Abstract
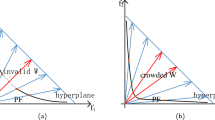
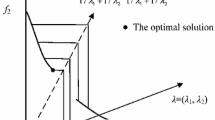
For solving multi-objective optimization problems with evolutionary algorithms, the decomposing the Pareto front by using a set of weight vectors is a promising approach. Although an appropriate distribution of weight vectors depends on the Pareto front shape, the uniformly distributed weight vector set is generally employed since the shape is unknown before the search. This work proposes a simple way to control the weight vector distribution appropriate for several Pareto front shapes. The proposed approach changes the distribution of the weight vector set based on the intermediate objective vector in the objective space. A user-defined parameter determines the intermediate objective vector in the static method, and the objective values of the obtained solutions dynamically determine the intermediate objective vector in the dynamic method. In this work, we focus on MOEA/D as a representative decomposition-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm and apply the proposed static and dynamic methods for it. The experimental results on WFG test problems with different Pareto front shapes show that the proposed static and dynamic methods improve the uniformity of the obtained solutions for several Pareto front shapes and the dynamic method can find an appropriate intermediate objective vector for each Pareto front shape.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deb, K.: Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms. Wiley, New York (2001)
Coello, C.A.C., Veldhuizen, D.A.V., Lamont, G.B.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston (2002)
Zhang, Q., Li, H.: MOEA/D: a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 11(6), 712–731 (2007)
Jiang, S., Cai, Z., Zhang, J., Ong, Y.S.: Multiobjective optimization by decomposition with Pareto-adaptive weight vectors. In: Proceedings of 2011 Natural Computation (ICNC), pp. 1260–1264 (2011)
Deb, K., Jain, H.: An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point based non-dominated sorting approach, Part II: handling constraints and extending to an adaptive approach. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 18(4), 602–622 (2014)
Hamada, N., Nagata, Y., Kobayashi, S., Ono, I.: On the stopping criterion of adaptive weighted aggregation for multiobjective continuous optimization. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Evol. Comput. 4(1), 13–27 (2013)
Hamada, N., Nagata, Y., Kobayashi, S., Ono, I.: BS-AWA: a more scalable adaptive weighted aggregation for continuous multiobjective optimization. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Evol. Comput. 5(1), 1–15 (2014)
Sato, H.: Analysis of inverted PBI and comparison with other scalarizing functions in decomposition based MOEAs. J. Heuristics 21(6), 819–849 (2015)
Li, K., Zhang, Q., Kwong, S., Li, M., Wang, R.: Stable matching based selection in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 18(6), 909–923 (2013)
Huband, S., Hingston, P., Barone, L., While, L.: A review of multi-objective test problems and a scalable test problem toolkit. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 10(5), 477–506 (2006)
Zitzler, E.: Evolutionary Algorithms for Multiobjective Optimization: Methods and Applications. Ph.D. thesis, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zurich (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Takagi, T., Takadama, K., Sato, H. (2019). A Distribution Control of Weight Vector Set for Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithms. In: Compagnoni, A., Casey, W., Cai, Y., Mishra, B. (eds) Bio-inspired Information and Communication Technologies. BICT 2019. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 289. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24202-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24202-2_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-24201-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-24202-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)