Abstract
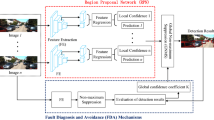
In the field of road estimation, incorporating multiple sensors is essential to achieve a robust performance. However, the reliability of each sensor changes due to environmental conditions. Thus, we propose a reliability-aware fusion concept, which takes into account the sensor reliabilities. By that, the reliabilities are estimated explicitly or implicitly by classification algorithms, which are trained with extracted information from the sensors and their past performance compared to ground truth data. During the fusion, these estimated reliabilities are then exploited to avoid the impact of unreliable sensors. In order to prove our concept, we apply our fusion approach to a redundant sensor setup for intelligent vehicles containing three-camera systems, several lidars, and radar sensors. Since artificial neural networks (ANN) have produced great results for many applications, we explore two ways of incorporating them into our fusion concept. On the one hand, we use ANN as classifiers to explicitly estimate the sensors’ reliabilities. On the other hand, we utilize ANN to directly predict the ego-lane from sensor information, where the reliabilities are implicitly learned. By the evaluation with real-world recording data, the direct ANN approach leads to satisfactory road estimation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Töpfer, J. Spehr, J. Effertz, C. Stiller, Efficient scene understanding for intelligent vehicles using a part-based road representation, in IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2013), pp. 65–70. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITSC.2013.6728212
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, M. Uhlemann, S. Zug, R. Kruse, Learning of lane information reliability for intelligent vehicles, in IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (2016), pp. 142–147. https://doi.org/10.1109/MFI.2016.7849480
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, J. Xiong, M. Baum, S. Zug, R. Kruse, Online reliability assessment and reliability-aware fusion for ego-lane detection using influence diagram and Bayes filter, in IEEE Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (2017), pp. 7–14
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, S. Zug, R. Kruse, Multi-source fusion for robust road detection using online estimated reliabilities. IEEE Trans. Indus. Inf. 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2018.2865582
C. Chen, A. Seff, A. Kornhauser, J. Xiao, DeepDriving: learning affordance for direct perception in autonomous driving, in IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (2015), pp. 2722–2730
D.A. Pomerleau, Efficient training of artificial neural networks for autonomous navigation. Neural Comput. 3(1), 88–97 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1991.3.1.88
M. Bojarski, D.D. Testa, D. Dworakowski, B. Firner, B. Flepp, P. Goyal, L.D. Jackel, M. Monfort, U. Muller, J. Zhang, X. Zhang, J. Zhao, K. Zieba, End to end learning for self-driving cars (2016). CoRR abs/1604.07316
Z. Chen, X. Huang, End-to-end learning for lane keeping of self-driving cars, in 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV) (2017), pp. 1856–1860. https://doi.org/10.1109/IVS.2017.7995975
F. Codevilla, M. Müller, A. Dosovitskiy, A. López, V. Koltun, End-to-end driving via conditional imitation learning (2017). CoRR abs/1710.02410
A. Oliva, A. Torralba, Modeling the shape of the scene: a holistic representation of the spatial envelope. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 42(3), 145–175 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011139631724
M. Al-Qizwini, I. Barjasteh, H. Al-Qassab, H. Radha, Deep learning algorithm for autonomous driving using googlenet, in 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV) (2017), pp. 89–96. https://doi.org/10.1109/IVS.2017.7995703
C. Szegedy, W. Liu, Y. Jia, P. Sermanet, S. Reed, D. Anguelov, D. Erhan, V. Vanhoucke, A. Rabinovich, Going deeper with convolutions (2014). ArXiv e-prints
K. Simonyan, A. Zisserman, Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition (2014). CoRR abs/1409.1556
M.D. Zeiler, R. Fergus, Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks (2013). CoRR abs/1311.2901
O. Hartmann, M. Gabb, R. Schweiger, K. Dietmayer, Towards autonomous self-assessment of digital maps, in Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (2014), pp. 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1109/IVS.2014.6856564
G.L. Rogova, V. Nimier, Reliability in information fusion: literature survey, in 7th International Conference On Information Fusion (2004), pp. 1158–1165
T. Brade, S. Zug, J. Kaiser, Validity-based failure algebra for distributed sensor systems, in IEEE International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (2013), pp. 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1109/SRDS.2013.23
H. Frigui, L. Zhang, P. Gader, Context-dependent multi-sensor fusion for landmine detection, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (2008), pp. II–371–II–374. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2008.4779005
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, J.-O. Perschewski, F. Engel, S. Zug, R. Kruse, Zuverlässigkeitsbasierte Fusion von Fahrstreifeninformationen für Fahrerassistenzfunktionen, in Proceedings 27. Workshop Computational Intelligence, ed. by F. Hoffmann, E. Hüllermeier, R. Mikut (KIT Scientific Publishing, Karlsruhe, 2017), pp. 33–49
