Abstract
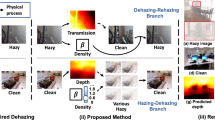
In this paper we propose a novel end-to-end convolution dehazing architecture, called De-Haze and Smoke GAN (DHSGAN). The model is trained under a generative adversarial network framework to effectively learn the underlying distribution of clean images for the generation of realistic haze-free images. We train the model on a dataset that is synthesized to include image degradation scenarios from varied conditions of fog, haze, and smoke in both indoor and outdoor settings. Experimental results on both synthetic and natural degraded images demonstrate that our method shows significant robustness over different haze conditions in comparison to the state-of-the-art methods. A group of studies are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of each module of the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, D., Treibitz, T., Avidan, S.: Non-local image dehazing. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1674–1682 (2016)
Berman, D., Treibitz, T., Avidan, S.: Air-light estimation using haze-lines. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography, pp. 1–9 (2017)
Cai, B., Xu, X., Jia, K., Qing, C., Tao, D.: DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(11), 5187–5198 (2016)
Chen, C., Do, M.N., Wang, J.: Robust image and video dehazing with visual artifact suppression via gradient residual minimization. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9906, pp. 576–591. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_36
Fattal, R.: Single image dehazing. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 27(3), 72 (2008)
Geiger, A., Lenz, P., Urtasun, R.: Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3354–3361 (2012)
Goodfellow, I.J., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
Gross, S., Wilber, M.: Training and investigating residual nets. Facebook AI Research, CA (2016). http://torch.ch/blog/2016/02/04/resnets.html
Handa, A., Whelan, T., McDonald, J., Davison, A.J.: A benchmark for RGB-D visual odometry, 3D reconstruction and SLAM. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 1524–1531 (2014)
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(12), 2341–2353 (2011)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1026–1034 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016)
Ioffe, S., Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 448–456 (2015)
Karras, T., Aila, T., Laine, S., Lehtinen, J.: Progressive growing of GANs for improved quality, stability, and variation. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2018)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.L.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1097–1105 (2012)
Ledig, C., et al.: Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 105–114 (2017)
Li, B., Peng, X., Wang, Z., Xu, J., Feng, D.: AOD-NET: all-in-one dehazing network. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4780–4788 (2017)
Li, B., et al.: Reside: a benchmark for single image dehazing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.04143 (2017)
Li, Y., You, S., Brown, M.S., Tan, R.T.: Haze visibility enhancement: a survey and quantitative benchmarking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 165, 1–16 (2017)
Liu, W., et al.: SSD: single shot multibox detector. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9905, pp. 21–37. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
McCartney, E.J., Hall, F.F.: Optics of the atmosphere: Scattering by molecules and particles. Phys. Today 30(5), 76–77 (1977)
McCormac, J., Handa, A., Leutenegger, S., Davison, A.J.: Scenenet RGB-D: Can 5M synthetic images beat generic imagenet pre-training on indoor segmentation? In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2697–2706 (2017)
Patraucean, V., Handa, A., Cipolla, R.: Spatio-temporal video autoencoder with differentiable memory. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06309 (2015)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R.B., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: NIPS 2015 Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 1, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Sharif Razavian, A., Azizpour, H., Sullivan, J., Carlsson, S.: CNN features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 806–813 (2014)
Shin, Y.S., Cho, Y., Pandey, G., Kim, A.: Estimation of ambient light and transmission map with common convolutional architecture. In: OCEANS 2016 MTS/IEEE Monterey, pp. 1–7, September 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/OCEANS.2016.7761342
Silberman, N., Hoiem, D., Kohli, P., Fergus, R.: Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S., Perona, P., Sato, Y., Schmid, C. (eds.) ECCV 2012. LNCS, vol. 7576, pp. 746–760. Springer, Heidelberg (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-33715-4_54
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2015)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
Tan, R.T.: Visibility in bad weather from a single image. In: 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8, June 2008
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Zhang, H., Patel, V.M.: Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3194–3203 (2018)
Zhang, H., Sindagi, V., Patel, V.M.: Image de-raining using a conditional generative adversarial network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.05957 (2017)
Zhu, J.Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2242–2251 (2017)
Zhu, Q., Mai, J., Shao, L.: A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3522–3533 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Malav, R., Kim, A., Sahoo, S.R., Pandey, G. (2019). DHSGAN: An End to End Dehazing Network for Fog and Smoke. In: Jawahar, C., Li, H., Mori, G., Schindler, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ACCV 2018. ACCV 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11365. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20873-8_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20873-8_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-20872-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-20873-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)