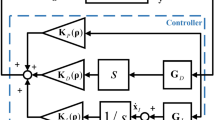
Overview
- Assists the reader in applied gain-scheduling control design using a novel output weight tuning algorithm Demonstrates LPV gain-scheduling controller design using three practical design examples Shows the reader LPV modeling based on either system identification or physical systems considerations
- Includes supplementary material: sn.pub/extras
Part of the book series: SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering (BRIEFSELECTRIC)
Part of the book sub series: SpringerBriefs in Control, Automation and Robotics (BRIEFSCONTROL)
Access this book
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
About this book
An important step in LPV control design, which is not well covered in the present literature, is the selection of weighting functions. The proper selection of weighting functions tunes the controller to obtain the desired closed-loop response. The selection of appropriate weighting functions is difficult and sometimes appears arbitrary. In this brief, gain-scheduling control with engineering applications is covered in detail, including the LPV modeling, the control problem formulation, and the weighting function optimization. In addition, an iterative algorithm for obtaining optimal output weighting functions with respect to the H2 norm bound is presented in this brief. Using this algorithm, the selection of appropriate weighting functions becomes an automatic process. The LPV design and control synthesis procedures in this brief are illustrated using:
• air-to-fuel ratio control for port-fuel-injection engines;
• variable valve timing control; and
• application to a vibration control problem.
After reading this brief, the reader will be able to apply its concepts to design gain-scheduling controllers for their own engineering applications. This brief provides detailed step-by-step LPV modeling and control design strategies along with an automatic weight-selection algorithm so that engineers can apply state-of-the-art LPV control synthesis to solve their own engineering problems. In addition, this brief should serve as a bridge between the H-infinity and H2 control theory and the real-world application of gain-scheduling control.
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
Table of contents (5 chapters)
-
Front Matter
-
Back Matter
Reviews
From the reviews:
“The authors present in this book of 110 pages, different applications in engineering of the Linear Parameter-Varying (LPV) method. The book contains 5 main chapters and two appendices. … The book is interesting and useful for those using the LPV method.” (Gheorghe Tigan, zbMATH, Vol. 1272, 2013)Authors and Affiliations
About the authors
Dr. Choi has been working on model set estimation for robust controller design; robust track-following controller design in hard disk drives (HHDs); and LPV modeling and controller synthesis for energy-efficient automotive engine systems and mobile robotic sensors based on LMI optimization. In his experience, the LPV modeling and control approach plays an important role in addressing challenging control problems in many applications ranging from HHDs and engine control to unmanned robotic vehicles. He also teaches graduate-level control systems courses such as ‘Linear Systems and Control’, and ‘Nonlinear Systems and Control’ at Michigan State University.
Bibliographic Information
Book Title: Linear Parameter-Varying Control for Engineering Applications
Authors: Andrew P. White, Guoming Zhu, Jongeun Choi
Series Title: SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-5040-4
Publisher: Springer London
eBook Packages: Engineering, Engineering (R0)
Copyright Information: The Author(s) 2013
Softcover ISBN: 978-1-4471-5039-8Published: 12 April 2013
eBook ISBN: 978-1-4471-5040-4Published: 30 March 2013
Series ISSN: 2191-8112
Series E-ISSN: 2191-8120
Edition Number: 1
Number of Pages: XIII, 110
Number of Illustrations: 35 b/w illustrations, 2 illustrations in colour
Topics: Control and Systems Theory, Automotive Engineering, Systems Theory, Control