Abstract
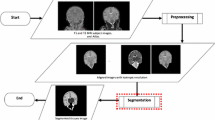
Detection of hemorrhages in the periventricular white matter region of infant brains is crucial since if left untreated it causes neuro-developmental deficits in later life. However, noise and motion artefacts are introduced while scanning infant brains due to small brain size and movement during scanning. Furthermore, a vast majority of traditional brain lesion detection algorithms which require accurate segmentation of the white matter region often rely on brain atlases to guide the segmentation. However, reliable brain atlases are hard to obtain for preterm infant brains which undergo rapid structural changes. To address this gap in published literature, we propose a novel method for hemorrhage detection which does not require a brain atlas. Instead of attempting accurate segmentation, the proposed method detects the ventricles and then samples a region of white matter around the ventricles. Based on the normal distribution of intensities in this tissue sample, the outliers are designated as hemorrhages. Heuristics based on size and location of the detected outliers are used to eliminate false positives. Results on an expert-annotated dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Supported by CIHR, NeuroDevNet, Alberta Innovates (iCORE) Research Chair program, and NSERC. DICOM slices with marked ground truth for preterm neonates’ periventricular hemorrhage detection provided by Dr. Steven Miller and his team at SickKids Hospital, Toronto, Canada.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asao, C., Korogi, Y., Kondo, Y., Yasunaga, T., Takahashi, M.: Neonatal periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage: subacute and chronic MR findings. Acta Radiol. 42(4), 370–375 (2001)
Ballabh, P.: Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants: mechanism of disease. Pediatr. Res. 67(1), 1–8 (2010)
Devi, C.N., Chandrasekharan, A., Sundararaman, V., Alex, Z.C.: Neonatal brainMRI segmentation: a review. Comput. Biol. Med. 64, 163–178 (2015)
Farzan, A.: Heuristically improved bayesian segmentation of brain MR images. Sci. World J. 9(3), 5–8 (2014)
Iyer, K.K., et al.: Early detection of preterm intraventricular hemorrhage from clinical electroencephalography. Crit. Care Med. 43(10), 2219–2227 (2015)
Jain, S., et al.: Automatic segmentation and volumetry of multiple sclerosis brain lesions from MR images. NeuroImage: Clin. 8, 367–375 (2015)
Liu, H.T., Sheu, T.W.H., Chang, H.H.: Automatic segmentation of brain mr images using an adaptive balloon snake model with fuzzy classification. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51(10), 1091–1104 (2013)
Marba, S.T.M., Caldas, J.P.S., Vinagre, L.E.F., Pessoto, M.A.: Incidence of periventricular/intraventricular hemorrhage in very low birth weight infants: a 15-year cohort study. J. Pediatr. 87, 505–511 (2011)
Matas, J., Chum, O., Urban, M., Pajdla, T.: Robust wide-baseline stereo from maximally stable extremal regions. Image Vis. Comput. 22(10), 761–767 (2004)
Nistér, D., Stewénius, H.: Linear time maximally stable extremal regions. In: Forsyth, D., Torr, P., Zisserman, A. (eds.) ECCV 2008. LNCS, vol. 5303, pp. 183–196. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88688-4_14
Ortiz, A., Gorriz, J., Ramirez, J., Salas-Gonzalez, D.: Improving MR brain image segmentation using self-organising maps and entropy-gradient clustering. Inf. Sci. 262, 117–136 (2014)
Otsu, N.: A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 9(1), 62–66 (1979)
Ou, X., et al.: Impaired white matter development in extremely low-birth-weight infants with previous brain hemorrhage. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 35(10), 1983–1989 (2014)
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12(7), 629–639 (1990)
Rosenfeld, A., Pfaltz, J.L.: Sequential operations in digital picture processing. J. ACM 13(4), 471–494 (1966)
Simon, N.P.: Periventricular/intraventricular hemorrhage (PVH/IVH) in the premature infant. http://www.pediatrics.emory.edu/divisions/neonatology/dpc/pvhivh.html. Accessed 02 Apr 2018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Mukherjee, S., Cheng, I., Basu, A. (2018). Atlas-Free Method of Periventricular Hemorrhage Detection from Preterm Infants’ T1 MR Images. In: Basu, A., Berretti, S. (eds) Smart Multimedia. ICSM 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11010. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04375-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04375-9_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-04374-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-04375-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)