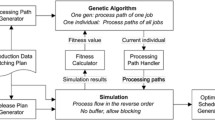
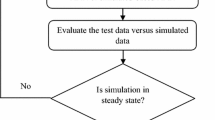
Abstract
The problem of FFSP (Flexible Flow Shop Problem) has been sufficiently investigated due to its importance for production programming and control, although many of the solution methods have been based on GA (Genetic Algorithm) and simulation, these techniques have been used in deterministic environments and under specific conditions of the problem, that is, complying with restrictions given in the Graham notation. In this paper we describe an application of these techniques to solve a very particular case where manual work stations and equipment with different degrees of efficiency, technological restrictions, recirculation process are used. The nesting of the GA is used within a simulation process. It is showed that the method proposed in adjustment and efficiency is better compared with other heuristics, in addition to the benefits of using different techniques in series to solve problems of real manufacturing environments.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinedo, M.L.: Scheduling: Theory, Algorithms, and Systems. Springer, Heidelberg (2016)
Sioud, A., Gagné, C., Gravel, M.: An ant colony optimization for solving a hybrid flexible flowshop. In: Proceedings of the Companion Publication of the 2014 Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, pp. 17–18. ACM, July 2014
Sukkerd, W., Wuttipornpun, T.: Hybrid genetic algorithm and tabu search for finite capacity material requirement planning system in flexible flow shop with assembly operations. Comput. Ind. Eng. 97, 157–169 (2016)
Zandieh, M., Hashemi, A.R.: Group scheduling in hybrid flexible flowshop with sequence-dependent setup times and random breakdowns via integrating genetic algorithm and simulation. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 21(3), 377–394 (2015)
Xu, Y., Tan, W.: The modeling and simulation of flow shop scheduling problem based on adaptive genetic algorithm. RISTI (Revista Iberica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informacao) (17A), 25–41 (2016)
Hong, T., Wang, T.: A heuristic Palmer-based fuzzy flexible flow-shop scheduling algorithm. In: Fuzzy Systems Conference Proceedings 1999, vol. 3, pp. 1493–1497 (1999)
Hong, T., Wang, C., Wang, S.: A heuristic Gupta-based flexible flow-shop scheduling algorithm. In: 2000 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, vol. 1, pp. 319–322 (2000)
Wang, L., Dawei, L.: A scheduling algorithm for flexible flow shop problem. In: Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation 2002, vol. 4, pp. 3106–3108 (2002)
Vásquez, J.A., Salhi, A.: Performance of single stage representation genetic algorithms in scheduling flexible flow shops. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation 2005, vol. 2, pp. 1364–1371 (2005)
Fenghe, J., Yaping, F.: Master-slave genetic algorithm for flow shop scheduling with resource flexibility. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Management Science (ICAMS), vol. 1, pp. 341–346 (2010)
Gao, H., Feng, B., Zhu, L.: An improved genetic algorithm for flow shop sequencing. In: International Conference on Neural Networks and Brain 2005, vol. 1, pp. 521–524 (2005)
Brucker, P., Schile, R.: Job-shop scheduling with multi-purpose machines. Computing 45, 369–375 (1990)
de Freitas Rodrigues, R., Dourado, M.C., Szwarcfiter, J.L.: Scheduling problem with multi-purpose parallel machines. Discret. Appl. Math. 164, 313–319 (2014)
Lowndes, V., Berry, S.: Appendix C: what to simulate to evaluate production planning and control methods in small manufacturing firm’s. In: Berry, S., Lowndes, V., Trovati, M. (eds.) Guide to Computational Modelling for Decision Processes. SFMA, pp. 377–379. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55417-4_18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mendez-Giraldo, G., Alvarez-Pomar, L., Franco, C. (2018). Hybrid Simulation and GA for a Flexible Flow Shop Problem with Variable Processors and Re-entrant Flow. In: Figueroa-García, J., López-Santana, E., Rodriguez-Molano, J. (eds) Applied Computer Sciences in Engineering. WEA 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 915. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00350-0_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00350-0_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-00349-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-00350-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)