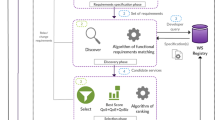
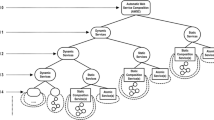
Abstract
Despite significant research efforts, automated service composition is neither taken up broadly nor can it be considered a solved problem. We believe that this is partly the case due to an unclear formulation of the actual business requirements and frame for this technology. In this paper, we formulate a list of 14 requirements for composition in the contexts of business process implementation, enterprise application integration, and interoperability, which can be considered quite challenging not only for current technology but also in terms computational complexity. However, if these requirements are met by an approach to composition — potentially by combining existing technology — the relevance of automated composition to enterprise application software could increase significantly, and also quicken its success in other usage scenarios. We give a list of requirements towards service composition along with a starting point for a composition approach and a short analysis of the computational complexity.1
This work has in part been funded through the European Union’s 6th Framework Programme, within Information Society Technologies (IST) priority under the SUPER project (http://www.ip-super.org)
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Andrews, F. Curbera, and more. Business Process Execution Language for Web Services. Version 1.1, 5 2003.
B. Benatallah, M. Dumas, Q. Sheng, and A. Ngu. Declarative Composition and Peer-to-Peer Provisioning of Dynamic Web Services. In ICDE’ 02: Proc. 18th Intl. Conf. on Data Engineering, page 297, Washington, DC, USA, 2002. IEEE Computer Society.
M. Burstein, J. Hobbs, and more (eds.). OWL-S: Semantic Markup for Web Services. OWL-S 1.1. http://www.daml.org/services/owl-s/1.1/, Nov. 2004. Version 1.1.
F. Casati, M. Sayal, and M.-C. Shan. Developing E-Services for Composing E-Services. In CAiSE’ 01: Proc. 13th Intl. Conf. on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, pages 171–186, London, UK, 2001. Springer.
S. Dustdar and W. Schreiner. A Survey on Web services Composition. Int. J. Web and Grid Services, 1(1):1–30, 2005.
B. Esfandiari and V. Tosic. Requirements for Web Service Composition Management. In Proceedings of the 11th HPOVUA Workshop, June 2004.
R. Hull, M. Benedikt, V. Christophides, and J. Su. E-Services: a Look Behind the Curtain. In Proc. 22nd Symposium on Principles Of Database Systems — PODS, San Diego, CA, USA, pages 1–14, June 2003.
J. Koehler, R. Hauser, J. Küster, K. Ryndina, J. Vanhatalo, and M. Wahler. The Role of Visual Modeling and Model Transformations in Business-driven Development. In 5th Intl. Workshop on Graph Transformation and Visual Modeling Techniques, April 2006.
P. Küngas and M. Matskin. Detection of missing web services: The partial deduction approach. Special Issue on Recent Innovations in Web Services Practices, Intl. Journal of Web Services Practices, 1(1–2):133–141, 2005.
J. Küster, J. Koehler, and K. Ryndina. Improving Business Process Models with Reference Models in Business-Driven Development. In Proc. 2nd Workshop on Business Processes Design (BPD’06), LNCS, Springer, 2006.
U. Küster, M. Stern, and B. König-Ries. A Classification of Issues and Approaches in Automatic Service Composition. In Proc. 1st Intl. Workshop on Engineering Service Compositions (WESC’05), pages 25–33, Dec. 2005.
U. Kuter, E. Sirin, D. S. Nau, B. Parsia, and J. A. Hendler. Information Gathering During Planning for Web Service Composition. In ISWC 2004: Proc. 3rd Intl. Sem. Web Conf., Hiroshima, Japan, pages 335–349, 2004.
S. McIlraith and T. C. Son. Adapting Golog for composition of semantic Web services. In KR-02: Proc. of the 8th Intl. Conf. on Principles and Knowledge Representation and Reasoning, Toulouse, France, 2002.
H. Meyer and D. Kuropka. Requirements for Service Composition. Technical report, Universität Potsdam, Hasso-Plattner-Instituts für Softwaresystemtechnik, Technische Berichte Nr. 11, Univ.-Verlag Potsdam, 2005.
B. Orriëns, J. Yang, and M. P. Papazoglou. A Framework for Business Rule Driven Service Composition. In TES-03: Proc. 4th Intl. Workshop on Technologies for E-Services, Berlin, Germany, pages 14–27, Sept. 2003.
J. Peer. Web Service Composition as AI Planning-A Survey. Technical report, Univ. of St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2005.
M. Pistore, P. Traverso, and P. Bertoli. Automated Composition of Web Services by Planning in Asynchronous Domains. In ICAPS-05: Proc. Intl. Conf. on Automated Planning and Scheduling, 2005.
J. Rao. Semantic Web Service Composition via Logic-based Program Synthesis. PhD thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2004.
J. Rao, D. Dimitrov, P. Hofmann, and N. Sadeh. A Mixed Initiative Approach to Semantic Web Service Discovery and Composition: SAP’s Guided Procedures Framework. In ICWS-06: Proc. IEEE Intl. Conf. on Web Services, Chicago, USA, Sept. 2006.
J. Rao and X. Su. A Survey of Automated Web Service Composition Methods. In SWSWPC, pages 43–54, 2004.
D. Roman, H. Lausen, and U. Keller. D2v1.2. Web Service Modeling Ontology (WSMO) WSMO Final Draft 13 April 2005. wsmo.org, 2005.
S. J. Russell and P. Norvig. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Pearson Education, 2003.
P. Traverso and M. Pistore. Automated Composition of Semantic Web Services into Executable Processes. In ISWC-04: Proc. 3rd Intl. Semantic Web Conf, Hiroshima, Japan, pages 380–394, 2004.
M. T. Tut and D. Edmond. The Use of Patterns in Service Composition. In AiSE’ 02/ WES’ 02: Intl. Workshop on Web Services, E-Business, and the Semantic Web, pages 28–40, London, UK, 2002. Springer.
W. M. P. van der Aalst, A. H. M. ter Hofstede, B. Kiepuszewski, and A. P. Barros. Workflow Patterns. Distrib. Parallel Databases, 14(1):5–51, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag London Limited
About this paper
Cite this paper
Weber, I. (2007). Requirements for Implementing Business Process Models through Composition of Semantic Web Services. In: Gonçalves, R.J., Müller, J.P., Mertins, K., Zelm, M. (eds) Enterprise Interoperability II. Springer, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84628-858-6_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84628-858-6_1
Publisher Name: Springer, London
Print ISBN: 978-1-84628-857-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-84628-858-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)