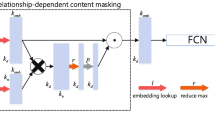
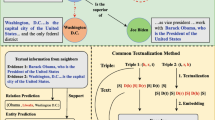
Abstract
The basic unit of knowledge graph is triplet, including head entity, relation and tail entity. Centering on knowledge graph, knowledge graph completion has attracted more and more attention and made great progress. However, these models are all verified by open domain data sets. When applied in specific domain case, they will be challenged by practical data distributions. For example, due to poor presentation of tail entities caused by their relation-oriented feature, they can not deal with the completion of enzyme knowledge graph. Inspired by question answering and rectilinear propagation of lights, this paper puts forward a tail-oriented method - Embedding for Multi-Tails knowledge graph (EMT). Specifically, it first represents head and relation in question space; then, finishes projection to answer one by tail-related matrix; finally, gets tail entity via translating operation in answer space. To overcome time-space complexity of EMT, this paper includes two improved models: EMT\(^v\) and EMT\(^s\). Taking some optimal translation and composition models as baselines, link prediction and triplets classification on an enzyme knowledge graph sample and Kinship proved our performance improvements, especially in tails prediction.
This research was partially supported by the grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91846204, 61532010, 61532016, 61379050, 91646203, 61762082); the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB1000602, 2016YFB1000603); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Research Funds of Renmin University (No. 11XNL010); and the Science and Technology Opening Up Cooperation Project of Henan Province (172106000077).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belleau, F., Nolin, M.A., Tourigny, N., Rigault, P., Morissette, J.: Bio2RDF: towards a mashup to build bioinformatics knowledge systems. J. Biomed. Inform. 41(5), 706–716 (2008)
Bollacker, K., Evans, C., Paritosh, P., Sturge, T., Taylor, J.: Freebase: a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In: SIGMOD, pp. 1247–1250. ACM (2008)
Bordes, A., Glorot, X., Weston, J., Bengio, Y.: A semantic matching energy function for learning with multi-relational data. Mach. Learn. 94(2), 233–259 (2014)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: NIPS, pp. 2787–2795 (2013)
Bordes, A., Weston, J., Collobert, R., Bengio, Y.: Learning structured embeddings of knowledge bases. In: AAAI, pp. 301–306 (2011)
Carlson, A., Betteridge, J., Kisiel, B., Settles, B.: Toward an architecture for never-ending language learning. In: AAAI (2010)
Dong, X., et al.: Knowledge vault: a web-scale approach to probabilistic knowledge fusion. In: KDD, pp. 601–610. ACM (2014)
Jenatton, R., Roux, N.L., Bordes, A., Obozinski, G.R.: A latent factor model for highly multi-relational data. In: NIPS, pp. 3167–3175 (2012)
Ji, G., He, S., Xu, L., Liu, K., Zhao, J.: Knowledge graph embedding via dynamic mapping matrix. In: ACL and IJCNLP, pp. 687–696 (2015)
Ji, G., Liu, K., He, S., Zhao, J.: Knowledge graph completion with adaptive sparse transfer matrix. In: AAAI, pp. 985–991 (2016)
Kemp, C., Tenenbaum, J.B., Griffiths, T.L., Yamada, T., Ueda, N.: Learning systems of concepts with an infinite relational model. In: AAAI, pp. 381–388. AAAI Press (2006). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1597538.1597600
Lin, Y., Liu, Z., Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, X.: Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion. In: AAAI, pp. 2181–2187 (2015)
Liu, H., Wu, Y., Yang, Y.: Analogical inference for multi-relational embeddings. CoRR abs/1705.02426 (2017). http://arxiv.org/abs/1705.02426
Liu, Q., Jiang, H., Ling, Z., Wei, S., Hu, Y.: Probabilistic reasoning via deep learning: neural association models. CoRR abs/1603.07704 (2016). http://arxiv.org/abs/1603.07704
Momtchev, V., Peychev, D., Primov, T., Georgiev, G.: Expanding the pathway and interaction knowledge in linked life data. In: ISWC (2009)
Nickel, M., Rosasco, L., Poggio, T.: Holographic embeddings of knowledge graphs. In: AAAI, pp. 1955–1961 (2016)
Nickel, M., Tresp, V., Kriegel, H.P.: A three-way model for collective learning on multi-relational data. In: ICML, pp. 809–816 (2011)
Rummel, R.J.: Dimensionality of nations project: attributes of nations and behavior of nation dyads, 1950–1965 (1992). https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR05409.v1
Ruttenberg, A., Rees, J.A., Samwald, M., Marshall, M.S.: Life sciences on the Semantic Web: the Neurocommons and beyond. Brief. Bioinform. 10(2), 193–204 (2009)
Socher, R., Chen, D., Manning, C.D., Ng, A.Y.: Reasoning with neural tensor networks for knowledge base completion. In: NIPS, pp. 926–934 (2013)
Suchanek, F.M., Kasneci, G., Weikum, G.: YAGO: a large ontology from Wikipedia and WordNet. Web Semant.: Sci. Serv. Agents World Wide Web 6(3), 203–217 (2008)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: AAAI, pp. 1112–1119. AAAI Press (2014)
Welbl, J., Riedel, S., Bouchard, G.: Complex embeddings for simple link prediction. In: ICML, pp. 2071–2080 (2016)
Wu, W., Li, H., Wang, H., Zhu, K.Q.: Probase: a probabilistic taxonomy for text understanding. In: SIGMOD, pp. 481–492. ACM (2012)
Yang, B., Yih, W., He, X., Gao, J., Deng, L.: Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. CoRR abs/1412.6575 (2014). http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6575
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Du, Z., Meng, X. (2019). EMT: A Tail-Oriented Method for Specific Domain Knowledge Graph Completion. In: Yang, Q., Zhou, ZH., Gong, Z., Zhang, ML., Huang, SJ. (eds) Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. PAKDD 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11441. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16142-2_40
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16142-2_40
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-16141-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-16142-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)