Abstract
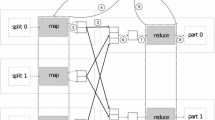
MapReduce is a design pattern for processing large datasets on a cluster. Its performances depend on some data skews and on the runtime environment. In order to tackle these problems, we propose an adaptive multiagent system. The agents interact during the data processing and the dynamic task allocation is the outcome of negotiations. These negotiations aim at improving the workload partition among the nodes within a cluster and so decrease the runtime of the whole process. Moreover, since the negotiations are iterative the system is responsive in case of node performance variations. In this paper, we show how, when a task is divisible, an agent may split it in order to negotiate its subtasks.
This project is supported by the CNRS Challenge Mastodons.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Fault tolerance is out of the scope of our study.
- 2.
- 3.
It is worth noticing that the negotiations and the data processing are not sequential but concurrent.
References
Dean, J., Ghemawat, S.: MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. In: SOSDI, pp. 137–150 (2004)
Kwon, Y., Balazinska, M., Howe, B., Rolia, J.: Skewtune: mitigating skew in MapReduce applications. In: ACM SIGMOD ICMD, pp. 25–36 (2012)
Kwon, Y., Ren, K., Balazinska, M., Howe, B.: Managing skew in Hadoop. IEEE Data Eng. Bull. 36(1), 24–33 (2013)
Baert, Q., Caron, A.C., Morge, M., Routier, J.C.: Fair multi-agent task allocation for large datasets analysis. KAIS (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-017-1087-4
Lama, P., Zhou, X.: Aroma: automated resource allocation and configuration of MapReduce environment in the cloud. In: ICAC, pp. 63–72 (2012)
Verma, A., Cherkasova, L., Campbell, R.: Aria: automatic resource inference and allocation for MapReduce environments. In: ICAC, pp. 235–244 (2011)
Chen, Q., Zhang, D., Guo, M., Deng, Q., Guo, S.: SAMR: a self-adaptive MapReduce scheduling algorithm in heterogeneous environment. In: ICCIT, pp. 2736–2743. IEEE (2010)
Liroz-Gistau, M., Akbarinia, R., Valduriez, P.: FP-Hadoop: efficient execution of parallel jobs over skewed data. VLDB Endow. 8(12), 1856–1859 (2015)
Li, W.: Random texts exhibit Zipf’s-law-like word frequency distribution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 38(6), 1842–1845 (1992)
Lin, J.: The curse of Zipf and limits to parallelization: a look at the stragglers problem in MapReduce. In: Workshop on Large-Scale Distributed Systems for Information Retrieval (2009)
Gufler, B., Augsten, N., Reiser, A., Kemper, A.: Handling data skew in MapReduce. In: ICCCSS, pp. 574–583 (2011)
Vinyals, M., Macarthur, K.S., Farinelli, A., Ramchurn, S.D., Jennings, N.R.: A message-passing approach to decentralized parallel machine scheduling. Comput. J. 57(6), 856–874 (2014)
Nongaillard, A., Mathieu, P.: Egalitarian negotiations in agent societies. AAI 25(9), 799–821 (2011)
Essa, Y.M., Attiya, G., El-Sayed, A.: Mobile agent based new framework for improving big data analysis. IJACSA 5(3), 25–32 (2014)
Gray, J., et al.: Data cube: a relational aggregation operator generalizing group-by, cross-tab, and sub-totals. Data Mining Knowl. Discov. 1(1), 29–53 (1997)
Baert, Q., Caron, A.C., Morge, M., Routier, J.C.: Stratégie de découpe de tâche pour le traitement de données massives. In: Garbay, C., Bonnet, G., (eds.) Journées Francophones sur les Systèmes Multi-Agents. Cohésion: fondement ou propriété émergente, Caen, France, Cépaudès édition, pp. 65–75, July 2017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Baert, Q., Caron, AC., Morge, M., Routier, JC. (2018). Negotiation Strategy of Divisible Tasks for Large Dataset Processing. In: Belardinelli, F., Argente, E. (eds) Multi-Agent Systems and Agreement Technologies. EUMAS AT 2017 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10767. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01713-2_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01713-2_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-01712-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-01713-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)