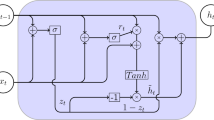
Abstract
The inference and prediction of fine-grained air quality are two important directions in urban air computing. Solving these two problems can provide useful information for urban environmental governance and residents’ health improvement. In this paper, we propose a general approach to solve these two problems with one model, while most other existing works use different models to solve them. Our model is based on deep bidirectional and unidirectional long short-term memory (DBU-LSTM) neural network, which can capture bidirectional temporal dependencies and spatial correlation from time series data containing spatial information. To infer and predict the air quality of the target region, we use the historical meteorological data of the target region and the historical air quality data of regions which are similar to the target. Urban heterogeneous data such as point of interest (POI) and road network are used to evaluate the similarities between urban regions. We also use a tensor decomposition method to complete the missing historical air quality data onto monitoring stations, which reduces the error of our model. We evaluated our approach on real data sources obtained in Beijing, and the results show its advantages over recent literature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amap. https://lbs.amap.com/api/webservice/guide/api/search. Accessed 4 June 2018
Bagieński, Z.: Traffic air quality index. Sci. Total Environ. 505, 606–614 (2015)
Basak, D., Pal, S., Patranabis, D.C.: Support vector regression. Neural Inf. Process. Lett. Rev. 11(10), 203–224 (2007)
Cho, K., et al.: Learning phrase representations using rnn encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078 (2014)
Graves, A., Jaitly, N., Mohamed, A.R.: Hybrid speech recognition with deep bidirectional lstm. In: 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU), pp. 273–278. IEEE (2013)
Graves, A., Schmidhuber, J.: Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Netw. 18(5–6), 602–610 (2005)
Grossberg, S.: Recurrent neural networks. Scholarpedia 8(2), 1888 (2013)
Hasenfratz, D., Saukh, O., Walser, C., Hueglin, C., Fierz, M., Thiele, L.: Pushing the spatio-temporal resolution limit of urban air pollution maps. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), pp. 69–77. IEEE (2014)
Kök, İ., Şimşek, M.U., Özdemir, S.: A deep learning model for air quality prediction in smart cities. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), pp. 1983–1990. IEEE (2017)
Kolda, T.G., Bader, B.W.: Tensor decompositions and applications. SIAM Rev. 51(3), 455–500 (2009)
Le, D.: Real-time air pollution prediction model based on spatiotemporal big data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.00432 (2018)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436 (2015)
OpenStreetMap. http://www.openstreetmap.org/. Accessed 4 June 2018
OpenWeatherMap. https://openweathermap.org/. Accessed 4 June 2018
Pearce, J.L., Beringer, J., Nicholls, N., Hyndman, R.J., Tapper, N.J.: Quantifying the influence of local meteorology on air quality using generalized additive models. Atmos. Environ. 45(6), 1328–1336 (2011)
Qi, Z., Wang, T., Song, G., Hu, W., Li, X., Zhang, Z.M.: Deep air learning: interpolation, prediction, and feature analysis of fine-grained air quality. IEEE Transact. Knowl. Data Eng. 30, 2285–2297 (2018)
Wong, D.W., Yuan, L., Perlin, S.A.: Comparison of spatial interpolation methods for the estimation of air quality data. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 14(5), 404 (2004)
Zhang, X., Gong, Z.: Spatiotemporal characteristics of urban air quality in china and geographic detection of their determinants. J. Geog. Sci. 28(5), 563–578 (2018)
Zheng, Y.: Forecasting fine-grained air quality based on big data (2015). https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/urban-air/. Accessed 4 June 2018
Zheng, Y., Capra, L., Wolfson, O., Yang, H.: Urban computing: concepts, methodologies, and applications. ACM Transact. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 5(3), 38 (2014)
Zheng, Y., Liu, F., Hsieh, H.P.: U-air: When urban air quality inference meets big data. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 1436–1444. ACM (2013)
Zheng, Y., Yi, X., Li, M., Li, R., Shan, Z., Chang, E., Li, T.: Forecasting fine-grained air quality based on big data. In: Proceedings of the 21th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 2267–2276. ACM (2015)
Zhu, J.Y., Sun, C., Li, V.O.: An extended spatio-temporal granger causality model for air quality estimation with heterogeneous urban big data. IEEE Transact. Big Data 3(3), 307–319 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ge, L., Zhou, A., Liu, J., Li, H. (2019). A Novel Approach for Air Quality Inference and Prediction Based on DBU-LSTM. In: Shao, J., Yiu, M., Toyoda, M., Zhang, D., Wang, W., Cui, B. (eds) Web and Big Data. APWeb-WAIM 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11641. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26072-9_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26072-9_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-26071-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-26072-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)