glover and P.P. Khargonecker and B.A. Francis. State space solutions to the standard H2 and H∞. In IEEE Trans. On Automat. Contr., vol. 34, pp. 831–847, 1989.
B. Karan. Robust position/force control of robot manipulator in contact with linear dynamic environment, In Proc. of the Third ECPD International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Intelligent Automation and Active Systems, pp 373–378, Bremen, September 15-17, 1997.
O. Khatib. A unified approach to motion and force control of robot manipulators. In IEEE J. Robot Automation, 43–53, 1987.
S. Komada and al.. Robust force control based on estimation of environment. In IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1362–1367, Nice, France, May,1992.
L. Laval and N.K. M’sirdi. Modeling, identification and robust force control of hydraulic actuator using H∞?approach. In Proceeding of IMACS, Berlin, Germany, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Saadia, N., Amirat, Y., Pontnaut, J., Ramdane-Cherif, A. (2001). Neural Adaptive Force Control for Compliant Robots. In: Mira, J., Prieto, A. (eds) Bio-Inspired Applications of Connectionism. IWANN 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2085. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45723-2_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45723-2_52
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42237-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45723-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive