Abstract
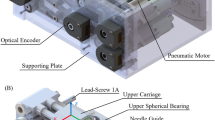
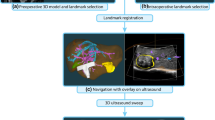
The purpose of this study was to evaluate our ability to insert magnetically tracked needles into liver phantom tumors which move simulating physiologic respiration. First, a novel image-guided platform based on a new magnetic tracking device (AURORA™) was constructed. Second, an accuracy evaluation of a compatible magnetically tracked needle (MagTrax) was performed. Finally, 16 liver tumor punctures were attempted using only the image-guided platform for guidance. The inherent MagTrax needle positional error was 0.71±0.43 mm in the non-surgical laboratory setting. Successful puncture of liver tumors was achieved in 14 of 16 attempts (87.5%) by two users. The average time of each procedure was short (163±57 seconds.) The system adequately displayed the moving liver allowing for tumor target visualization and targeting. The AURORA based navigation platform and the compatible MagTrax needle appear promising for more rigorous phantom accuracy studies and in vivo tumor puncture testing in a respiring animal.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
- Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
- Total Procedure Time
- Magnetic Tracking
- Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement
- Liver Motion
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
References
Davies, S.C., et al., Ultrasound quantitation of respiratory organ motion in the upper abdomen. Br J Radiol, 1994. 67(803): p. 1096–102.
Suramo, I., M. Paivansalo, and V. Myllyla, Cranio-caudal movements of the liver, pancreas and kidneys in respiration. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh), 1984. 25(2): p. 129–31.
Herline, A.J., et al., Surface registration for use in interactive, image-guided liver surgery. Comput Aided Surg, 2000. 5(1): p. 11–7.
Herline, A.J., et al., Image-guided surgery: preliminary feasibility studies of frameless stereotactic liver surgery. Arch Surg, 1999. 134(6): p. 644–9; discussion 649-50.
Zaaroor, M., et al., Novel magnetic technology for intraoperative intracranial frameless navigation: in vivo and in vitro results. Neurosurgery, 2001. 48(5): p. 1100–7
Gepstein, L., G. Hayam, and S.A. Ben-Haim, A novel method for nonfluoroscopic catheter-based electroanatomical mapping of the heart. In vitro and in vivo accuracy results. Circulation, 1997. 95(6): p. 1611–22.
Solomon, S.B., et al., TIPS placement in swine, guided by electromagnetic real-time needle tip localization displayed on previously acquired 3-D CT. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 1999. 22(5): p. 411–4.
Howard, M.H., et al., An electronic device for needle placement during sonographically guided percutaneous intervention. Radiology, 2001. 218(3): p. 905–11.
Krombach, G.A., et al., US-guided nephrostomy with the aid of a magnetic field-based navigation device in the porcine pelvicaliceal system. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2001. 12(5): p. 623–8.
Wood, B.J., et al., Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with three-dimensional position sensor guidance. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2001 (in print).
Cleary, K., et al. Development of a Liver Respiratory Motion Simulator to Investigate Magnetic Tracking for Abdominal Interventions. in SPIE Medical Imaging. 2002. San Diego, CA.
Banovac, F., et al. Design and Construction of a Liver Phantom for CT Imaging and Interventions that Simulates Liver Motion Seen During Respiration. in Radiologic Society of North America. 2001. Chicago, IL.
Cleary, K., et al. Feasibility of Magnetic Tracking for Image-Guided Abdominal Interventions Based on a Liver Respiratory Motion Simulator. submitted to IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. 2002. Washington, DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Banovac, F., Glossop, N., Lindisch, D., Tanaka, D., Levy, E., Cleary, K. (2002). Liver Tumor Biopsy in a Respiring Phantom with the Assistance of a Novel Electromagnetic Navigation Device. In: Dohi, T., Kikinis, R. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention — MICCAI 2002. MICCAI 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2488. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45786-0_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45786-0_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-44224-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-45786-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive