Abstract
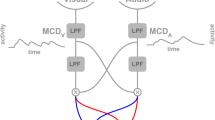
There is experimental evidence forthe separate processing of different features that belong to a complex visual stimulus in different brain areas. The temporal correlation betw een neurons responding to each of these features is often thought to be the binding element. In this paper we present a neural netw ork that separately processes objects and positions, in whic hthe association between each stimulus and its spatial location is done by means of temporal correlation. Pools of neurons responding to the stimulus and its corresponding location tend to synchronize their responses, while other stimuli and other locations tend to activate in different time frames.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, L.F.: Firing rate models for neural populations. In Benhar, O., Bosio, C., Del Giudice, P., Tabet, E., eds. Neural Networks: From Biology to High-Energy Physics (ETS Editrice, Pisa, 1991) 179–196
Deco, G., Zihl, J.: Top-down selective visual attention: a neurodynamical approach. Vis. Cog. 8 (2001) 118–139
Duncan, J., Humphreys, G.: Visual search and stimulus similarity. Psychol. Rev. 96 (1989) 433–458
Gray, C.M.: Synchronous oscillations in neuronal systems: mechanisms and function. J. Comput. Neurosci. 1 (1994) 11–38
von der Malsburg, C.: The correlation theory of brain function. In Domany, E., van Hemmen, J.L., Schulten, K., eds. Models of Neural networks II (Springer, Berlin, 1994) 95–119
Usher, M., Niebur, E.: Modelling the temporal dynamics of IT neurons in visual search: a mechanism for top-down selective attention. J. Cog. Neurosci. 8 (1996) 311–327
Wilson, H.R., Cowan, J.D.: Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys. J. 12 (1972) 1–24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lago-Fernández, L.F., Deco, G. (2001). Simultaneous Parallel Processing of Object and Position by Temporal Correlation. In: Mira, J., Prieto, A. (eds) Bio-Inspired Applications of Connectionism. IWANN 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2085. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45723-2_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45723-2_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42237-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45723-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive