Abstract
This paper presents the results of a study which aimes at defining an error correcting scheme matched to the troposcatter (Rayleigh) channel, which would permit to insure very high reliability links for digital data transmissions.
Forward Error Correction (FEC) and interleaving methods are not compliant to the high variability of the fades durations, and insuring an excellent quality by these means is quite impossible, even with very efficient, complex and expensive codes associated with deep interleavers.
Usual Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) systems are not satisfactory either, because of three reasons at least. First, an error detecting code would be overwhelmed and the retransmissions would be too numerous ; moreover, an error burst may be undetected and the residual BER can be relatively high. Secondly, each retransmission request increases the delay which may become incompatible with telephony applications or even diverge. In the third place, ARQ systems usualy assume that the feedback channel is noiseless ; in our applications the backward channel is also a Rayleigh channel, and the acknowledgement may sometimes be erased by fades.
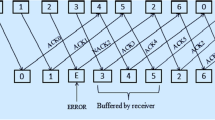
We propose a hybrid ARQ+FEC system using a long constraint length convolutional code and the sequential decoding algorithm (Stack or MultiStack Algorithm), associated with a modified Go-Back-N ARQ protocol, able to cope with a two-way noisy channel. The data are sent in a continuous stream of blocks, according to an adaptive frame structure permitting to catch up the transmission delay due to the repeat requests. The protocol control is achieved by a modified HDLC structure.
The features of this system will be given for a particular implementation example : for a data rate of 1 Mbit/s and a rate 1/2 convolutional code of constraint length 35, the effective throughput rate is about 1/4, and a zero-error transmission is assured with a bounded transmission delay (<250 ms) as soon as the average SNR is better than 1 dB in threefold diversity.
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
V. References
Shu Lin, D.J. Costello, ”Error Control Coding” Prentice Hall 1983
Shu Lin, P.S. Yiu, ”An Efficient Error Control Scheme for Satellite Communications”, IEEE Trans on Comm. March 1980
H. Yamamoto, K. Itoh, ”Viterbi Decoding Algorithm for Convolutional Codes with Repeat Request”, IEEE Trans on Inf. Theory, Sept. 1980
A. Drukarev, D.J. Costello, ”Hybrid ARQ Error Control Using Sequentiel Decoding”, IEEE Trans on Inf. Theory, jul. 1983
P.Y. Pau, D. Haccoun, ”Sequential Decoding with ARQ”, IEEE ISIT, Saint-Jovite 1983
J.M. Wozencraft, I.M. Jacobs, ”Principles of Communication Engineering”, Wiley, New York, 1965
G.D. Forney, E.K. Bower, ”A High-Speed Sequential Decoder. Prototype Design and Test”, IEEE Trans on Comm. March 1980
F. Jelinek, ”A Fast Sequential Decoding Algorithym Using a Stack”, IBM J. Res. and Dev. Nov. 1969
M. Cerdervall, R. Johanesson, K. Zigangirov, ”Creeper. A New Algorithm for Sequential Decoding”, IEEE ISIT Brighton June 1985
D. Haccoun, ”A branching Process Analysis of the Average Number of Computations of the Stack Algorithm”, IEEE Trans on I.T. May 1984
R. Johanesson, IEEE Trans on I.T., Jul. 1975, ”Robustly Optimal Rate One-Half Binary Convolutionnal Codes”
J.L. Massey, ”Variable-Length Codes and the Fano Metric”, IEEE Trans on I.T., Jan 1972
G.D. Forney, ”Convolutiuonal Codes III: Sequential Decoding”, Information and Control, Jul. 1974
S. Kallel, D. Haccoun, ”Sequentiel Decoding with ARQ and Code Combining”, IEEE Trans on Comm., n7, jul. 1988
S. Lsaku, K. Hatori, ”Performance Analysis of Some ARQ Protocols”, Electronics and Communications in Japan, Vol. 65–8 n4, 1982
G.C. Clark, J.B. Cain, ”Error-Correction Coding for Digital Communications”, Ed. Plenum Press 1981
J.J. Metzner, ”Improvements in Block-Retransmission Schemes”, IEEE Trans on Comm., n2, Feb. 1979
B. Arazi, ”Improving the Throughput of an ARQ Stop-and-Wait Sceme for Burst Noise Channels”, IEEE Trans on Comm., June 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Darmon, M.M., Sadot, P.R. (1991). A hybrid FEC-ARQ communication system using sequential decoding. In: Cohen, G., Charpin, P. (eds) EUROCODE '90. EUROCODE 1990. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 514. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-54303-1_147
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-54303-1_147
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-54303-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-47546-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive