Abstract
Context: A significant effort has been devoted to the design and implementation of various domain-specific modeling languages (DSMLs) for the software agents domain.
Problem: Language usability is often tackled in an ad-hoc way, with the collection of anecdotal evidence supporting the process. However, usability plays an important role in the productivity, learnability and, ultimately, in the adoption of a MAS DSML by agent developers.
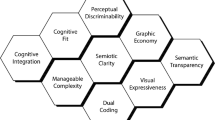
Method: In this chapter, we discuss how the principles of The “Physics” of Notations (PoN) can be applied to improve the visual notation of a MAS DSML, called SEA_ML and evaluate the result in terms of usability.
Results: The evolved version of the language, SEA_ML++, was perceived as significantly improved in terms of icons comprehensibility, adequacy and usability, as a direct result of employing the principles of PoN. However, users were not significantly more efficient and effective with SEA_ML++, suggesting these 2 properties were not chiefly constrained by the identified shortcomings of the SEA_ML concrete syntax.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barišić, A., Amaral, V., Goulão, M.: Usability driven DSL development with USE-ME. Comput. Lang. Syst. Struct. (ComLan) 51, 118–157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cl.2017.06.005
Basili, V., Caldiera, G., Rombach, H.: Goal question metric paradigm. Encycl. Softw. Eng. 1, 528–532 (2001)
Bergenti, F., Iotti, E., Monica, S., Poggi, A.: Agent-oriented model-driven development for JADE with the JADEL programming language. Comput. Lang. Syst. Struct. 50, 142–158 (2017)
Beydoun, G., et al.: FAML: a generic metamodel for mas development. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 35(6), 841–863 (2009)
Brooke, J.: SUS-a quick and dirty usability scale. Usability Eval. Ind. 189(194), 4–7 (1996)
Caire, P., Genon, N., Heymans, P., Moody, D.L.: Visual notation design 2.0: towards user comprehensible requirements engineering notations. In: RE 2013, pp. 115–124. IEEE (2013)
Challenger, M., Demirkol, S., Getir, S., Mernik, M., Kardas, G., Kosar, T.: On the use of a domain-specific modeling language in the development of multiagent systems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 28, 111–141 (2014)
Challenger, M., Kardas, G., Tekinerdogan, B.: A systematic approach to evaluating domain-specific modeling language environments for multi-agent systems. Softw. Qual. J. 24(3), 755–795 (2016)
Ciobanu, G., Juravle, C.: Flexible software architecture and language for mobile agents. Concurr. Comput. Pract. E 24(6), 559–571 (2012)
Da Silva, V.T., Choren, R., De Lucena, C.J.: MAS-ML: a multiagent system modelling language. IJAOSE 2(4), 382–421 (2008)
Demirkol, S., Challenger, M., Getir, S., Kosar, T., Kardas, G., Mernik, M.: Sea\(\_\)l: a domain-specific language for semantic web enabled multi-agent systems. In: 2012 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS), pp. 1373–1380. IEEE (2012)
Faccin, J., Nunes, I.: A tool-supported development method for improved BDI plan selection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 62, 195–213 (2017)
Gabriel, P., Goulão, M., Amaral, V.: Do software languages engineers evaluate their languages? In: Proceedings of the XIII Congreso Iberoamericano en “Software Engineering” (CIbSE 2010) (2011)
Gascueña, J.M., Navarro, E., Fernández-Caballero, A.: Model-driven engineering techniques for the development of multi-agent systems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 25(1), 159–173 (2012)
Genon, N., Amyot, D., Heymans, P.: Analysing the cognitive effectiveness of the UCM visual notation. In: Kraemer, F.A., Herrmann, P. (eds.) SAM 2010. LNCS, vol. 6598, pp. 221–240. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-21652-7_14
Genon, N., Heymans, P., Amyot, D.: Analysing the cognitive effectiveness of the BPMN 2.0 visual notation. In: Malloy, B., Staab, S., van den Brand, M. (eds.) SLE 2010. LNCS, vol. 6563, pp. 377–396. Springer, Heidelberg (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-19440-5_25
