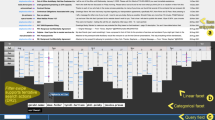
Multimedia presentation of dynamic rheological experimental and simulated data sets is a complex process, due to the dynamic interrelation of the data. In this work we address the problem of direct data interaction, focusing particularly on the case where the application has to dynamically handle changes at runtime. Interactivity modeling relies on visual metadata representations, which are both used to relate directly to the underlying system-graph and formally describe content-connectivity. Under this context a novel user-interaction structure (Multi-Menu) is introduced, allowing valid-only data comparison across the vast number of possible results combinations, supporting discussion-based data combinations and user-driven scenarios, which can in turn trigger automated simulation execution to generate missing data. The proposed methodology applies to other complex data investigation scenarios and systems with adaptive interactivity and automatic system-adjustment requirements.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Botafogo RA, Mossé D (1996) The Capoeira Model for Distributed and Reconfigurable Multimedia Systems. Technical Research Report, Computer Science Department, Universidade Federal Fluminense, Brazil
Carter J (2000) Developments in Web Research and Practice. In Proc. Motivating Multimedia. San Diego, California, US
Deliyannis I (2002) Interactive Multimedia Systems for Science and Rheology. In: Computer Science. Ph.D Thesis, University of Wales, Swansea, p 285
Deliyannis I, Harvey J, Webster MF (2003) Content-Based Interactive Multimedia Systems for Rheological Science. In Proc. e-Society. Lisbon Portugal, p 181–186
Doherty G, Harrison MD (1997) A Representational Approach to the Specification of Presentations. In Proc. 4th Eurographics Workshop on the Design Specification and Verification of Interactive Systems (DSV-IS '97). Granada, Spain
Geurts JPTM, Ossenbruggen JRv, Hardman HL (2001) Application-specific constraints for multimedia presentation generation. In Proc. Eighth International Conference on Multimedia Modeling (MMM01). Amsterdam, Netherlands
ISO-Standard (1988) Information technology - Computer graphics and image processing -Presentation Environment for Multimedia Objects (PREMO).
J. Dakss, S. Agamanolis, E. Chalom, Bove MVJ (1998) Hyperlinked Video. In: Proc. SPIE Multimedia Systems and Applications.
Martinez OR (2002) Design Dependencies within the Automatic Generation of Hypermedia Presentations. Technical University of Catalonia, Catalonia
Pittarello F, Celentano A (2001) Interaction locus: a multimodal approach for the structuring of virtual spaces. In Proc. HCItaly. Firenze, Italy
Rees DLL, Stephenson K, Tucker JV (2000) Towards an Algebraic Structure of Interface Definition Languages and Architectures. Computer Science Department Research Report, University of Wales Swansea, Swansea
Tsandilas T, Schraefel MC (2004) Usable adaptive hypermedia systems. New Review of Hypermedia and Multimedia J 10:5–29
Vazirigiannis M, Theodoridis Y, Sellis T (1998) Spatio-temporal composition and indexing for large multimedia applications. Multimedia Systems J 6:284–298
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ioannis, D., Floros, A., Webster, M.F. (2009). An Adaptive Complex Data Investigation Methodology using Interactive Multi-Menus. In: Sicilia, MA., Lytras, M.D. (eds) Metadata and Semantics. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-77745-0_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-77745-0_38
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-77744-3
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-77745-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)