Article Outline
Keywords
The Primal Problem and the Lagrangian Dual Problem
Weak and Strong Duality
Properties of the Lagrangian Dual Function
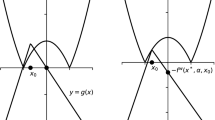
Geometrical Interpretations of Lagrangian Duality
The Resource-Payoff Space
Gap Function
Summary
See also
References
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balinski ML, Baumol WJ (1968) The dual in nonlinear programming and its economic interpretation. Rev Economic Stud 35:237–256
Bazaraa MS, Goode JJ (1979) A survey of various tactics for generating Lagrangian multipliers in the context of Lagrangian duality. Europ J Oper Res 3:322–338
Bertsekas DP (1975) Nondifferentiable optimization. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Bertsekas DP (1982) Constrained optimization and Lagrange multiplier methods. Acad. Press, New York
Bertsekas DP (1995) Nonlinear programming. Athena Sci., Belmont, MA
Brooks R, Geoffrion A (1966) Finding Everett's Lagrange multipliers by linear programming. Oper Res 16:1149–1152
Everett H (1973) Generalized Lagrange multiplier method for solving problems of optimum allocation of resources. Oper Res 4:72–97
Falk JE (1967) Lagrange multipliers and nonconvex programming. J Math Anal Appl 19:141–159
Fiacco AV, McCormick GP (1968) Nonlinear programming: Sequential unconstrained minimization techniques. Wiley, New York
Fisher ML, Northup WD, Shapiro JF (1975) Using duality to solve discrete optimization problems: theory and computational experience. In: Balinski ML, Wolfe P (eds) Nondifferentiable Optimization. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Fletcher R (ed) (1969) Optimization. Acad. Press, New York
Geoffrion AM (1970) Elements of large- scale mathematical programming I-II. Managem Sci 16:652–675; 676–691
Geoffrion AM (1971) Duality in nonlinear programming: A simplified application-oriented development. SIAM Rev 13:1–7
Hearn DW (1982) The gap function of a convex program. Oper Res Lett 1:67–71
Hearn DW, Lawphongpanich S (1989) Lagrangian dual ascent by generalized linear programming. Oper Res Lett 8:189–196
Hearn DW, Lawphongpanich S (1990) A dual ascent algorithm for traffic assignment problems. Transport Res B 248(6):423–430
Kiwiel KC (1985) Methods of descent for nondifferentiable optimization. Springer, Berlin
Lasdon LS (1970) Optimization theory for large systems. MacMillan, New York
Luenberger DG (1969) Optimization by vector space methods. Wiley, New York
Luenberger DG (1973) Introduction to linear and nonlinear programming. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Mangasarian OL (1969) Nonlinear programming. McGraw-Hill, New York
Nemhauser GL, Wolsey LA (1988) Integer and combinatorial optimization. Wiley, New York
Powell MJD (1978) Algorithms for nonlinear constraints that use Lagrangian functions. Math Program 14:224–248
Rockafellar RT (1970) Convex analysis. Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton
Rockafellar RT (1975) Lagrange multipliers in optimization. In: Cottle RW, Lemke CE (eds) Nonlinear Programming, SIAM-AMS Proc. vol IX, pp 23–24
Whittle P (1971) Optimization under constraints. Wiley, New York
Wolfe P (1961) A duality theorem for nonlinear programming. Quart Appl Math 19:239–244
Zangwill WI (1969) Nonlinear programming: A unified approach. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag
About this entry
Cite this entry
Hearn, D.W., Lowe, T.J. (2008). Lagrangian Duality: BASICS . In: Floudas, C., Pardalos, P. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-74759-0_320
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-74759-0_320
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-74758-3
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-74759-0
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsReference Module Computer Science and Engineering