Abstract
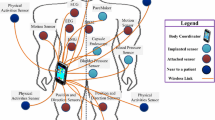
This work describes the implementation of a complete Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) that is capable of monitoring multiple physiological signals of a patient by means of IEEE 802.15.6 scheduled access MAC protocol. In the WBAN setup, data from multiple sensors are sent to a Body Network Controller (BNC) using low power transceivers. To this end, the BNC is designed to multiplex the data from multiple sensors, and send them to a remote server over the Internet using a backhaul cellular network, thereby enabling ubiquitous remote health monitoring. Furthermore, to facilitate an energy efficient backhaul transmission that incurs low data transfer costs to the users, we introduce the concept of data compression at the BNC. In this regard, we propose a fast Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) based data compression algorithm at the BNC, termed herein as B-DWT, that is implementable in real-time using the limited on-board resources. The remote server is configured to accept data from multiple patients, de-multiplex different data of a single patient and store them in a database for pervasive access. Issues related to the hardware implementation of sensor nodes and BNC, and the design of the scheduled access mechanism and B-DWT are addressed. Detailed performance analysis of the WBAN is performed in OPNET simulator to determine the optimum allocation intervals for the sensor nodes that maximizes network capacity while maintaining a frame delay constraint. Further, in order to prolong the battery life of sensor nodes, we obtain the optimal payload sizes that maximizes their energy efficiency. Additionally, through implementation of B-DWT at the BNC we determine the optimal wavelet filer and compression levels, that allow maximum data compression within acceptable limits of information loss. The resulting B-DWT algorithm is shown to outperform traditional DWT with significant gains in execution speed and low memory footprint at the BNC.
The first author deeply acknowledges the financial assistance by CSIR, Govt. of India.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 April 2019
The original version of this chapter was revised. Reference no. 23 (“References” section) was updated because the chapter which was under review has now been published.
References
World Health Organization: Life expectancy at birth (years) (2017). http://www.gamapserver.who.int/gho/interactive_charts/mbd/life_expectancy/atlas.html
The World Bank: World health organization global health expenditure database (2018). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.XPD.TOTL.ZS?end=2014&start=1995
Movassaghi, S., Abolhasan, M., Lipman, J., Smith, D., Jamalipour, A.: Wireless body area networks: a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 16(3), 1658–1686 (2014)
Latré, B., Braem, B., Moerman, I., Blondia, C., Demeester, P.: A survey on wireless body area networks. Wirel. Netw. 17(1), 1–18 (2011)
IEEE: IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks - Part 15.4: Low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs). IEEE Std (2011)
Gao, T., Greenspan, D., Welsh, M., Juang, R.R., Alm, A.: Vital signs monitoring and patient tracking over a wireless network. In: 27th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, China, pp. 102–105. IEEE (2006)
Chan, C.H., Poon, C.C.Y., Wong, R.C.S., Zhang, Y.T.: A hybrid body sensor network for continuous and long-term measurement of arterial blood pressure. In: 4th IEEE/EMBS International Summer School and Symposium on Medical Devices and Biosensors, ISSS-MDBS, United Kingdom, pp. 121–123. IEEE (2007)
IEEE: IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks - Part 15.1: Wireless personal area networks (WPANs), IEEE Std (2005)
Choi, J.M., Istepanian, R.S.H., Alesanco, A., Wang, H.: Hardware design and compression issues in compact bluetooth enabled wireless telecardiology system. In: 2nd International Conference on Broadband Networks, BroadNets, MA, USA, pp. 1014–1015. IEEE (2005)
Rasid, M.F.A., Woodward, B.: Bluetooth telemedicine processor for multichannel biomedical signal transmission via mobile cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 9(1), 35–43 (2005)
IEEE: IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks - part 15.6: Wireless body area networks. IEEE Std. (2012)
Manikandan, M.S., Dandapat, S.: Wavelet-based electrocardiogram signal compression methods and their performances: a prospective review. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 14, 73–107 (2014)
Lu, Z., Kim, D.Y., Pearlman, W.A.: Wavelet compression of ECG signals by the set partitioning in hierarchical trees algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47(7), 849–856 (2000)
Proakis, J.G., Manolakis, D.G.: Digital Signal Processing: Principles, Algorithms, and Applications. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River (2007)
Riverbed Technolgies: OPNET (2012). www.opnet.com
Jalaleddine, S.M.S., Hutchens, C.G., Strattan, R.D., Coberly, W.A.: ECG data compression techniques: a unified approach. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 37(4), 329–343 (1990)
Mallat, S.G.: A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(7), 674–693 (1989)
Texas Instruments: CC1101 low-power sub-1 GHz RF transceiver datasheet (2018). www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/cc1101.pdf
Interaction Design Institute: Arduino Uno (2018). www.arduino.org/products/boards/arduino-uno
Analog Devices Inc.: AD8232 datasheet (2018). www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/AD8232.pdf
panStamp: Panstamp library (2018). http://www.github.com/panStamp/panstamp/wiki
Interaction Design Institute: Arduino mega (2018). www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ArduinoBoardMega
Manna, T., Misra, I.S.: Performance analysis of scheduled access mode of the IEEE 802.15.6 MAC protocol under non-ideal channel conditions. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. PP(99) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2019.2901852
Zigel, Y., Cohen, A., Katz, A.: The Weighted Diagnostic Distortion (WDD) measure for ECG signal compression. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 47(11), 1422–1430 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Manna, T., Misra, I.S. (2019). Implementation of Energy Efficient WBAN Using IEEE 802.15.6 Scheduled Access MAC with Fast DWT Based Backhaul Data Compression for e-Healthcare. In: Biswas, S., et al. Communication Systems and Networks. COMSNETS 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11227. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10659-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10659-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-10658-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-10659-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)