Abstract
Constraint-logic object-oriented programming, for example using Muli, facilitates the integrated development of business software that occasionally involves finding solutions to constraint-logic problems. The availability of object-oriented features calls for the option to use objects as logic variables as well, as opposed to being limited to primitive type logic variables. The present work contributes a concept for reference type logic variables in constraint-logic object-oriented programming that takes arbitrary class hierarchies of programs written in object-oriented languages into account. The concept discusses interactions between constraint-logic object-oriented programs and reference type logic variables, particularly invocations on and access to logic variables, type operations, and equality. Furthermore, it proposes approaches as to how these interactions can be handled by a corresponding execution environment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
Even though
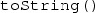 is not declared explicitly in the given interface, the Java language specification implicitly augments interfaces with abstract methods that correspond to every method that is declared in
is not declared explicitly in the given interface, the Java language specification implicitly augments interfaces with abstract methods that correspond to every method that is declared in
 [5, Sect. 9.2]. Among others, this includes an implicit declaration of
[5, Sect. 9.2]. Among others, this includes an implicit declaration of
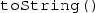 that is consistent with the corresponding declaration in
that is consistent with the corresponding declaration in
 .
. - 2.
Note that only the standalone use of type variables is disregarded here. Consequently, the reference types that we consider in the following may still make use of type variables as part of parameterised (generic) types.
- 3.
In general, this includes parameterised (generic) types that remain in parameterised form (e.g.,
 ). Therefore, this set is finite.
). Therefore, this set is finite. - 4.
Note that here \(fields(o_1) = fields(o_2)\) since \(type(o_1) = type(o_2)\), so \(fields(o_2)\) could be used just as well.
- 5.
References
Antoy, S., Hanus, M.: From boolean equalities to constraints. In: Falaschi, M. (ed.) LOPSTR 2015. LNCS, vol. 9527, pp. 73–88. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-27436-2_5
Dageförde, J.C., Kuchen, H.: A constraint-logic object-oriented language. In: SAC 2018, pp. 1185–1194. ACM (2018). https://doi.org/10.1145/3167132.3167260
Dageförde, J.C., Kuchen, H.: An operational semantics for constraint-logic imperative programming. In: Seipel, D., Hanus, M., Abreu, S. (eds.) WFLP/WLP/INAP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10997, pp. 64–80. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00801-7_5
Denti, E., Omicini, A., Ricci, A.: Multi-paradigm Java-Prolog integration in tuProlog. Sci. Comput. Program. 57(2), 217–250 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scico.2005.02.001
Gosling, J., Joy, B., Steele, G., Bracha, G., Buckley, A.: The Java® Language Specification - Java SE 8 Edition (2015). https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se8/jls8.pdf
Hanus, M., Kuchen, H., Moreno-Navarro, J.J., Votano, J., Parham, M., Hall, L.: Curry: a truly functional logic language. In: Workshop on Visions for the Future of Logic Programming, ILPS 1995, pp. 95–107 (1995)
King, J.C.: Symbolic execution and program testing. Commun. ACM 19(7), 385–394 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1145/360248.360252
Lazutkin, E.: Unification for JS (2014). http://www.lazutkin.com/blog/2014/05/18/unification-for-js/
Meijer, E., Beckman, B., Bierman, G.: LINQ: reconciling objects, relations and XML in the .NET framework. In: ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, p. 706 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1145/1142473.1142552
Microsoft: Reference Types (C# Reference) (2015). https://docs.microsoft.com/de-de/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/keywords/reference-types
Odersky, M., et al.: Scala Language Specification (2017). http://www.scala-lang.org/files/archive/spec/2.12/
Ostermayer, L.: Seamless cooperation of Java and Prolog for rule-based software development. In: Proceedings of RuleML 2015 (2015). http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1417/paper2.pdf
Plümicke, M.: Java type unification with wildcards. In: Seipel, D., Hanus, M., Wolf, A. (eds.) INAP/WLP 2007. LNCS, vol. 5437, pp. 223–240. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00675-3_15
Urma, R.G., Fusco, M., Mycroft, A.: Java 8 in Action: Lambdas, Streams, and Functional-Style Programming. Manning Publications Co., Greenwich (2014)
Van Roy, P., Brand, P., Duchier, D., Haridi, S., Schulte, C., Henz, M.: Logic programming in the context of multiparadigm programming: the Oz experience. Theory Pract. Logic Program. 3(6), 717–763 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1471068403001741
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Dageförde, J.C. (2019). Reference Type Logic Variables in Constraint-Logic Object-Oriented Programming. In: Silva, J. (eds) Functional and Constraint Logic Programming. WFLP 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11285. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16202-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16202-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-16201-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-16202-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)





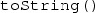 is not declared explicitly in the given interface, the Java language specification implicitly augments interfaces with abstract methods that correspond to every method that is declared in
is not declared explicitly in the given interface, the Java language specification implicitly augments interfaces with abstract methods that correspond to every method that is declared in
 [
[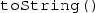 that is consistent with the corresponding declaration in
that is consistent with the corresponding declaration in
 .
. ). Therefore, this set is finite.
). Therefore, this set is finite.