Abstract
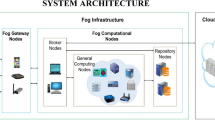
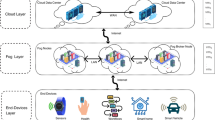
Reducing delay and latency in the cloud computing environment is a challenge for the present research community. This study performed a rigorous, comparative analysis of the fog computing paradigm and the conventional cloud computing paradigm in the context of the Smart Grid (SG). To meet the consumers’ demand and optimize cloud services to achieve service level objectives is of great importance. The fog is introduced to enhance the efficiency of the cloud and to fulfill the consumer requests at the edge of the network. When the requests of Smart Societies (SSs) are huge on fog, the increased demand for real-time response is becoming a challenge for the SG. In this study, Particle Swarm Optimization is implemented and compared with the proposed techniques: Improved PSO with Lewy Walk (IPSOLW). These load balancing algorithms are compared on the basis of Closest Data Center (CDC) and Optimize Response Time (ORT). These proposed algorithms handle the load of SS on fog. The proposed IPSOLW handles more requests because of LW, the requests are directly allocated to best DC.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z., Hayat, M.M., Ghani, N., Shaban, K.B.: Optimizing cloud-service performance: efficient resource provisioning via optimal workload allocation. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 28(6), 1689–1702 (2017)
Anderson, D., Gkountouvas, T., Meng, M., Birman, K., Bose, A., Hauser, C., Litvinov, E., Luo, X., Zhang, F.: GridCloud: infrastructure for cloud-based wide area monitoring of bulk electric power grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, 1–10 (2018)
Wang, W., Zhou, F., Li, J.: Cloud-based parallel power flow calculation using resilient distributed datasets and directed acyclic graph. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy, 1–13 (2018)
Yu, L., Jiang, T., Zou, Y.: Fog-assisted operational cost reduction for cloud data centers. IEEE Access 5, 13578–13586 (2017)
Buksh, R., Javaid, N., Fatima, I.: Towards efficient resource utilization exploiting collaboration between HPF and 5G enabled energy management controllers in smart homes. Sustainability 10(10), 3592 (2018). 3–24
Leontiou, N., Dechouniotis, D., Denazis, S., Papavassiliou, S.: A hierarchical control framework of load balancing and resource allocation of cloud computing services. Comput. Electr. Eng. 67, 235–251 (2018)
Zhao, H., Wang, J., Liu, F., Wang, Q., Zhang, W., Zheng, Q.: Power-aware and performance-guaranteed virtual machine placement in the cloud. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 29(6), 1385–1400 (2018)
Xue, S., Zhang, Y., Xiaolong, X., Xing, G., Xiang, H., Ji, S.: QET: a QoS-based energy-aware task scheduling method in cloud environment. Cluster Comput. 20(4), 3199–3212 (2017)
Mann, Z.Á.: Resource optimization across the cloud stack. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 29(1), 169–182 (2018)
Liao, D., Sun, G., Yang, G., Chang, V.: Energy-efficient virtual content distribution network provisioning in cloud-based data centers. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 83, 347–357 (2018)
Pau, M., Patti, E., Barbierato, L., Estebsari, A., Pons, E., Ponci, F., Monti, A.: A cloud-based smart metering infrastructure for distribution grid services and automation. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 15, 14–25 (2017)
Abdel-Basset, M., Abdle-Fatah, L., Sangaiah, A.K.: An improved Lévy based whale optimization algorithm for bandwidth-efficient virtual machine placement in cloud computing environment. Cluster Comput., 1–16 (2018)
Mirjalili, S., Saremi, S., Mirjalili, S.M., dos Coelho, L.: Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 47, 106–119 (2016)
Jensi and Wiselin Jiji: An enhanced particle swarm optimization with levy flight for global optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 43, 248–261 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Butt, A.A., Khan, Z.A., Javaid, N., Chand, A., Fatima, A., Islam, M.T. (2020). Optimization of Response and Processing Time for Smart Societies Using Particle Swarm Optimization and Levy Walk. In: Barolli, L., Takizawa, M., Xhafa, F., Enokido, T. (eds) Advanced Information Networking and Applications. AINA 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 926. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15032-7_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15032-7_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-15031-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-15032-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)