Abstract
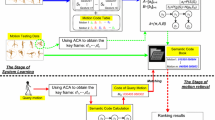
Motion retrieval has important practical value for the reuse of motion capture data. However, it is a challenging task to represent the motion data effectively due to the complexity of the motion data structure. As graph models is an effective way to represent structured data. This paper proposes a new method for human motion retrieval based on graph model. First, a method of graph model constructing based on Maximum Range of the Distance (MRD) is proposed. The MRD is used to select the joint pairs that are deemed important for a given motion, and different motions have different graph model structures. After that, similar motions can be retrieved by matching the similarity of the attributes of graph model. In the process of motion retrieval, cosine similarity is defined to measure the similarity of graph models. The experimental results show that the method proposed in this article is better than the previous methods of motion retrieval in many ways.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varkey, J.P., Pompili, D., Walls, T.A.: Human motion recognition using a wireless sensor-based wearable system. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 16(7), 897–910 (2012)
Xiao, J., et al.: Sketch-based human motion retrieval via selected 2D geometric posture descriptor. Sig. Process. 113, 1–8 (2015)
Chen, C., Liu, K., Kehtarnavaz, N.: Real-time human action recognition based on depth motion maps. J. R.-Time Image Process. 12(1), 155–163 (2016)
Li, M., Leung, H.: Graph-based approach for 3D human skeletal action recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 87, 195–202 (2017)
Li, M., et al.: 3D human motion retrieval using graph kernels based on adaptive graph construction. Comput. Graph. 54, 104–112 (2016)
CMU Graphics Lab Motion Capture Database. http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu/
Mocap Database HDM05. http://resources.mpi-inf.mpg.de/HDM05/
Muller, M., Roder, T., Clausen, M.: Efficient content-based retrieval of motion capture data. In: International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 677–685 (2005)
Muller, M., Roder, T.: Motion templates for automatic classification and retrieval of motion capture data. In: International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (2006)
Chen, S., et al.: Partial similarity human motion retrieval based on relative geometry features. In: Fourth International Conference on Digital Home (2012)
Liu, X.M., Zhao, D., Hao, A.M.: Human motion data retrieval based on dynamic time warping optimization algorithm. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 25(2), 352–360 (2012)
Liu, L., Lu, Y., Suen, C.Y.: Retrieval of envelope images using graph matching. In: International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (2011)
Xiao, Q., Wang, Y., Wang, H.: Motion retrieval using weighted graph matching. Soft. Comput. 19(1), 133–144 (2015)
Celiktutan, O., et al.: Fast exact hyper-graph matching with dynamic programming for spatio-temporal data. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 51(1), 1–21 (2015)
Zhou, L., et al.: Spatial temporal pyramid matching using temporal sparse representation for human motion retrieval. Vis. Comput. 30, 845–854 (2014)
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61402164 and 61751203), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT_15R07), Program for the Liaoning Distinguished Professor, by the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Dalian (No. 2018J12GX036), and by the High-level talent innovation support project of Dalian (No. 2017RD11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wu, Q., Liu, R., Zhou, D., Zhang, Q. (2019). 3D Human Motion Retrieval Based on Graph Model. In: El Rhalibi, A., Pan, Z., Jin, H., Ding, D., Navarro-Newball, A., Wang, Y. (eds) E-Learning and Games. Edutainment 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11462. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23712-7_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23712-7_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-23711-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-23712-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)