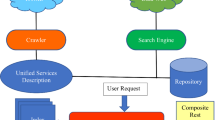
This chapter compares the solutions to the SWS-Challenge discovery problems provided by DERI Galway and the joint solution from the Technical University of Dortmund and University of Postdam. The two approaches are described in depth in Chapters 10 and 13. The discovery scenario raises problems associated with making service discovery an automated process. It requires fine-grained specifications of search requests and service functionality including support for fetching dynamic information during the discovery process (e.g., shipment price). Both teams utilize semantics to describe services, service requests and data models in order to enable search at the required fine-grained level of detail.
The DERI solution is based on the Semantic Web services framework described in Chapter 10, including a conceptual model for Semantic Web services (Web Service Modeling Ontology, WSMO[1]), a language for service modeling (Web Service Modeling Language, WSML[2]), a middleware system (Web Service Execution Environment, WSMX[3]) and a modelling framework (Web Service Modelling Toolkit, WSMT5). In order to model the scenario, WSMO has been used for modeling of goals, services (i.e. required and offered capabilities) and ontologies (i.e. information models on which services and goals are defined), all expressed in the WSML ontology language. WSMO Mediators were not utilized since a common domain shipment ontology was used in both the goal and service descriptions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roman, D., Keller, U., Lausen, H., de Bruijn, J., Lara, R., Stollberg, M., Polleres, A., Feier, C., Bussler, C., Fensel, D.: Web Service Modeling Ontology. Applied Ontologies 1(1) (2005) 77–106
de Bruijn, J., Lausen, H., Polleres, A., Fensel, D.: The Web Service Modeling Language: An Overview. In: Proc. of the European Semantic Web Conference. (2006)
Vitvar, T., Mocan, A., Kerrigan, M., Zaremba, M., Zaremba, M., Moran, M., Cimpian, E., Haselwanter, T., Fensel, D.: Semantically-enabled service oriented architecture: Concepts, technology and application. In Service Oriented Computing and Applications, Springer London 1(2) (2007)
Jörges, S., Kubczak, C., Nagel, R., Margaria, T., Steffen, B.: Model-driven development with the jABC. In: HVC — IBM Haifa Verification Conference. LNCS 4383, Haifa, Israel, IBM, Springer Verlag (2006)
Zaremba, M., Vitvar, T., Moran, M.: Towards Optimized Data Fetching for Service Discovery. In: In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE European Conference on Web Services (ECOWS), IEEE Computer Society. (2007)
Braun, V., Margaria, T., Weise, C.: Integrating tools in the ETI platform. Int. Journal on Software Tools for Technology Transfer (STTT) 1(2) (1997) 31–48
Steffen, B., Margaria, T., Nagel, R.: Remote Integration and Coordination of Verification Tools in jETI. In: Proc. ECBS 2005, 12th IEEE Int. Conf. on the Engineering of Computer Based Systems, Greenbelt (USA), IEEE Computer Soc. Press (2005) 431–436
Margaria, T., Kubzcak, C., Steffen, B.: Bio-jETI: a Service Integration, Design, and Provisioning Platform for Orchestrated Bioinformatics Processes. In: Supplement dedicated to Network Tools and Applications in Biology 2007 Workshop (NETTAB 2007). Number 9 (Suppl 4):S12 in BioMed Central (BMC) Bioinformatics (2008) Published online 2008 April 25
Roman, D., Scicluna, J.: Ontology-based Choreography of WSMO Services. Wsmo final draft v0.3, DERI (2006) Available at: http://www.wsmo.org/TR/d14/v0.3/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kubczak, C., Vitvar, T., Winkler, C., Zaharia, R., Zaremba, M. (2009). Comparison: Discovery on WSMOLX and miAamics/jABC. In: Petrie, C., Margaria, T., Lausen, H., Zaremba, M. (eds) Semantic Web Services Challenge. Semantic Web And Beyond, vol 8. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-72496-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-72496-6_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-72495-9
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-72496-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)