Abstract
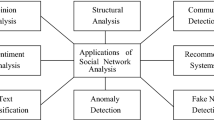
With the development of the technology, social software such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, QQ, WeChat has also achieved great development. According to the existing data, in the first quarter of 2018, WeChat’s monthly number has reached 1 billion [1]. At the same time, these large-scale nodes also carry a large amount of external information such as texts and pictures, forming a complex information network. Information networks are widely used in real life and have enormous academic and economic value. Academically, artificial intelligence, big data, deep learning and other technologies are developing rapidly. Large and complex neural networks and complex information networks urgently need to make a reasonable analysis of data [2]. In terms of application value, information networks and social networks also have a wide range of application scenarios, such as recommendation systems, community discovery and other tasks [3]. Therefore, the research and application of complex information networks is a hot issue in the field of artificial intelligence, and it is necessary to study it.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, M., Zhu, L., Zou, X.: A document vector representation based on Word2Vec. Comput. Sci. 43(06), 214–217+269 (2016)
Zhou, L.: The working principle and application of Word2vec. Sci. Technol. Inf. Dev. Econ. 25(02), 145–148 (2015)
Feng, W., Zhu, F., Liu, S.: Label discovery community discovery algorithm based on deep walk model. Comput. Eng. 44(03), 220–225+232 (2018)
Li, J., Zhao, Y., Wang, L.: A network representation method with multiple structures and text fusion. Comput. Sci. 45(07), 38–41+77 (2018)
Cao, S.: Graph node feature vector learning algorithm based on global information. Xidian University (2016)
Tang, J., Qu, M., Wang, M., et al.: LINE: large-scale information network embedding. In: International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, pp. 1067–1077 (2015)
Ding, J., Huang, T., Wang, J., Hu, W., Liu, J., Liu, Y.: Virtual network em-bedding through node connectivity. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 22(01), 17–23+56 (2015)
Wang, L., Qu, H., Zhao, J.: Virtual network embedding algorithm for load balance with various requests. Chin. J. Electron. 23(02), 382–387 (2014)
Chen, W., Zhang, Y., Li, X.: Netw. Represent. Learn. Big Data 1(03), 8–22+7 (2015)
Gong, S., Chen, J., Huang, C., Zhu, Q.: Trust-aware secure virtual network mapping algorithm. Trans. Commun. 36(11), 180–189 (2015)
Liu, S., Liu, H., He, C., Chao-bo, H.E.: Link prediction algorithm based on network representation learning and random walk. J. Comput. Appl. 37(08), 2234–2239 (2017)
Tu, C., Yang, C., Liu, Z., Sun, M.: Review of network representation learning. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 47(08), 980–996 (2017)
Cao, H., Qu, Z., Xue, Y., Yang, L.: Efficient virtual network embedding algorithm based on restrictive selection and optimization theory approach. China Commun. 14(10), 39–60 (2017)
Yang, Z., Guo, Y.: An exact virtual network embedding algorithm based on integer linear programming for virtual network request with location constraint. China Commun. 13(08), 177–183 (2016)
Xing, X., Wu, T.: Knowledge mapping and network representation learning. Ind. Technol. Forum 15(17), 61–62 (2016)
Hu, H., Zhang, F., Mao, Y., Wang, Z.: A forwarding map mapping algorithm based on regional topology information. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 18(11), 1854–1867 (2017)
Cao, H., Hu, H., Qu, Z., Yang, L.: Heuristic solutions of virtual network embedding: a survey. China Commun. 15(03), 186–219 (2018)
Chen, L., Zhu, Y., Qian, T., Zhu, H., Zhou, J.: Network representation learning model based on edge sampling. J. Softw. 29(03), 756–771 (2018)
Chai, Y., Liu, W., Si, Y., Qiu, J.: A review of research on knowledge semantic modeling technology for big data. Inf. Technol. Cyber Secur. 37(04), 11–17 (2018)
Liu, J., Wang, J., Wang, W.: Research and application of text network representation. China Sci. Technol. Pap. Online 10, 755–760 (2007)
Wang, W., Huang, W., Wu, L., Ke, W., Tang, W.: Network representation learning algorithm based on improved random walk. Comput. Appl. 1–6 (2018). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1307.TP.20180929.0951.024.html
A new algorithm based on the proximity principle for the virtual network embedding problem. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C (Comput. Electron.) 12(11), 910–918 (2011)
Wu, B.: Virtual network embedding algorithm based on resource locality index. In: Proceedings of 2016 2nd Workshop on Advanced Research and Technology in Industry Applications (WARTIA 2016), p. 8. International Society of Engineering and Engineering (2016)
