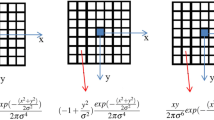
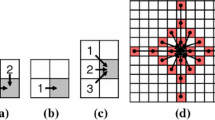
Abstract
The current state of the art of Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping, or SLAM, on low power embedded systems is about sparse localisation and mapping with low resolution results in the name of efficiency. Meanwhile, research in this field has provided many advances for information rich processing and semantic understanding, combined with high computational requirements for real-time processing. This work provides a solution to bridging this gap, in the form of a scalable SLAM-specific architecture for depth estimation for direct semi-dense SLAM. Targeting an off-the-shelf FPGA-SoC this accelerator architecture achieves a rate of more than 60 mapped frames/sec at a resolution of \(640 \times 480\) achieving performance on par to a highly-optimised parallel implementation on a high-end desktop CPU with an order of magnitude improved power consumption. Furthermore, the developed architecture is combined with our previous work for the task of tracking, to form the first complete accelerator for semi-dense SLAM on FPGAs, establishing the state of the art in the area of embedded low-power systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
For example, the tool always rounds up memory size to the next power of two for BRAM utilization. To reduce that overhead we partitioned memory cyclically by a factor of 5, saving BRAMs at the cost of increased DSPs and LUTs.
- 2.
These were the Room and Machine Hall trajectory from TUM’s website: https://vision.in.tum.de/research/vslam/lsdslam.
- 3.
The power figures were often not mentioned in works, or measured with varying methods. Thus, in the interest of providing a qualitative view, we include a typical expected power for the chip/platform mentioned in the publications (e.g. nVidia 680GTX, Jetson TX1, Intel i7-4700MQ etc.). For our work, we report the estimated chip power instead of the board power to be in line with other papers.
References
Boikos, K., Bouganis, C.S.: A high-performance system-on-chip architecture for direct tracking for SLAM. In: 27th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL). IEEE (2017)
Engel, J., Schöps, T., Cremers, D.: LSD-SLAM: large-scale direct monocular SLAM. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8690, pp. 834–849. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10605-2_54
Engel, J., Usenko, V., Cremers, D.: A photometrically calibrated benchmark for monocular visual odometry. arXiv:1607.02555 (2016)
Forster, C., Pizzoli, M., Scaramuzza, D.: SVO: fast semi-direct monocular visual odometry. In: International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE (2014)
Handa, A., Newcombe, R.A., Angeli, A., Davison, A.J.: Real-time camera tracking: when is high frame-rate best? In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7578, pp. 222–235. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33786-4_17
Honegger, D., Oleynikova, H., Pollefeys, M.: Real-time and low latency embedded computer vision hardware based on a combination of FPGA and mobile CPU. In: International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), IEEE/RSJ (2014)
Leutenegger, S., Lynen, S., Bosse, M., Siegwart, R., Furgale, P.: Keyframe-based visual-inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 34(3), 314–334 (2015)
Mur-Artal, R., Montiel, J.M.M., Tardos, J.D.: ORB-SLAM: a versatile and accurate monocular slam system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(5), 1147–1163 (2015)
Sturm, J., Bylow, E., Kerl, C., Kahl, F., Cremer, D.: Dense tracking and mapping with a quadrocopter. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle in Geomatics (UAV-g) (2013)
Suleiman, A., et al.: Navion: a fully integrated energy-efficient visual-inertial odometry accelerator for autonomous navigation of nano drones. In: IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits (2018)
Vincke, B., Elouardi, A., Lambert, A., Merigot, A.: Efficient implementation of EKF-SLAM on a multi-core embedded system. In: IECON 2012–38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, pp. 3049–3054. IEEE (2012)
Weberruss, J., Kleeman, L., Boland, D., Drummond, T.: FPGA acceleration of multilevel ORB feature extraction for computer vision. In: 27th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL). IEEE (2017)
Whelan, T., et al.: Real-time large-scale dense RGB-D SLAM with volumetric fusion. Int. J. Robot. Res. 34(4–5), 598–626 (2015)
Acknowledgments
The support of the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in High Performance Embedded and Distributed Systems (HiPEDS, Grant Reference EP/L016796/1) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Boikos, K., Bouganis, CS. (2019). A Scalable FPGA-Based Architecture for Depth Estimation in SLAM. In: Hochberger, C., Nelson, B., Koch, A., Woods, R., Diniz, P. (eds) Applied Reconfigurable Computing. ARC 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11444. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17227-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17227-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-17226-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-17227-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)