Abstract
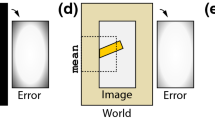
Learning the principle of a task should always be the primary goal of a learning system. Otherwise it reduces to a memorizing system and there always exists edge cases. In spite of its recent success in visual recognition tasks, convolutional neural networks’ (CNNs) ability to learn principles is still questionable. While CNNs exhibit a certain degree of generalization, they eventually break when the variability exceeds their capacity, indicating a failure to learn the underlying principles. We use edge cases of a closed contour detection task to support our arguments. We argue that lateral interactions, which are not a part of pure feed-forward CNNs but common in biological vision, are essential to this task.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elder, J.H., Velisavljevi, L.: Cue dynamics underlying rapid detection of animals in natural scenes. J. Vis. (2018)
Field, D., Hayes, A., Hess, R.: Contour integration by the human visual system: evidence for a local “association field”. Vis. Res. 33, 173–193 (1993)
Gintautas, V., et al.: Model cortical association fields account for the time course and dependence on target complexity of human contour perception. PLoS Comput. Biol. 7, e1002162 (2011)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: CVPR (2016)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., van der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: CVPR (2017)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: CVPR (2009)
Jo, J., Bengio, Y.: Measuring the tendency of CNNs to Learn Surface Statistical Regularities. ArXiv e-prints (2017)
Krizhevsky, A.: Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images. Technical report (2009)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: NIPS (2012)
Noh, H., Hong, S., Han, B.: Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: ICCV (2015)
Recht, B., Roelofs, R., Schmidt, L.: Do CIFAR-10 Classifiers Generalize to CIFAR-10? ArXiv e-prints (2018)
Ricci, M., Kim, J., Serre, T.: Not-So-CLEVR: Visual Relations Strain Feedforward Neural Networks. ArXiv e-prints (2018)
Williams, L.R., Jacobs, D.W.: Stochastic completion fields; a neural model of illusory contour shape and salience. Neural Comput. 9, 837–858 (1997)
Williams, L.R., Thornber, K.K.: A comparison of measures for detecting natural shapes in cluttered backgrounds. In: Burkhardt, H., Neumann, B. (eds.) ECCV 1998. LNCS, vol. 1407, pp. 432–448. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0054757
Yang, J., Price, B., Cohen, S., Lee, H., Yang, M.H.: Object contour detection with a fully convolutional encoder-decoder network. In: CVPR (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, X., Watkins, Y., Kenyon, G.T. (2018). Can Deep Learning Learn the Principle of Closed Contour Detection?. In: Bebis, G., et al. Advances in Visual Computing. ISVC 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11241. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03801-4_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03801-4_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-03800-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-03801-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)