Abstract
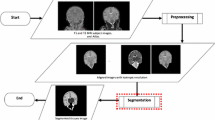
Morphometric analysis of brain structures is of high interest for premature neonates, in particular for defining predictive neurodevelopment biomarkers. This requires beforehand, the correct segmentation of structures of interest from MR images. Such segmentation is however complex, due to the resolution and properties of data. In this context, we investigate the potential of hierarchical image models, and more precisely the binary partition tree, as a way of developing efficient, interactive and user-friendly 3D segmentation methods. In particular, we experiment the relevance of texture features for defining the hierarchy of partitions constituting the final segmentation space. This is one of the first uses of binary partition trees for 3D segmentation of medical images. Experiments are carried out on 19 MR images for cerebellum segmentation purpose.
The research leading to these results has been supported by the ANR MAIA project (http://recherche.imt-atlantique.fr/maia), grant ANR-15-CE23-0009 of the French National Research Agency; and the American Memorial Hospital Foundation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
© Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine and I. S. Gousias 2013.
- 2.
Epirmex is a part of the French epidemiologic study Epipage 2 [1], http://epipage2.inserm.fr.
References
Ancel, P.Y., Goffinet, F.: EPIPAGE 2 writing group: EPIPAGE 2: a preterm birth cohort in France in 2011. BMC Pediatr. 14, 97 (2014)
Bogovic, J.A., Bazin, P.L., Ying, S.H., Prince, J.L.: Automated segmentation of the cerebellar lobules using boundary specific classification and evolution. In: IPMI, Proceedings, pp. 62–73 (2013)
Cardoso, M.J., et al.: AdaPT: an adaptive preterm segmentation algorithm for neonatal brain MRI. NeuroImage 65, 97–108 (2013)
Cettour-Janet, P., et al.: Watervoxels. HAL Research Report hal-02004228 (2019)
Coupé, P., Manjón, J.V., Fonov, V., Pruessner, J., Robles, M., Collins, D.L.: Patch-based segmentation using expert priors: application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. NeuroImage 54, 940–954 (2011)
Gousias, I.S., et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging of the newborn brain: manual segmentation of labelled atlases in term-born and preterm infants. NeuroImage 62, 1499–1509 (2012)
Gousias, I.S., et al.: Magnetic resonance imaging of the newborn brain: automatic segmentation of brain images into 50 anatomical regions. PLoS One 8, e5999 (2013)
Gui, L., Lisowski, R., Faundez, T., Hüppi, P., Lazeyras, F., Kocher, M.: Morphology-based segmentation of newborn brain MR images. In: MICCAI NeoBrainS12, Proceedings, pp. 1–8 (2012)
Hack, M., Fanaroff, A.A.: Outcomes of children of extremely low birthweight and gestational age in the 1990s. Semin. Neonatol. 5, 89–106 (2000)
Haralick, R.M., Shanmugam, K., Dinstein, I.: Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. SMC–3, 610–621 (1973)
Hwang, J., Kim, J., Han, Y., Park, H.: An automatic cerebellum extraction method in T1-weighted brain MR images using an active contour model with a shape prior. Magn. Reson. Imaging 29, 1014–1022 (2011)
Kim, H., Lepage, C., Evans, A.C., Barkovich, J., Xu, D.: NEOCIVET: extraction of cortical surface and analysis of neonatal gyrification using a modified CIVET pipeline. In: MICCAI, Proceedings, pp. 571–579 (2015)
van der Lijn, F., et al.: Cerebellum segmentation in MRI using atlas registration and local multi-scale image descriptors. In: ISBI, Proceedings, pp. 221–224 (2009)
Machairas, V., Faessel, M., Cárdenas-Peña, D., Chabardes, T., Walter, T., Decencière, E.: Waterpixels. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3707–3716 (2015)
Mahapatra, D.: Skull stripping of neonatal brain MRI: using prior shape information with graph cuts. J. Digit. Imaging 25, 802–814 (2012)
Makris, N., et al.: MRI-based surface-assisted parcellation of human cerebellar cortex: an anatomically specified method with estimate of reliability. NeuroImage 25, 1146–1160 (2005)
Makropoulos, A., Counsell, S.J., Rueckert, D.: A review on automatic fetal and neonatal brain MRI segmentation. NeuroImage 170, 231–248 (2017)