Gonçalves, E.J.T., et al.: MAS-ML 2.0: supporting the modelling of multi-agent systems with different agent architectures. J. Syst. Softw. 108, 77–109 (2015)
Granada, D., Vara, J.M., Brambilla, M., Bollati, V., Marcos, E.: Analysing the cognitive effectiveness of the webML visual notation. Softw. Syst. Model. 16(1), 195–227 (2017)
Hahn, C.: A domain specific modeling language for multiagent systems. In: Proceedings of the 7th international joint conference on Autonomous agents and multiagent systems, vol. 1, pp. 233–240 (2008)
Hosein Doost, S., Adamzadeh, T., Zamani, B., Fatemi, A.: A model-driven framework for developing multi-agent systems in emergency response environments. Softw. Syst. Model. 18, 1–28 (2017)
ISO: Standard graphical symbols: Safety colours and safety signs-registered safety signs (ISO 7010: 2003). International Standards Organisation (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland (2003)
ISO: ISO standard graphical symbols: Public information symbols (ISO 7001:2007). International Standards Organisation (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland (2007)
Johnson, P.: Human Computer Interaction: Psychology, Task Analysis, and Software Engineering. McGraw-Hill, London (1992)
Kardas, G., Bircan, E., Challenger, M.: Supporting the platform extensibility for the model-driven development of agent systems by the interoperability between domain-specific modeling languages of multi-agent systems. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 14(3), 875–912 (2017)
Kardas, G., Gomez-Sanz, J.J.: Special issue on model-driven engineering of multi-agent systems in theory and practice. Comput. Lang. Syst. Struct. 50, 140–141 (2017)
Kardas, G., Tezel, B.T., Challenger, M.: Domain-specific modelling language for belief-desire-intention software agents. IET Softw. 12(4), 356–364 (2018)
Matulevičius, R., Heymans, P.: Comparing goal modelling languages: an experiment. In: Sawyer, P., Paech, B., Heymans, P. (eds.) REFSQ 2007. LNCS, vol. 4542, pp. 18–32. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-73031-6_2
McGuinness, D.L., van Harmelen, F.: OWL web ontology language overview. W3C (2004)
Miranda, T.R.: Software language engineering : interaction and usability modeling of language editors. MSc thesis, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Monte Caparica, Portugal (2017)
Moody, D.: The “physics” of notations: toward a scientific basis for constructing visual notations in software engineering. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 35(6), 756–779 (2009)
Moody, D.L., Heymans, P., Matulevičius, R.: Visual syntax does matter: improving the cognitive effectiveness of the i* visual notation. Requir. Eng. 15(2), 141–175 (2010)
Nielsen, J.: How many test users in a usability study. Nielsen Norman, vol. 4, no. 06 (2012)
Pokahr, A., Braubach, L., Walczak, A., Lamersdorf, W.: JADEX-engineering goal-oriented agents. In: Developing multi-agent systems with JADE, pp. 254–258 (2007)
Saleh, F., El-Attar, M.: A scientific evaluation of the misuse case diagrams visual syntax. Inform. Softw. Tech. 66, 73–96 (2015)
Shadbolt, N., Berners-Lee, T., Hall, W.: The semantic web revisited. IEEE Intell. Syst. 21(3), 96–101 (2006)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the followings: (i) the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) under grant 115E591, and (ii) Portuguese grants NOVA LINCS Research Laboratory (Grant: FCT/MCTES PEst UID/ CEC/04516/2013) and DSML4MA Project (Grant: FCT/MCTES TUBITAK/0008/2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix A. Descriptions of the Selected SEA_ML Concepts
Appendix A. Descriptions of the Selected SEA_ML Concepts


Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Miranda, T. et al. (2019). Improving the Usability of a MAS DSML. In: Weyns, D., Mascardi, V., Ricci, A. (eds) Engineering Multi-Agent Systems. EMAS 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11375. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-25693-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-25693-7_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-25692-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-25693-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)