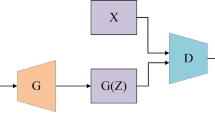
Abstract
Data missing problem is one of the most important issues in the field of wind turbine (WT). The missing data can lead to many problems that negatively affect the safety of power system and cause economic loss. However, under some complicated conditions, the WT data changes according to different environments, which would reduce the efficiency of some traditional data interpolation methods. In order to solve this problem and improve data interpolation accuracy, this paper proposed a WT data imputation method using generative adversarial nets (GAN) with deep learning models. First, conditional GAN is used as the framework to train the generative network. Then convolutional neural network is applied for both the generative model and the discriminative model. Through the zero-sum game between the two models, the imputation model can be well trained. Due to the deep learning models, the trained data imputation model can effectively recover the data with a few parameters of the input data. A case study based on real WT SCADA data was conducted to verify the proposed method. Two more data imputation methods were used to make the comparison. The experiments results showed that the method proposed in this paper is effective.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craigmile, P.F., Guttorp, P.: Space-time modelling of trends in temperature series. J. Time Ser. Anal. 32(4), 378–395 (2011)
Oriani, F., et al.: Missing data simulation inside flow rate time-series using multiple-point statistics. Environ. Model. Softw. 86(C), 264–276 (2016)
Shao, Y., Sun, Y., Liang, L.: Wind speed short-term forecast for wind farms based on ARMA model. Power Syst. Clean Energy 24(7), 52–55 (2008)
Zjavka, L.: Wind speed forecast correction models using polynomial neural networks. Renew. Energy 83, 998–1006 (2015)
Petković, D., et al.: Estimation of fractal representation of wind speed fluctuation by artificial neural network with different training algorithms. Flow Meas. Instrum. 54, 172–176 (2017)
Sun, W., Wang, Y.: Short-term wind speed forecasting based on fast ensemble empirical mode decomposition, phase space reconstruction, sample entropy and improved back-propagation neural network. Energy Convers. Manag. 157, 1–12 (2018)
Goodfellow, I.J., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680. MIT Press (2014)
Chen, Y., et al.: Model-free renewable scenario generation using generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. PP(99), 1 (2017)
Li, J., et al.: WaterGAN: unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images, p. 99 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Qu, F., Liu, J., Hong, X., Zhang, Y. (2018). Data Imputation of Wind Turbine Using Generative Adversarial Nets with Deep Learning Models. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A., Ozawa, S. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11301. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04167-0_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04167-0_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04166-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04167-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)