Makropoulos, A., et al.: Automatic tissue and structural segmentation of neonatal brain MRI using expectation-maximization. In: MICCAI NeoBrainS12, Proceedings, pp. 9–15 (2012)
Marlow, N., Wolke, D., Bracewell, M.A., Samara, M., Group, E.S.: Neurologic and developmental disability at six years of age after extremely preterm birth. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 9–19 (2005)
Melbourne, A., Cardoso, M.J., Kendall, G.S., Robertson, N.J., Marlow, N., Ourselin, S.: NeoBrainS12 challenge: adaptive neonatal MRI brain segmentation with myelinated white matter class and automated extraction of ventricles I–IV. In: MICCAI NeoBrainS12, Proceedings, pp. 16–21 (2012)
Péporté, M., Ghita, D.E.I., Twomey, E., Whelan, P.F.: A hybrid approach to brain extraction from premature infant MRI. In: SCIA, Proceedings, pp. 719–730 (2011)
Prastawa, M., Gilmore, J.H., Lin, W., Gerig, G.: Automatic segmentation of MR images of the developing newborn brain. Med. Image Anal. 9, 457–466 (2005)
Randrianasoa, J.F., Kurtz, C., Desjardin, E., Passat, N.: Binary partition tree construction from multiple features for image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 84, 237–250 (2018)
Randrianasoa, J.F., Kurtz, C., Gançarski, P., Desjardin, E., Passat, N.: Evaluating the quality of binary partition trees based on uncertain semantic ground-truth for image segmentation. In: ICIP, Proceedings, pp. 3874–3878 (2017)
Randrianasoa, J.F., Kurtz, C., Gançarski, P., Desjardin, E., Passat, N.: Intrinsic quality analysis of binary partition trees. In: ICPRAI, Proceedings, pp. 114–119 (2018)
Romero, J.E.: CERES: a new cerebellum lobule segmentation method. NeuroImage 147, 916–924 (2017)
Rousseau, F., et al.: BTK: an open-source toolkit for fetal brain MR image processing. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 109, 65–73 (2013)
Saeed, N., Puri, B.: Cerebellum segmentation employing texture properties and knowledge based image processing: applied to normal adult controls and patients. Magn. Reson. Imaging 20, 425–429 (2002)
Salembier, P., Garrido, L.: Binary partition tree as an efficient representation for image processing, segmentation, and information retrieval. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9, 561–576 (2000)
Salembier, P., Wilkinson, M.H.F.: Connected operators: a review of region-based morphological image processing techniques. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 26, 136–157 (2009)
Serag, A., et al.: Accurate learning with few atlases (ALFA): an algorithm for MRI neonatal brain extraction and comparison with 11 publicly available methods. Sci. Rep. 6, 23470 (2016)
Stoodley, C.J., Limperopoulos, C.: Structure-function relationships in the developing cerebellum: evidence from early-life cerebellar injury and neurodevelopmental disorders. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 21, 356–364 (2016)
Tustison, N.J., et al.: N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 29, 1310–1320 (2010)
Wang, L., Shi, F., Lin, W., Gilmore, J.H., Shen, D.: Automatic segmentation of neonatal images using convex optimization and coupled level sets. NeuroImage 58, 805–817 (2011)
Wang, L., Shi, F., Yap, P.T., Gilmore, J.H., Lin, W., Shen, D.: 4D multi-modality tissue segmentation of serial infant images. PLoS One 7, e44596 (2012)
Xue, H., et al.: Automatic segmentation and reconstruction of the cortex from neonatal MRI. NeuroImage 38, 461–477 (2007)
Yang, Z., et al.: Automated cerebellar lobule segmentation with application to cerebellar structural analysis in cerebellar disease. NeuroImage 127, 435–444 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cettour-Janet, P. et al. (2019). Hierarchical Approach for Neonate Cerebellum Segmentation from MRI: An Experimental Study. In: Burgeth, B., Kleefeld, A., Naegel, B., Passat, N., Perret, B. (eds) Mathematical Morphology and Its Applications to Signal and Image Processing. ISMM 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11564. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20867-7_37
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20867-7_37
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-20866-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-20867-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)