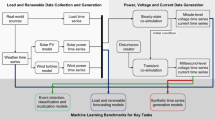
Abstract
Power system analysis algorithms increasingly use time series with a high temporal resolution to assess operational and planning aspects of the power grid. By using time series with high temporal resolution, information is getting more detailed, but at the same time, the computational costs of the algorithms increase. With the help of our algorithm, we create representative time series that have similar characteristics to the original time series. With the help of these representative time series, it is possible to reduce the computational cost of power system analysis algorithms having nearly the same results as with the original time series. In this work, we improve our previous algorithm with the help of specialized sampling strategies. Furthermore, we provide a new method to compare power analysis results achieved with the representative time series to the original time series.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henze, J., Kneiske, T., Braun, M., Sick, B.: Identifying representative load time series for load flow calculations. In: Woon, W.L., Aung, Z., Kramer, O., Madnick, S. (eds.) DARE 2017. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 10691, pp. 83–93. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71643-5_8
Green, R., Staffell, I., Vasilakos, N.: Divide and Conquer? k-means clustering of demand data allows rapid and accurate simulations of the British electricity system. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 61(2), 251–260 (2014)
Poncelet, K., Hoschle, H., Delarue, E., Virag, A., D’haeseleer, W.: Selecting representative days for capturing the implications of integrating intermittent renewables in generation expansion planning problems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 32(3), 1936–1948 (2017)
Räsänen, T., Kolehmainen, M.: Feature-based clustering for electricity use time series data. In: Kolehmainen, M., Toivanen, P., Beliczynski, B. (eds.) ICANNGA 2009. LNCS, vol. 5495, pp. 401–412. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04921-7_41
Li, X., Bowers, C.P., Schnier, T.: Classification of energy consumption in buildings with outlier detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(11), 3639–3644 (2010)
Merrick, J.H.: On representation of temporal variability in electricity capacity planning models. Energy Econ. 59, 261–274 (2016)
Hajian, M., Rosehart, W.D., Zareipour, H.: Probabilistic power flow by Monte Carlo simulation with Latin supercube sampling. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 28, 1550–1559 (2013)
Kabir, M., Mishra, Y., Bansal, R.: Probabilistic load flow for distribution systems with uncertain PV generation. Appl. Energy 163, 343–351 (2016)
Mitra, J., Singh, C.: Incorporating the DC load flow model in the decomposition-simulation method of multi-area reliability evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 11(3), 1245–1254 (1996)
Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Kang, C., Zhang, M., Wang, K., Zhao, Y.: Load profiling and its application to demand response: a review. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 20(2), 117–129 (2015)
Fischer, D., Härtl, A., Wille-Haussmann, B.: Model for electric load profiles with high time resolution for German households. Energy Build. 92, 170–179 (2015)
McInnes, L., Healy, J., Astels, S.: hdbscan: Hierarchical density based clustering. J. Open Source Softw. Open J 2(11) (2017)
Kerber, G.: Aufnahmefähigkeit von Niederspannungsverteilnetzen für die Einspeisung aus Photovoltaikkleinanlagen. Dissertation, Technische Universität München (2011)
Lindner, M., Aigner, C., Witzmann, R., Wirtz, F., Berber, I., Gödde, M., Frings, R.: Aktuelle musternetze zur untersuchung von spannungsproblemen in der niederspannung. In: 14. Symposium Energieinnovation (2016)
Thurner, L., Scheidler, A., Schafer, F. (et.al): Pandapower - an open source python tool for convenient modeling, analysis and optimization of electric power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 33(6), 6510–6521 (2018)
Kolmogorov, A.: On the empirical determination of a distribution function. In: Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L. (eds.) Breakthroughs in Statistics. SSS, pp. 106–113. Springer, New York (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4380-9_10
Acknowledgment
This work was created within the PrIME (03EK3536A) project and funded by BMBF: Deutsches Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung/German Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendices
Appendix A Detailed Results - Univariate
Appendix B Detailed Results - Segmentwise Correlation
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Henze, J., Kutzner, S., Sick, B. (2018). Sampling Strategies for Representative Time Series in Load Flow Calculations. In: Woon, W., Aung, Z., Catalina Feliú, A., Madnick, S. (eds) Data Analytics for Renewable Energy Integration. Technologies, Systems and Society. DARE 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11325. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04303-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04303-2_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04302-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04303-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)