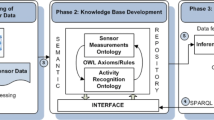
Abstract
The aging population, prevalence of chronic diseases, and outbreaks of infectious diseases are some of the major healthcare challenges. To address these unmet healthcare challenges, monitoring and Activity Recognition (AR) are considered as a subtask in pervasive computing and context-aware systems. Innumerable interdisciplinary applications exist, underpinning the obtrusive sensory data using the revolutionary digital technologies for the acquisition, transformation, and fusion of recognized activities. However, little importance is given by the research community to make the use of non-wearables i.e. unobtrusive sensing technologies. The physical state of human pervasively in daily living for AR can be seamlessly presented by acquiring health-related information by using unobtrusive sensing technologies to enable long-term health monitoring without violating an individual’s privacy. This paper aims to propose and provide supervised recognition of Activities of Daily Livings (ADLs) by observing unobtrusive sensor events using statistical reasoning. Furthermore, it also investigates their semantic correlations by defining semantic constraints with the support of ontological reasoning. Extensive experiments were performed with real-world dataset shared by the University of Jaén Ambient Intelligence (UJAmI) Smart Lab in order to recognize the human activities in the smart environment. The evaluations show that the accuracy of the supervised method (87%) is comparable to the one, state of the art semantic approach (91%).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bulling, A., Blanke, U., Schiele, B.: A tutorial on human activity recognition using body-worn inertial sensors. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 46(3), 33 (2014)
Chen, L., Nugent, C.D., Okeyo, G.: An ontology-based hybrid approach to activity modeling for smart homes. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 44(1), 92–105 (2014)
Dernbach, S., Das, B., Krishnan, N.C., Thomas, B.L., Cook, D.J.: Simple and complex activity recognition through smart phones. In: 2012 8th International Conference on Intelligent Environments (IE), pp. 214–221. IEEE (2012)
van der Gaag, M., Hoffman, T., Remijsen, M., Hijman, R., de Haan, L., van Meijel, B., van Harten, P.N., Valmaggia, L., De Hert, M., Cuijpers, A., et al.: The five-factor model of the positive and negative syndrome scale ii: a ten-fold cross-validation of a revised model. Schizophr. Res. 85(1–3), 280–287 (2006)
Ghosh, A., Chakraborty, D., Prasad, D., Saha, M., Saha, S.: Can we recognize multiple human group activities using ultrasonic sensors? In: 2018 10th International Conference on Communication Systems & Networks (COMSNETS), pp. 557–560. IEEE (2018)
Gochoo, M., Tan, T.H., Liu, S.H., Jean, F.R., Alnajjar, F., Huang, S.C.: Unobtrusive activity recognition of elderly people living alone using anonymous binary sensors and DCNN. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 23(2), 693–702 (2018)
Gravina, R., Alinia, P., Ghasemzadeh, H., Fortino, G.: Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: state-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 35, 68–80 (2017)
Mokhtari, G., Bashi, N., Zhang, Q., Nourbakhsh, G.: Non-wearable human identification sensors for smart home environment: a review. Sens. Rev. 38(3), 391–404 (2018)
World Health Organization: WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization: sixty-eighth report. World Health Organization (2018)
Python: Python (2018). https://www.python.org/
Razzaq, M.A., Amin, M.B., Lee, S.: An ontology-based hybrid approach for accurate context reasoning. In: 2017 19th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), pp 403–406 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/APNOMS.2017.8094159
Razzaq, M.A., Villalonga, C., Lee, S., Akhtar, U., Ali, M., Kim, E.S., Khattak, A.M., Seung, H., Hur, T., Bang, J., et al.: mlCAF: multi-level cross-domain semantic context fusioning for behavior identification. Sensors 17(10), 2433 (2017)
Razzaq, M.A., Cleland, I., Nugent, C., Lee, S.: Multimodal sensor data fusion for activity recognition using filtered classifier, vol. 2, no. 19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2191262. http://www.mdpi.com/2504-3900/2/19/1262
Riboni, D., Sztyler, T., Civitarese, G., Stuckenschmidt, H.: Unsupervised recognition of interleaved activities of daily living through ontological and probabilistic reasoning. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, pp. 1–12. ACM (2016)
Tschumitschew, K., Klawonn, F.: Effects of drift and noise on the optimal sliding window size for data stream regression models. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 46(10), 5109–5132 (2017)
UJAmI: UJAmI (2018). http://ceatic.ujaen.es/ujami/sites/default/files/2018-07/UCAmI%20Cup.zip
Weka: Weka (2018). https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/
Yang, J., Nguyen, M.N., San, P.P., Li, X., Krishnaswamy, S.: Deep convolutional neural networks on multichannel time series for human activity recognition. In: IJCAI, vol. 15, pp. 3995–4001 (2015)
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2017-0-00655). This work was also supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2017-0-01629) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion) and NRF-2016K1A3A7A03951968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Razzaq, M.A., Lee, S. (2019). MMOU-AR: Multimodal Obtrusive and Unobtrusive Activity Recognition Through Supervised Ontology-Based Reasoning. In: Lee, S., Ismail, R., Choo, H. (eds) Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (IMCOM) 2019. IMCOM 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 935. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-19063-7_75
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-19063-7_75
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-19062-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-19063-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)