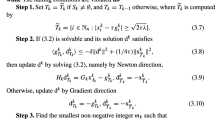Abstract
Many problems of interest where more than one solution is possible seek, among these, the one that is sparsest. The objective that most directly accounts for sparsity, the ℓ 0 metric, is usually avoided since this leads to a combinatorial optimization problem. The function \(\|{x\|}_{0}\) is often viewed as the limit of the ℓ p metrics. Naturally, there have been some attempts to use this as an objective for p small, though this is a nonconvex function for p < 1. We propose instead a scaled and shifted Fermi-Dirac entropy with two parameters, one controlling the smoothness of the approximation and the other the steepness of the metric. Our proposed metric is a convex relaxation for which a strong duality theory holds, yielding dual methods for metrics approaching the desired \(\|{\cdot \|}_{0}\) function. Without smoothing, we propose a dynamically reweighted subdifferential descent method with “exact” line search that is finitely terminating for constraints that are well-separated. This algorithm is shown to recapture in a special case certain well-known “greedy” algorithms. Consequently we are able to provide an explicit algorithm whose fixed point, under the appropriate assumptions, is the sparsest possible solution. The variational perspective yields general strategies to make the algorithm more robust.
AMS 2010 Subject Classification: 49M20, 65K10, 90C30
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borwein, J., Vanderwerff, J.: Convex Functions: Constructions, Characterizations and Counterexamples, Encyclopedias in Mathematics, vol. 109. Cambridge University Press, New York (2010)
Borwein, J.M., Lewis, A.S.: Convex analysis and nonlinear optimization: theory and examples, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Borwein, J.M., Luke, D.R.: Duality and convex programming. In: O. Scherzer (ed.) Handbook of Mathematical Methods in Imaging, pp. 229–270. Springer-Verlag (2011)
Bruckstein, A.M., Donoho, D.L., Elad, M.: From sparse solutions of systems of equations to sparse modeling of signals and images. SIAM Rev. 51, 34–81 (2009)
Candès, E., Recht, B.: Exact matrix completion via comvex optimization. Found. of Comput. Math. 9, 717–772 (2009)
Candès, E., Tao, T.: Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 52, 5406–5425 (2006)
Chen, S.S., Donoho, D.L., Saunders, M.A.: Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 20, 33–61 (1998)
Donoho, D.L., Elad, M.: Optimally sparse representation in general (non-orthogonal) dictionaries via l1 minimization,. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100, 2197–2202 (2003)
Gribonval, R., Nielsen, M.: Sparse decompositions in unions of bases. IEEETrans. Inform. Theory 49, 3320–3325 (2003)
Luke, D.R.: Relaxed averaged alternating reflections for diffraction imaging. Inverse Problems 21, 37–50 (2005)
Luke, D.R.: Finding best approximation pairs relative to a convex and a prox-regular set in Hilbert space. SIAM J. Optim. 19, 714–739 (2008)
Natarajan, B.K.: Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems. SIAM J. Comput. 24, 227–234 (1995)
Recht, B., Fazel, M., Parrilo, P.: Guaranteed minimum rank solutions of matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization. SIAM Rev. 52, 471–501 (2010)
Rockafellar, R.T., Wets, R.J.: Variational Analysis. Grundlehren der mathematischen Wissenschaften. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Santosa, F., Symes, W.W.: Linear inversion of band-limited reflection seismograms. SIAM J. Sci. Statist Comput. 7, 1307–1330 (1986)
Acknowledgements
Jonathan M. Borwein, Research was supported by the Australian Research Council. D. Russell Luke, Research was supported by the US National Science Foundation grant DMS-0712796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Borwein, J.M., Luke, D.R. (2011). Entropic Regularization of the ℓ 0 Function. In: Bauschke, H., Burachik, R., Combettes, P., Elser, V., Luke, D., Wolkowicz, H. (eds) Fixed-Point Algorithms for Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering. Springer Optimization and Its Applications(), vol 49. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9569-8_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9569-8_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-9568-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-9569-8
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)