Abstract
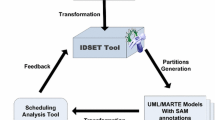
The process of verifying whether Real-Time Embedded Systems (RTES) meet their temporal requirements is a major step during the system design. This step, called schedulability analysis, must be carried out at early design stages to avoid system failures. Currently, researchers are interested in using high-level techniques to raise the abstraction level and reduce the designers’ effort. Nevertheless, only the scheduling approaches that prohibit task migration have been supported. An attempt to consider semi-partitioned and global scheduling approaches, which allow task migration, has been recently proposed. However, it doesn’t support dependent tasks. In this context, this paper proposes an automatic process for early schedulability analysis considering dependent tasks and scheduling approaches with task migration. The focus is on the transformation of dynamic models annotated through the Unified Modeling Language (UML) profile for Modeling and Analysis of Real-Time Embedded systems (MARTE) to the model of SimSo tool.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chéramy, M., Hladik, P.-E., Déplanche, A.-M.: SimSo: a simulation tool to evaluate real-time multiprocessor scheduling algorithms. In: WATERS 2014 (2014)
Gonzalez Harbour, M., Gutierrez Garcia, J.J., Palencia Gutierrez, J.C., Drake Moyano, J.M.: Mast: modeling and analysis suite for real time applications. In: 2001 13th Euromicro Conference on Real-Time Systems, pp. 125–134 (2001)
Jensen, K.E.A.: Schedulability analysis of embedded applications modelled using MARTE. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University of Denmark (2009)
Manacero Jr., A.: Real time systems (2006). http://www.dcce.ibilce.unesp.br/spd/rtsim/english
Madl, G.: Model-based analysis of event-driven distributed real-time embedded systems. Ph.D. thesis, Long Beach, CA, USA (2009)
Magdich, A., Kacem, Y.H., Mahfoudhi, A., Abid, M.: From UML/MARTE models of multiprocessor real-time embedded systems to early schedulability analysis based on SimSo tool. In: ICSOFT, Lisbon, Portugal (2016)
Medina, J.L., Cuesta, Á.G.: From composable design models to schedulability analysis with UML and the UML profile for MARTE. SIGBED Rev. 8(1), 64–68 (2011)
Naija, M., Ahmed, S.B., Bruel, J.-M.: New schedulability analysis for real-time systems based on MDE and petri nets model at early design stages. In: ICSOFT-EA 2015, Colmar, Alsace, France, 20–22 July 2015, pp. 330–338 (2015)
Rubini, S., Fotsing, C., Singhoff, F., Tran, H.N., Dissaux, P.: Scheduling analysis from architectural models of embedded multi-processor systems. In: EWiLi Workshop (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Magdich, A., Hadj Kacem, Y., Dammak, B., Mahfoudhi, A., Abid, M. (2020). From Dynamic UML/MARTE Models to Early Schedulability Analysis of RTES with Dependent Tasks. In: Abraham, A., Cherukuri, A., Melin, P., Gandhi, N. (eds) Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. ISDA 2018 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 941. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16660-1_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16660-1_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-16659-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-16660-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)