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, J. Sitzmann, M. Baum, S. Zug, R. Kruse: Improving ego-lane detection by incorporating source reliability, in Multisensor Fusion and Integration in the Wake of Big Data, Deep Learning and Cyber Physical System, ed. by S. Lee, H. Ko, S. Oh. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol. 501 (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2018)
M. Realpe, B.X. Vintimilla, L. Vlacic, A fault tolerant perception system for autonomous vehicles, in Proceedings of the 35th Chinese Control Conference (2016), pp. 6531–6536. https://doi.org/10.1109/ChiCC.2016.7554385
A. Rechy Romero, P.V. Koerich Borges, A. Elfes, A. Pfrunder, Environment-aware sensor fusion for obstacle detection, in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (2016), pp. 114–121. https://doi.org/10.1109/MFI.2016.7849476
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, D. Vock, M. Baum, S. Zug, R. Kruse, A general reliability-aware fusion concept using DST and supervised learning with its applications in multi-source road estimation, in 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV) (2018), pp. 597–604
F.E. White, A model for data fusion, in Proceedings of the First National Symposium on Sensor Fusion (1988)
C. Gackstatter, P. Heinemann, S. Thomas, B. Rosenhahn, G. Klinker: Fusion of clothoid segments for a more accurate and updated prediction of the road geometry, in 13th International IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (2010), pp. 1691–1696. https://doi.org/10.1109/ITSC.2010.5625270
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, H. Lin, D. Lipinski, Fused raised pavement marker detection using 2D-Lidar and mono camera, in IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2015), pp. 2346–2351
E.D. Dickmanns, B.D. Mysliwetz, Recursive 3-D road and relative ego-state recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14(2), 199–213 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1109/34.121789
T.T. Nguyen, J. Spehr, J. Xiong, M. Baum, S. Zug, R. Kruse, A survey of performance measures to evaluate ego-lane estimation and a novel sensor-independent measure along with its applications, in IEEE Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (2017), pp. 239–246
A. Kraskov, H. Stögbauer, P. Grassberger, Estimating mutual information. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matt. Phys. 69(6 Pt 2), 066138 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.69.066138
J. Pradeep, E. Srinivasan, S. Himavathi, Diagonal based feature extraction for handwritten character recognition system using neural network, in 2011 3rd International Conference on Electronics Computer Technology (ICECT) (2011), pp. 364–368. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECTECH.2011.5941921
A. Graves, A.R. Mohamed, G. Hinton, Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks, in 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (2013), pp. 6645–6649. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638947
R. Kruse, C. Borgelt, C. Braune, S. Mostaghim, M. Steinbrecher, Computational Intelligence: A Methodological Introduction. Texts in Computer Science, 2nd edn./2016 edn. (Springer, London, 2016)
C.M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Information Science and Statistics (Springer, New York, 2006)
L. Bottou, Stochastic gradient descent tricks, in Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, ed. by G. Montavon, G.B. Orr, K.R. Müller, 2nd edn. (Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 2012), pp. 421–436
L. Bottou, Stochastic gradient learning in neural networks. Proc. Neuro-Nımes 91(8), 687–696 (1991)
N. Qian, On the momentum term in gradient descent learning algorithms. Neural Netw. 12(1), 145–151 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-6080(98)00116-6, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0893608098001166
I. Sutskever, J. Martens, G. Dahl, G. Hinton, On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning, in Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning – Volume 28, ICML’13 (2013), pp. III–1139–III–1147. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3042817.3043064
G. Shafer, A Mathematical Theory of Evidence (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1976)
M. Aeberhard, S. Paul, N. Kaempchen, T. Bertram, Object existence probability fusion using dempster-shafer theory in a high-level sensor data fusion architecture, in Proceedings of IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (2011), pp. 770–775. https://doi.org/10.1109/IVS.2011.5940430
A.E. Albert, A.L. Albert, Regression and the Moore-Penrose Pseudoinverse. Mathematics in Science and Engineering: A Series of Monographs and Textbooks (Academic, New York, 1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nguyen, T.T. et al. (2019). Reliability-Aware and Robust Multi-sensor Fusion Toward Ego-Lane Estimation Using Artificial Neural Networks. In: Bossé, É., Rogova, G. (eds) Information Quality in Information Fusion and Decision Making. Information Fusion and Data Science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03643-0_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03643-0_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-03642-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-03643-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)