Abstract
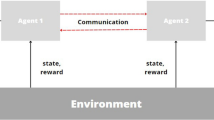
We present the application of multiagent reinforcement learning to the problem of traffic light signal control to decrease travel time. We model roads as a collection of agents for each signalized junction. Agents learn to set phases that jointly maximize a reward function that encourages short vehicle queuing delays and queue lengths at all junctions. The first approach that we tested exploits the fact that the reward function can be splitted into contributions per agent. Junctions are modeled as vertices in a coordination graph and the joint action is found with the variable elimination algorithm. The second method exploits the principle of locality to compute the best action for an agent as its best response for a two player game with each member of its neighborhood. We apply the learning methods to a simulated network of 6 intersections, using data from the Transit Department of Bogotá, Colombia. These methods obtained significant reductions in queuing delay with respect to the fixed time control, and in general achieve shorter travel times across the network than some other reinforcement learning based methods found in the literature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camponogara, E., Kraus, W.: Distributed learning agents in urban traffic control. In: Pires, F.M., Abreu, S. (eds.) EPIA 2003. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 2902, pp. 324–335. Springer, Heidelberg (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24580-3_38
Department, N.P.: Dnp advierte que se avecina colapso de movilidad en las principales capitales (2016). https://www.dnp.gov.co/Paginas/DNP advierte que se avecina colapso de movilidad en las principales capitales.aspx
El-Tantawy, S., Abdulhai, B., Abdelgawad, H.: Multiagent reinforcement learning for integrated network of adaptive traffic signal controllers (MARLIN-ATSC): methodology and large-scale application on downtown toronto. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 14(3), 1140–1150 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2013.2255286
Guestrin, C., Koller, D., Parr, R.: Multiagent planning with factored MDPS. In: NIPS-14, pp. 1523–1530. The MIT Press (2001)
Guestrin, C., Lagoudakis, M.G., Parr, R.: Coordinated reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2002, pp. 227–234. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco (2002)
Guestrin, C.E.: Planning under uncertainty in complex structured environments. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA (2003). https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/ac33/ea3606d5a50f3893b1d5dd964904a5291545.pdf
Kok, J.R.: Cooperation and learning in cooperative multiagent systems (2006)
Kok, J.R.: Cooperation and learning in cooperative multiagent systems. Ph.D. thesis, University of Amsterdam (2006)
Kok, J.R., Vlassis, N.: Collaborative multiagent reinforcement learning by payoff propagation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7(Sep), 1789–1828 (2006)
Krajzewicz, D., Erdmann, J., Behrisch, M., Bieker, L.: Recent development and applications of SUMO - Simulation of Urban MObility. Int. J. Adv. Syst. Measure. 5(3&4), 128–138 (2012)
Krajzewicz, D., Erdmann, J., Behrisch, M., Bieker, L.: Traci - SUMO (2017). http://sumo.dlr.de/wiki/TraCI
Li, T., Zhao, D., Yi, J.: Adaptive dynamic programming for multi-intersections traffic signal intelligent control. In: 2008 11th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 286–291 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITSC.2008.4732718
Bogota District Mobility Office: Vehicular Flow and Phase Diagrams (2015)
de Oliveira, D., Bazzan, A.L.C., da Silva, B.C., Basso, E.W., Nunes, L.: Reinforcement learning based control of traffic lights in non-stationary environments: a case study in a microscopic simulator. In: ResearchGate, vol. 223 (2006)
Richter, S., Aberdeen, D., Yu, J.: Natural actor-critic for road traffic optimisation. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2006, pp. 1169–1176. MIT Press, Canada (2006)
Robles, D., \(\tilde{\rm N}\)anez, P., Quijano, N.: Control y simulación de tráfico urbano en colombia: Estado del arte. Revista de Ingeniería 0, 59–69 (2009), https://ojsrevistaing.uniandes.edu.co/ojs/index.php/revista/article/view/245
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement Learning : An Introduction. MIT Press, Cambridge (1998). https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/reinforcement-learning
Wiering, M.: Multi-agent reinforcement learning for traffic light control (2000)
Xu, L.H., Xia, X.H., Luo, Q.: The study of reinforcement learning for traffic self-adaptive control under multiagent markov game environment. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, e962869 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/962869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Higuera, C., Lozano, F., Camacho, E.C., Higuera, C.H. (2019). Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Applied to Traffic Light Signal Control. In: Demazeau, Y., Matson, E., Corchado, J., De la Prieta, F. (eds) Advances in Practical Applications of Survivable Agents and Multi-Agent Systems: The PAAMS Collection. PAAMS 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11523. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24209-1_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24209-1_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-24208-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-24209-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)