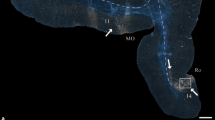
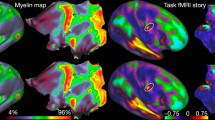
Abstract
Cytoarchitectonic fields of the human neocortex are defined by characteristic variations in the composition of a general six-layer structure. It is commonly accepted that these fields correspond to functionally homogeneous entities. Diligent techniques were developed to characterize cytoarchitectonic fields by staining sections of post-mortem brains and subsequent statistical evaluation. Fields were found to show a considerable interindividual variability in extent and relation to macroscopic anatomical landmarks. With upcoming new high-resolution magnetic resonance (MR) scanning protocols, it appears worthwile to examine the feasibility of characterizing the neocortical fine-structure from anatomical MR scans, thus, defining cytoarchitectonic fields by in-vivo techniques.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amunts, K., Schleicher, A., Bürgel, U., Mohlberg, H., Uylings, H.B.M., Zilles, K.: Broca’s region revisited: cytoarchitecture and intersubject variability. J. Comp. Neurol. 412 (1999), 319–341.
Brodmann, K.: Die vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde. Barth, Leipzig (1909).
Garland, M., Heckbert, P.S. Optimal triangulation and quadric-based surface simplification. J. Comp. Geom. 14 (1999), 49–65.
Hopf, A.: Registration of the myeloarchitecture of the human frontal lobe with an extinction method. J. Hirnforschung 10 (1968), 259–269.
Hellwig, B.: How the myelin picture of the human cerebral cortex can be computed from cytoarchitectonic data. A bridge between von Economo and Vogt. J. Hirnforschung 34 (1993), 387–402.
Kruggel, F., von Cramon D.Y.: Measuring the neocortical thickness. In: Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (Hilton Head), pp. 154–161. IEEE Press, Los Alamitos (2000).
Lee, J.H., Garwood, M., Menon, R., Adriany, G., Andersen, P., Truwit, C.L., Ugurbil, K.: High contrast and fast three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging at high fields. Magn. Reson. Med. 34 (1995), 308–312.
MacDonald, D, Kabani, N., Avis, D., Evans, A.C.: Automated 3-D extraction of inner and outer surfaces of cerebral cortex from MRI. Neuroimage 12 (2000), 340–356.
Payne, B.A., Toga, A.W.: Surface mapping of brain function on 3D models. IEEE CGA 10 (1990), 33–41.
Pham, D.L., Prince J.L.: An adaptive fuzzy segmentation algorithm for threedimensional magnetic resonance images. In: Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI’99), LNCS 1613, pp. 140–153. Springer, Heidelberg (1999).
Rademacher, J., Caviness, V.S., Steinmetz, H., Galaburda, A.M.: Topographical variation of the human primary cortices: implications for neuroimaging, brain mapping and neurobiology. Cereb. Cortex 3 (1995), 313–329.
Rajkowska, G., Goldman-Rakic, P.S.: Cytoarchitectonic definition of prefrontal areas in the normal human cortex: II. Variability in locations of areas 9 and 46 and relationship to the Talairach coordinate system. Cereb. Cortex 5 (1995), 323–337.
Schleicher, A., Zilles, K.: A quantitative approach to cytoarchitectonics: analysis of structural inhomogeneities in nervous tissue using an image analyzer. J. Microscopy 157 (1990), 367–381.
ptvon Economo, C.: Zellaufbau der Grosshirnrinde des Menschen. Springer-Verlag, Wien (1927).
Zilles, K., Werners, R., Büsching, U., Schleicher, A.: Ontogenesis of the laminar structure in areas 17 and 18 of the human visual cortex. Anat. Embryol. 174 (1986), 339–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kruggel, F., Wiggins, C.J., von Cramon, D.Y., Brückner, M.K., Arendt, T. (2001). Analyzing the Neocortical Fine-Structure. In: Insana, M.F., Leahy, R.M. (eds) Information Processing in Medical Imaging. IPMI 2001. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2082. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45729-1_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45729-1_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-42245-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45729-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive