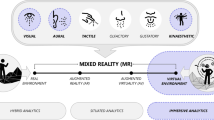
Abstract
We present an initial design framework for immersive analytics based on Brehmer and Munzner’s “What-Why-How” data visualisation framework. We extend their framework to take into account Who are the people or teams of people who are going to use the system, and Where is the system to be used and what are the available devices and technology. In addition, the How component is extended to cater for collaboration, multisensory presentation, interaction with an underlying computational model, degree of fidelity and organisation of the workspace around the user. By doing so we provide a framework for understanding immersive analytics research and applications as well as clarifying how immersive analytics differs from traditional data visualisation and visual analytics.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amar, R., Eagan, J., Stasko, J.: Low-level components of analytic activity in information visualization. In: IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization, INFOVIS 2005, pp. 111–117. IEEE (2005)
Andrienko, N., Andrienko, G.: Exploratory Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Data a Systematic Approach. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-31190-4
Bertin, J.: Semiology of Graphics: Diagrams, Networks, Maps. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison (1983)
Brehmer, M., Munzner, T.: A multi-level typology of abstract visualization tasks. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(12), 2376–2385 (2013)
Butscher, S., Hubenschmid, S., Müller, J., Fuchs, J., Reiterer, H.: Clusters, trends, and outliers: how immersive technologies can facilitate the collaborative analysis of multidimensional data. In: Proceedings SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp. 90:1–90:12 (2018)
Card, S.K., Mackinlay, J.: The structure of the information visualization design space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization, pp. 92–99. IEEE (1997)
Card, S.K., Mackinlay, J.D., Shneiderman, B.: Readings in Information Visualization: Using Vision to Think. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco (1999)
Chen, J., Pyla, P.S., Bowman, D.A.: Testbed evaluation of navigation and text display techniques in an information-rich virtual environment. In: Proceeedings of IEEE Virtual Reality, pp. 181–289. IEEE (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/VR.2004.1310072
Collins, C., Carpendale, S.: VisLink: revealing relationships amongst visualizations. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13(6), 1192–1199 (2007)
Cordeil, M., Cunningham, A., Dwyer, T., Thomas, B.H., Marriott, K.: ImAxes: immersive axes as embodied affordances for interactive multivariate data visualisation. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pp. 71–83. ACM (2017)
Dinh, H.Q., Walker, N., Hodges, L.F., Song, C., Kobayashi, A.: Evaluating the importance of multi-sensory input on memory and the sense of presence in virtual environments. In: Proceedings IEEE Virtual Reality, pp. 222–228 (1999)
Dourish, P.: Where the Action Is: The Foundations of Embodied Interaction. MIT Press, Cambridge (2001)
Elmqvist, N., Vande Moere, A., Jetter, H.C., Cernea, D., Reiterer, H., Jankun-Kelly, T.J.: Fluid interaction for information visualization. Inf. Vis. 10(4), 327–340 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1177/1473871611413180
ElSayed, N.A., Smith, R.T., Marriott, K., Thomas, B.H.: Context-aware design pattern for situated analytics: blended model view controller. J. Vis. Lang. Comput. 44 (2018)
Ens, B., Hincapié-Ramos, J.D., Irani, P.: Ethereal planes: a design framework for 2D information space in 3D mixed reality environments. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Symposium on Spatial User Interaction, pp. 2–12. ACM (2014)
Feiner, S., MacIntyre, B., Haupt, M., Solomon, E.: Windows on the world: 2D windows for 3D augmented reality. In: Proceedings of the 6th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pp. 145–155. ACM (1993)
Heer, J., Shneiderman, B.: Interactive dynamics for visual analysis. Queue 10(2), 30 (2012)
Hoffman, H.G.: Physically touching virtual objects using tactile augmentation enhances the realism of virtual environments. In: IEEE 1998 Virtual Reality Annual International Symposium Proceedings, pp. 59–63 (1998)
Hoffman, H.G., Hollander, A., Schroder, K., Rousseau, S., Furness, T.: Physically touching and tasting virtual objects enhances the realism of virtual experiences. Virtual Real. 3(4), 226–234 (1998)
Jansen, Y., Dragicevic, P.: An interaction model for visualizations beyond the desktop. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(12), 2396–2405 (2013)
Jota, R., Nacenta, M.A., Jorge, J.A., Carpendale, S., Greenberg, S.: A comparison of ray pointing techniques for very large displays. In: Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2010. pp. 269–276. Canadian Information Processing Society (2010)
Keim, D., Kohlhammer, J., Ellis, G. (eds.): Mastering the Information Age: Solving Problems with Visual Analytics. Eurographics Association (2010)
Keller, P.R., Keller, M.M.: Visual Cues: Practical Data Visualization. IEEE Press (1993)
Kwon, O.H., Muelder, C., Lee, K., Ma, K.L.: A study of layout, rendering, and interaction methods for immersive graph visualization. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 22(7), 1802–1815 doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2016.2520921 (July 2016)
Kwon, O.H., Muelder, C., Lee, K., Ma, K.L.: Spherical layout and rendering methods for immersive graph visualization. In: 2015 IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium (PacificVis). pp. 63–67 https://doi.org/10.1109PACIFICVIS.2015.7156357 (April 2015)
LaViola Jr, J.J., Kruijff, E., McMahan, R.P., Bowman, D., Poupyrev, I.P.: 3D User Interfaces: Theory and Practice. Addison-Wesley Professional (2017)
Lee, B., Isenberg, P., Riche, N.H., Carpendale, S.: Beyond mouse and keyboard: Expanding design considerations for information visualization interactions. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 18(12), 2689–2698 (2012)
