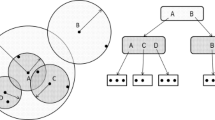
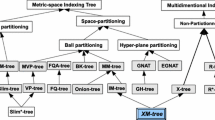
Abstract
In this paper we present the Slim-tree, a dynamic tree for organizing metric datasets in pages of fixed size. The Slim-tree uses the “fat-factor” which provides a simple way to quantify the degree of overlap between the nodes in a metric tree. It is well-known that the degree of overlap directly affects the query performance of index structures. There are many suggestions to reduce overlap in multidimensional index structures, but the Slim-tree is the first metric structure explicitly designed to reduce the degree of overlap.
Moreover, we present new algorithms for inserting objects and splitting nodes. The new insertion algorithm leads to a tree with high storage utilization and improved query performance, whereas the new split algorithm runs considerably faster than previous ones, generally without sacrificing search performance. Results obtained from experiments with real-world data sets show that the new algorithms of the Slim-tree consistently lead to performance improvements. After performing the Slim-down algorithm, we observed improvements up to a factor of 35% for range queries.
On leave at Carnegie Mellon University. His research has been funded by FAPESP (São Paulo State Foundation for Research Support - Brazil, under Grants 98/05556-5).
On leave at Carnegie Mellon University. Her research has been funded by FAPESP (São Paulo State Foundation for Research Support - Brazil, under Grants 98/0559-7).
His work has been supported by Grant No. SE 553/2-1 from DFG (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft).
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grants No. IRI-9625428, DMS-9873442, IIS-9817496, and IIS-9910606, and by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency under Contract No. N66001-97-C-8517. Additional funding was provided by donations from NEC and Intel. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation, DARPA, or other funding parties.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaede, V., Gunther, O.: Multidimensional Access Methods. ACM Computing Surveys, 30(2) (1998) 170–231.
Ciaccia, P., Patella, M., Zezula, P.: M-tree: An Efficient Access Method for Similarity Search in Metric Spaces, VLDB (1997) 426–435.
Burkhard, W.A., Keller R.M.: Some Approaches to Best-Match File Searching. CACM 16(4) (1973) 230–236.
Uhlmann, J.K.: Satisfying General Proximity/Similarity Queries with Metric Trees. IPL 40(4) (1991) 175–179.
Yianilos, P. N.: Data Structures and Algorithms for Nearest Neighbor Search in General Metric Spaces. ACM SODA (1993) 311–321.
Baeza-Yates, R.A., Cunto, W., Manber, U., Wu S.: Proximity Matching Using Fixed-Queries Trees. CPM, (1994) 198–212.
Bozkaya, T., Özsoyoglu, Z.M. Distance-Based Indexing for High-Dimensional Metric Spaces, ACM-SIGMOD (1997) 357–368.
Brin S.: Near Neighbor Search in Large Metric Spaces, VLDB (1995) 574–584.
Guttman A.: R-Tree: Adynamic Index Structure for Spatial Searching. ACMSIGMOD (1984) 47–57.
Ciaccia, P., Patella, M.: Bulk Loading the M-tree. ADC’98 (1998) 15–26.
Kruskal Jr., J.B.: On the Shortest Spanning Subtree of a Graph and the Traveling Salesman Problem. Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. (7) (1956) 48–50.
Ciaccia, P., Patella, M., Rabitti, F., Zezula, P.: Indexing Metric Spaces with M-tree. Proc. Quinto convegno Nazionale SEBD (1997).
Faloutsos, C., Kamel, L.: Beyond Uniformity and Independence: Analysis of R-tree Using the Concept of Fractal Dimension. ACM-PODS (1994) 4–13.
Traina Jr., C., Traina, A., Faloutsos, C.: Distance Exponent: A New Concept for Selectivity Estimation in Metric Trees. CMU-CS-99-110 Technical Report (1999).
Sellis, T., Roussopoulos, N., Faloutsos, C.: The R+-tree: A Dynamic Index for Multidimensional Objects. VLDB (1987) 507–518.
Beckmann, N., Kriegel, H.-P., Schneider R., Seeger, B.: The R*-tree: An Efficient and Robust Access Method for Points and Rectangles. ACM-SIGMOD (1990) 322–331.
Berchtold, S., Böhm, C., Keim, D.A., Kriegel, H.-P.: A Cost Model For Nearest Neighbor Search in High-Dimensional Data Space. ACM-PODS (1997) 78–86.
Wactlar, H.D., Kanade, T., Smith, M.A., Stevens, S.M.: Intelligent Access to Digital Video: Informedia Project. IEEE Computer, 29(3) (1996) 46–52.
Visionics Corp.-Available at http://www.visionics.com/live/frameset.html (12-Feb-1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Traina, C., Traina, A., Seeger, B., Faloutsos, C. (2000). Slim-Trees: High Performance Metric Trees Minimizing Overlap between Nodes. In: Zaniolo, C., Lockemann, P.C., Scholl, M.H., Grust, T. (eds) Advances in Database Technology — EDBT 2000. EDBT 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1777. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-46439-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-46439-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67227-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46439-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive