Abstract
A neural net based methodology for phonetic classification with telephone speech in spanish is described. Because of the high computational requirements and error rates obtained by using a unique Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), a different approach is needed in order to improve the performance of the task.
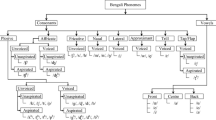
In the proposed approach, the basic set of spanish phonemes is separated in groups according to articulation mode criteria and a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) is trained for every phonetic group, along with a front-end MLP whose function is to distinguish between phonetic groups.
Experiments were made with speakers from the telephone speech OGI corpus in order to tune the parameters of the MLPs, as well as to evaluate the performance of the proposed methodology under different representations of the speech signal and modifying some parameters of the ANNs such as learning rate, topology and transfer functions.
Results of the experiments are summarized and some remarks are passed. Both, results and remarks, are based on the analysis of the confusion matrixes obtained when the trained MLPs are used to classify speech used for training as well as speech data that the MLPs haven’t “seen”.
The authors wish to thank the Center for Spoken Language Understanding (CSLU) at the OGI for their kindness in providing the corpus for this worh.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourlard, H. A. and Morgan N. “Connectionist Speech Recognition: A Hybrid approach”. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell Massachusetts, USA, 1994, 312 p. 373, 378
Morgan, N. y Bourlard, H. (1995). “Continuous speech recognition”. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, May 1995, pp. 25–41. 374, 376, 384
Lander, T., (1996). “The CSLU Labeling Guide”. Internal Report. Center for Spoken Language Understanding (CSLU) of the Oregon Graduate Institute of Science and Technology, Beaverton, Oregon, USA, 93 p. 374, 375, 376, 379
Hermansky, H., (1990). “Perceptual linear predictive (PLP) analysis of speech”. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, Vol. 87, No. 4, pp. 1738–1752. 376
Tebelskis, J. (1995). “Speech recognition using neural networks”. Ph. D. thesis. School of computer science, Carnegie Mellon University. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, U.S.A. 180 p. 378, 381
Quilis, A. “Fonética acústica de la lengua española”. Serie Biblioteca Románica Hispánica. Editorial Gredos. Madrid, España, 1988, 502 p. 378
Fuentes, J. L. “Gramática moderna de la lengua española” Serie biblioteca didáctica. Editorial Universitaria, Santiago de Chile, 1991, 520 p. 378, 379
Jordan, M. I. and Jacobs, R. A., (1993). “Hierarchical mixture of experts and the EM algorithm”. Technical Report 9301, Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), U.S.A., 34 p. 378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Silva-Varela, H., Cardeñoso-Payo, V. (1998). Phonetic Classification in Spanish Using a Hierarchy of Specialized ANNs. In: Coelho, H. (eds) Progress in Artificial Intelligence — IBERAMIA 98. IBERAMIA 1998. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 1484. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-49795-1_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-49795-1_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-64992-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-49795-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive