Abstract
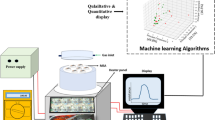
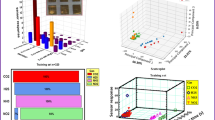
In this work a proof of concept for discriminating explosive substances is presented, where a discrimination model for the classification of TNT and gunpowder is developed. An electronic nose was designed for sensing volatile organic compounds present in TNT and gunpowder, and a model that combines Principal Component Analysis and Fisher Discriminant Analysis was built for enhancing class discrimination. The model was tested in two scenarios: discriminating among the two explosive substances and one non-explosive, and discriminating between explosives and non-explosives, obtaining better results in the second case. In order to test model confidence a permutation test was used proving an accuracy of 67% with a p-value <0.01 for the first scenario, and an accuracy of 86.6% for the second one. These results make us think that by enhancing the prototype characteristics in both hardware and software, we would be able to achieve better results.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gui, Y., Xie, C., Xu, J., Wang, G.: Detection and discrimination of low concentration explosives using MOS nanoparticle sensors. J. Hazard. Mater. 164, 1030–1035 (2009)
Redacción el Comercio: Gobierno confirma secuestro de equipo periodístico de EL COMERCIO en Mataje (2018). http://www.elcomercio.com/actualidad/mataje-secuestro-equipoperiodistas-elcomercio-ecuador.html
Castillo Egüez, J.L.: Armas de fuego y políticas públicas (Ecuador 2.009–2.015) (Opinión) (2015)
Nebbia, G., Pesente, S., Lunardon, M., Moretto, S., Viesti, G., Cinausero, M., Barbui, M., Fioretto, E., Filippini, V., Sudac, D., Nađ, K., Blagus, S., Valković, V.: Detection of hidden explosives in different scenarios with the use of nuclear probes. Nucl. Phys. A 752, 649–658 (2005)
Aleksandrov, V.D., Bogolubov, E.P., Bochkarev, O.V., Korytko, L.A., Nazarov, V.I., Polkanov, Y.G., Ryzhkov, V.I., Khasaev, T.O.: Application of neutron generators for high explosives, toxic agents and fissile material detection. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 63, 537–543 (2005)
Barthet, C., Montméat, P., Eloy, N., Prené, P.: Detection of explosives vapours using a multi-quartz crystal microbalance system. Procedia Eng. 5, 472–475 (2010)
Brudzewski, K., Osowski, S., Pawlowski, W.: Metal oxide sensor arrays for detection of explosives at sub-parts-per million concentration levels by the differential electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 161, 528–533 (2012)
Guillemot, M., Dayber, F., Montméat, P., Barthet, C., Prené, P.: Detection of explosives vapours on quartz crystal microbalances: generation of very low-concentrated vapours for sensors calibration. Procedia Chem. 1, 967–970 (2009)
Rousier, R., Bouat, S., Bordy, T., Grateau, H., Darboux, M., Hue, J., Gaillard, G., Besnard, S., Veignal, F., Montméat, P., Lebrun, G., Larue, A.: T-REX: a portable device to detect and identify explosives vapors. Procedia Eng. 47, 390–393 (2012)
Stetter, J.R., Strathmann, S., McEntegart, C., Decastro, M., Penrose, W.R.: New sensor arrays and sampling systems for a modular electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 69, 410–419 (2000)
Röck, F., Barsan, N., Weimar, U.: Electronic nose: current status and future trends. Chem. Rev. 108, 705–725 (2008)
Lopez, P., Trivino, R., Calderon, D., Arcentales, A., Guaman, A.V.: Electronic nose prototype for explosive detection. Presented at the 2017 CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies (CHILECON), Chile, October 2017
Banerjee, R., Tudu, B., Bandyopadhyay, R., Bhattacharyya, N.: A review on combined odor and taste sensor systems. J. Food Eng. 190, 10–21 (2016)
Di Carlo, S., Falasconi, M.: Drift correction methods for gas chemical sensors in artificial olfaction systems: techniques and challenges. In: Advances in Chemical Sensors, p. 326. InTech, Rijeka (2012)
Jollife, I.T.: Principal Component Analysis. Springer, New York (2002)
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G.: Pattern Classification (Pt. 1). Wiley, New York (2001)
Wang, M., Perera, A., Gutierrez-Osuna, R.: Principal discriminants analysis for small-sample-size problems: application to chemical sensing. 2004 Presented at the Sensors. IEEE (2004)
Luo, D., Ding, C., Huang, H.: Linear discriminant analysis: new formulation and overfit analysis. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 417–422 (2011)
Gupta, V., Mittal, M.: KNN and PCA classifier with Autoregressive modelling during different ECG signal interpretation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 125, 18–24 (2018)
Arlot, S., Celisse, A.: A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection. Stat. Surv. 4, 40–79 (2010)
Good, P.I.: Permutation, Parametric, and Bootstrap Tests of Hypotheses. Springer-Verlag, New York (2005)
Mukherjee, S., Golland, P., Panchenko, D.: Permutation Tests for Classification. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, #2003-019 (2003)
Ojala, M.: Permutation tests for studying classifier performance. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11, 1833–1863 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was founded by Universidad de las Fuerzas Armadas ESPE under the project 2016-pic-009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Guaman, A.V., Lopez, P., Torres-Tello, J. (2019). Multivariate Discrimination Model for TNT and Gunpowder Using an Electronic Nose Prototype: A Proof of Concept. In: Rocha, Á., Ferrás, C., Paredes, M. (eds) Information Technology and Systems. ICITS 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 918. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11890-7_28
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11890-7_28
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-11889-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-11890-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)