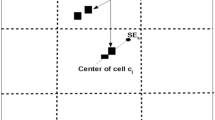
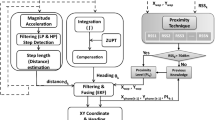
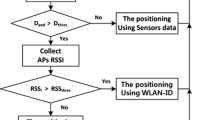
Abstract
Moving distance measurement is an indispensable component for the indoor localization and user trace tracking, which is of great importance to a wide range of applications in the era of mobile computing. The maturity of inertial sensors in smartphones and the ubiquity of WiFi technology ensure the accuracy for indoor distance measurement. Despite its importance, moving distance estimation in the indoor environment for mobile devices is still lacking a cost-effective and precise solution. The state-of-the-art work mostly use build-in sensors, e.g. accelerometer, gyroscope, rotation vector sensor and etc. in the mobile devices for the movement distance measurement. Wireless signal is considered to estimate a humans moving distance as well in prior work. However, both methods suffer from complex deployment and inaccurate estimation results. In this paper, we propose a multi-modal approach to measure moving distance for the user. We mainly innovate in proposing a fusion estimation method leveraging sensors and wireless signals to accurately estimate the human’s moving distance indoor. We implement a prototype with smartphones and commercial WiFi devices. Then we evaluate it in distinct indoor environments. Experimental results show that the proposed method can estimate target’s moving distance with an average accuracy of 90.7%, which sheds light on sub-meter level distance measurements in indoor environments.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manikanta, K., Kiran, J., Dinesh, B., Sachin, K.: SpotFi: decimeter level localization using WiFi. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 45(4), 269–282 (2015)
Graham, H., Alan, F.: Spatially augmented audio delivery: applications of spatial sound awareness in sensor-equipped indoor environments. In: 10th MDM International Conference on Mobile Data Management, pp. 704–708. ACM, New York (2009)
Wang, W., Alex, X., Ling, K., et al.: Understanding and modeling of WiFi signal based human activity recognition. In: 2015 International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, pp. 65–76. ACM, New York (2015)
Chen, S., Li, M., Ren, K., et al.: Rise of the indoor crowd: reconstruction of building interior view via mobile crowdsourcing. In: 2015 ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, pp. 59–67. ACM, New York (2015)
Hm, A., Alaa, H.: Floor identification using smartphone barometer sensor for indoor positioning. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Technol. 4(2), 329–340 (2015)
Daniel, C., Victoria, M., Benito, U., et al.: MagicFinger: 3D magnetic fingerprints for indoor location. Sensors 15(7), 17168–17194 (2015)
Yu, N., Wang, W., Alex, X., et al.: QGesture: quantifying gesture distance and direction with WiFi signals. ACM Interacti. Mob. Wearable Ubiquit. Technol. 2(2), 1–23 (2018)
Li, X., Li, S., Zhang, D., et al.: Dynamic-music: accurate device-free indoor localization. In: 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 196–207. ACM, New York (2016)
Liu, Z., Cheng, L., Liu, A., et al.: Multiview and multimodal pervasive indoor localization. In: 2017 ACM Conference on Multimedia, pp. 109–117. ACM, New York (2017)
Savvas, P., Wen, H.: Fusion of radio and camera sensor data for accurate indoor positioning. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems, pp. 109–117. ACM, New York (2015)
John, C., Cha, H.: LifeMap: a smartphone-based context provider for location-based services. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 10(2), 58–67 (2011)
Lu, Y., Wei, Y., Liu, L.: Towards unsupervised physical activity recognition using smartphone accelerometers. Multimedia Tools Appl. 76(8), 10701–10719 (2017)
Josep, M., Aleix, R.: Sensor localization from distance and orientation constraints. Sensors 16(7), 1096 (2016)
Xiong, J., Qin, Q.: A distance measurement wireless localization correction algorithm based on RSSI. In: 7th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, pp. 276–278. ACM, New York (2014)
Wu, D., Zhang, D.: WiDir: walking direction estimation using wireless signals. In: 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 351–362. ACM, New York (2016)
Xu, H., Yang, Z.: Enhancing WiFi-based localization with visual clues. In: 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 963–974. ACM, New York (2015)
Xu, H., Yang, Z., Zhou, Z.: Indoor localization via multi-modal sensing on smartphones. In: 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 208–219. ACM, New York (2016)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under grant kfjj20171607.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, J., Qian, H., Zhao, Y. (2018). Accurate Moving Distance Estimation via Multi-modal Fusion from IMU Sensors and WiFi Signal. In: Sun, X., Pan, Z., Bertino, E. (eds) Cloud Computing and Security. ICCCS 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11067. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00018-9_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00018-9_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-00017-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-00018-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)