Lee, B., Plaisant, C., Parr, C.S., Fekete, J.D., Henry, N.: Task taxonomy for graph visualization. In: Proceedings of the 2006 AVI Workshop on Beyond Time and Errors: Novel Evaluation Methods for Information Visualization. pp. 1–5. ACM (2006)
Li, G., Bragdon, A.C., Pan, Z., Zhang, M., Swartz, S.M., Laidlaw, D.H., Zhang, C., Liu, H., Chen, J.: VisBubbles: a workflow-driven framework for scientific data analysis of time-varying biological datasets. In: SIGGRAPH Asia 2011 Posters. p. 27. ACM (2011)
Liu, J., Dwyer, T., Marriott, K., Millar, J., Haworth, A.: Understanding the relationship between interactive optimisation and visual analytics in the context of prostate brachytherapy. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 24(1), 319–329 (2018)
Mackinlay, J.: Automating the design of graphical presentations of relational information. ACM Transactions On Graphics (ToG) 5(2), 110–141 (1986)
McDonnel, B., Elmqvist, N.: Towards utilizing GPUs in information visualization: A model and implementation of image-space operations. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 15(6), 1105–1112 http://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/TVCG.2009.191 (2009)
Milgram, P., Takemura, H., Utsumi, A., Kishino, F.: Augmented reality: a class of displays on the reality-virtuality continuum. Proc. SPIE 2351, 282–292 (1995)
Munzner, T.: Visualization Analysis and Design. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2014)
Nacenta, M.A., et al.: E-conic: a perspective-aware interface for multi-display environments. In: Proceedings of the 20th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, pp. 279–288. ACM (2007)
Patterson, R.E., Blaha, L.M., Grinstein, G.G., Liggett, K.K., Kaveney, D.E., Sheldon, K.C., Havig, P.R., Moore, J.A.: A human cognition framework for information visualization. Comput. Graph. 42, 42–58 (2014)
Petford, J., Nacenta, M.A., Gutwin, C.: Pointing all around you: selection performance of mouse and ray-cast pointing in full-coverage displays. In: Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, p. 533. ACM (2018)
Piringer, H., Kosara, R., Hauser, H.: Interactive focus+ context visualization with linked 2D/3D scatterplots. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Coordinated and Multiple Views in Exploratory Visualization, pp. 49–60. IEEE (2004)
Pirolli, P., Card, S.: The sensemaking process and leverage points for analyst technology as identified through cognitive task analysis. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligence Analysis (2005)
Ragan, E.D., Endert, A., Sanyal, J., Chen, J.: Characterizing provenance in visualization and data analysis an organizational framework of provenance types and purposes. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 22(1), 31–40 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2015.2467551
Ranasinghe, N., et al.: Season traveller: multisensory narration for enhancing the virtual reality experience. In: Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), pp. 577:1–577:13. ACM, New York (2018)
Sacha, D., Stoffel, A., Stoffel, F., Kwon, B.C., Ellis, G., Keim, D.A.: Knowledge generation model for visual analytics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 20(12), 1604–1613 (2014)
Sanchez-Vives, M.V., Slater, M.: From presence to consciousness through virtual reality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6(4), 332–339 (2005)
Shneiderman, B.: The eyes have it: a task by data type taxonomy for information visualizations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages, pp. 336–343. IEEE Press (1996)
Veas, E., Grasset, R., Ferencik, I., Grünewald, T., Schmalstieg, D.: Mobile augmented reality for environmental monitoring. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 17(7), 1515–1531 (2013)
Wang, X.M., Zhang, T.Y., Ma, Y.X., Xia, J., Chen, W.: A survey of visual analytic pipelines. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 31(4), 787–804 (2016)
Ward, M.O., Grinstein, G., Keim, D.: Interactive Data Visualization: Foundations, Techniques, and Applications, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2015)
Ware, C.: Information Visualization: Perception for Design, 3rd edn. Elsevier, New York City (2013)
Wickham, H.: A layered grammar of graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 19(1), 3–28 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1198/jcgs.2009.07098
Wilkinson, L.: The Grammar of Graphics. Springer, New York (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-28695-0
Willett, W., Jansen, Y., Dragicevic, P.: Embedded data representations. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 23(1), 461–470 (2017)
Wright, H.: Introduction to Scientific Visualization. Springer, London (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84628-755-8
Yi, J.S., ah Kang, Y., Stasko, J.: Toward a deeper understanding of the role of interaction in information visualization. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13(6), 1224–1231 (2007)
Zhao, H., Bryant, G.W., Griffin, W., Terrill, J.E., Chen, J.: Validation of SplitVectors encoding for quantitative visualization of large-magnitude-range vector fields. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 23(6), 1691–1705 (2017)
Zhao, H., Chen, J.: Bivariate separable-dimension glyphs can improve visual analysis of holistic features. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. (2018, under revision). https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.02333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Marriott, K. et al. (2018). Just 5 Questions: Toward a Design Framework for Immersive Analytics. In: Marriott, K., et al. Immersive Analytics. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11190. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01388-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01388-2_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-01387-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-01388-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)