Gong, S.: Energy-efficient virtual network embedding for heterogeneous networks. In: Proceedings of 2016 First IEEE International Conference on Computer Communication and the Internet (ICCCI 2016), p. 6. IEEE Huazhong Normal University (2016)
Lai, M.: Research on algorithm for virtual network embedding based on integer programming. In: Proceedings of 2015 3rd International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2015), p. 4. International Informatization and Engineering Associations, Atlantis Press (2015)
Liang, N.N.: Dynamic virtual network embedding based on auction-game theory. In: Proceedings of 2015 International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 2015), p. 6. International Society for Information and Engineering (2015)
Lin, R.: Virtual network embedding in flexi-grid optical networks. In: Proceedings of 2017 17th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT 2017), p. 6. IEEE Beijing Section, Sichuan Institute of Electronics (2017)
Zhu, Q.: Heuristic survivable virtual network embedding based on node migration and link remapping. In: Proceedings of 2014 IEEE 7th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference, p. 5. IEEE Beijing Section (2014)
Qin, Z.: Knowledge representation and its application based on semantic neural network. In: Proceedings of Global Manufacturing Advanced Forum and 21st Century Simulation Technology Seminar, p. 4. China System Simulation Society, Guizhou University, Guizhou Provincial Economic and Trade Commission, Guizhou Provincial Department of Science and Technology, Guizhou Provincial Information Industry Department, Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Association, Guiyang Municipal People’s Government (2004)
Zheng, D.: Reasoning strategy of knowledge representation of expert system based on pattern recognition and neural network. In: 1995 China Control Conference Proceedings (Part 2), p. 4. China Automation Society Control Theory Professional Committee (1995)
Qi, J., Liang, X., Li, Z., Chen, Y., Xu, Y.: Large-scale complex information network representation learning: concepts, methods and challenges. Chin. J. Comput. 41(10), 2394–2420 (2018)
Wu, S., Zhang, Z., Qian, Q.: Research on text representation model based on language network. Inf. Sci. 31(12), 119–125 (2013)
Lu, B., Huang, T., Sun, X., Chen, J., Liu, Y.: Dynamic recovery for survivable virtual network embedding. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 21(03), 77–84 (2014)
Cao, S., Lu, W., Xu, Q.: GraRep: Learning graph representations with global structural information. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM 2015), pp. 891–900. ACM, New York (2015). https://doi.org/10.1145/2806416.2806512
Liu, Z., Ma, H., Liu, S., Yang, Y., Li, X.: A network representation learning algorithm based on node text attribute information. Comput. Eng. 44(11), 165–171 (2018)
Xie, S.: Research on cross-network node association based on node representation. University of Electronic Science and Technology (2018)
Wen, W., Huang, J., Cai, R., Hao, Z., Wang, L.: A graph representation learning method based on prior information of nodes. J. Softw. 29(03), 786–798 (2018)
Tu, C., Yang, C., Liu, Z., Sun, M.: A review of network representation learning. Sci. Sin. Inf. Sci. 47(08), 980–996 (2017)
Zhao, S., Chen, J., Gong, S.: Virtual SDN network mapping algorithm based on particle swarm optimization. Comput. Eng. 42(12), 84–90 (2016)
Xiong, Z., Shen, Q., Wang, Y., et al.: Paragraph vector representation based on word to vector and CNN learning. CMC Comput. Mater. Contin. 55, 213–227 (2018)
Wang, C., Feng, Y., Li, T., et al.: A new encryption-then-compression scheme on gray images using the markov random field. Comput. Mater. Contin. 56(1), 107–121 (2018)
Gao, Z., Xia, S., Zhang, Y., et al.: Real-time visual tracking with compact shape and color feature. Comput. Mater. Contin. 55(3), 509–521 (2018)
Chen, Y., Yin, B., He, H., et al.: Reversible data hiding in classification-scrambling encrypted-image based on iterative recovery. CMC Comput. Mater. Contin. 56(2), 299–312 (2018)
Acknowledgement
This research was funded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61871140, 61872100, 61572153, U1636215), the National Key research and Development Plan (Grant No. 2018YFB0803504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, D., Wang, L., Qiu, J., Lu, H. (2019). A Review of Network Representation Learning. In: Sun, X., Pan, Z., Bertino, E. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Security. ICAIS 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11633. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24265-7_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24265-7_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-24264-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-24265-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)