Abstract
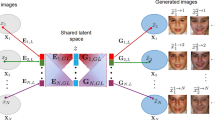
This paper addresses the modeling and simulation of progressive changes over time, such as human face aging. By treating the age phases as a sequence of image domains, we construct a chain of transformers that map images from one age domain to the next. Leveraging recent adversarial image translation methods, our approach requires no training samples of the same individual at different ages. Here, the model must be flexible enough to translate a child face to a young adult, and all the way through the adulthood to old age. We find that some transformers in the chain can be recursively applied on their own output to cover multiple phases, compressing the chain. The structure of the chain also unearths information about the underlying physical process. We demonstrate the performance of our method with precise and intuitive metrics, and visually match with the face aging state-of-the-art.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross-age reference coding for age-invariant face recognition and retrieval. http://bcsiriuschen.github.io/CARC/. Accessed 18 May 2018
Antipov, G., Baccouche, M., Berrani, S., Dugelay, J.: Apparent age estimation from face images combining general and children-specialized deep learning models. In: CVPR Workshops (2016)
Antipov, G., Baccouche, M., Dugelay, J.L.: Face aging with conditional generative adversarial networks. In: ICIP (2017)
Chen, B.-C., Chen, C.-S., Hsu, W.H.: Cross-age reference coding for age-invariant face recognition and retrieval. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8694, pp. 768–783. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10599-4_49
Choi, Y., Choi, M., Kim, M., Ha, J.W., Kim, S., Choo, J.: StarGAN: unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.09020 (2017)
Danihelka, I., Lakshminarayanan, B., Uria, B., Wierstra, D., Dayan, P.: Comparison of maximum likelihood and GAN-based training of real NVPs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.05263 (2017). https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.05263
Duong, C., Quach, K., Luu, K., Savvides, M.: Temporal non-volume preserving approach to facial age-progression and age-invariant face recognition. In: ICCV (2017)
Goodfellow, I.J., et al.: Generative adversarial networks. In: NIPS (2014)
Isola, P., Zhu, J.Y., Zhou, T., Efros, A.A.: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: CVPR (2017)
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., Li, F.: Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: ECCV (2016)
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.: Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196 (2017)
Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I., Suwajanakorn, S., Seitz, S.: Illumination-aware age progression. In: CVPR (2014)
Kim, T., Cha, M., Kim, H., Lee, J.K., Kim, J.: Learning to discover cross-domain relations with generative adversarial networks. In: ICML. PMLR, vol. 70, pp. 1857–1865 (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR (2015). https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
Lample, G., Zeghidour, N., Usunier, N., Bordes, A., Denoyer, L., Ranzato, M.: Fader networks: Manipulating images by sliding attributes. In: NIPS (2017)
Lee, M., Seok, J.: Controllable generative adversarial network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.00598 (2017)
Liu, M.Y., Breuel, T., Kautz, J.: Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. In: NIPS (2017)
Lopez-Paz, D., Oquab, M.: Revisiting classifier two-sample tests. In: ICLR (2017). https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.06545
LynnHo (GitHub user): CycleGAN Tensorflow PyTorch. https://github.com/LynnHo/CycleGAN-Tensorflow-PyTorch-Simple, gitHub repository
Mitchell, D.P., Netravali, A.N.: Reconstruction filters in computer-graphics. ACM Siggraph Comput. Graph. 22(4), 221–228 (1988)
Rothe, R., Timofte, R., Gool, L.V.: DEX: Deep EXpectation of apparent age from a single image. In: ICCV, Looking at People Workshop (2015)
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., Philbin, J.: FaceNet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In: CVPR (2015)
Shrivastava, A., Pfister, T., Tuzel, O., Susskind, J., Wang, W., Webb, R.: Learning from simulated and unsupervised images through adversarial training. In: CVPR (2017). https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.07828
Theis, L., van den Oord, A., Bethge, M.: A note on the evaluation of generative models. In: ICLR (2016). https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.01844
Tiddeman, B., Burt, M., Perrett, D.: Prototyping and transforming facial textures for perception research. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 21(5), 42–50 (2001)
Wu, Y., Burda, Y., Salakhutdinov, R., Grosse, R.: On the quantitative analysis of decoder-based generative models. In: ICLR (2017). https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.04273
Yi, Z., Zhang, H., Tan, P., Gong, M.: DualGAN: unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In: ICCV (2017)
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: ICCV (2017)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by GenMind Ltd. and the Academy of Finland grants 308640, 277685, and 295081. We acknowledge the computational resources provided by the Aalto Science-IT project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Heljakka, A., Solin, A., Kannala, J. (2018). Recursive Chaining of Reversible Image-to-Image Translators for Face Aging. In: Blanc-Talon, J., Helbert, D., Philips, W., Popescu, D., Scheunders, P. (eds) Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems. ACIVS 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11182. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01449-0_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01449-0_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-01448-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-01449-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)