Abstract
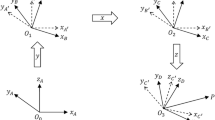
Though the kinematic parameters had been well identified, there are still existing some non-negligible non-geometric error sources such as friction, gear backlash, gear transmission, temperature variation etc. They need to be eliminated to further improve the accuracy of the robotic system. In this paper, a new hybrid calibration method for improving the absolute positioning accuracy of robot manipulators is proposed. The geometric errors and joint deflection errors are simultaneously calibrated by robot model identification technique and a radial basis function neural network is applied for compensating the robot positions errors, which are caused by the non-geometric error sources. A real implementation was performed with Hyundai HH800 robot and a laser tracker to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brisan, C., Hiller, M.: Aspects of calibration and control of PARTNER robots. In: 2006 IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, pp. 272–277. IEEE (2006)
Manne, R.: Analysis of two PLS algorithms for multivariate calibration. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2, 187–197 (1987)
Denavit, J., Hartenberg, R.S.: A kinematic notation for lower-pair mechanisms based on matrices. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 77, 215–221 (1955)
Hayati, S., Mirmirani, M.: Improving the absolute positioning accuracy of robot manipulators. J. Field Robot. 2, 397–413 (1985)
Hayati, S., Tso, K.S., Roston, G.: Robot geometry calibration. In: Proceedings. 1988 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA. IEEE (1988)
Mooring, B.W., Tang, G.R.: An improved method for identifying the kinematic parameters in a six-axis robot. In: Computers in Engineering Proceedings of the International Computers in Engineering Conference and Exhibit, pp. 79–84. ASME, Las Vegas, Nevada (1984)
Zhuang, H., Roth, Z.S., Hamano, F.: A complete and parametrically continuous kinematic model. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 8, 451–463 (1992)
Zhuang, H., Wang, L.K., Roth, Z.S.: Error-model-based robot calibration using a modified CPC model. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 10, 287–299 (1993)
Okamura, K., Park, F.: Kinematic calibration using the product of exponentials formula. Robotica 14(4), 415–421 (1996)
Chen, G., Kong, L., Li, Q., Wang, H., Lin, Z.: Complete, minimal and continuous error models for the kinematic calibration of parallel manipulators based on POE formula. Mech. Mach. Theory 121, 844–856 (2018)
Chen, G., Wang, H., Lin, Z.: Determination of the identifiable parameters in robot calibration based on the POE formula. IEEE Trans. Robot. 30(5), 1066–1077 (2014)
Zhou, J., Nguyen, H.N., Kang, H.J.: Simultaneous identification of joint compliance and kinematic parameters of industrial robots. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 15(11), 2257–2264 (2014)
Dumas, C., Caro, S., Garnier, S., Furet, B.: Joint stiffness identification of six-revolute industrial serial robots. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 27(4), 881–888 (2011)
Lightcap, C., Hamner, S., Schmitz, T., Banks, S.: Improved positioning accuracy of the PA10-6CE robot with geometric and flexibility calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. 24(2), 452–456 (2008)
Martinelli, A., Tomatis, N., Tapus, A., Siegwart, R.: Simultaneous localization and odometry calibration for mobile robot. In: Proceedings 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, pp. 1499–1504. IEEE (2004)
Song, Y., Zhang, J., Lian, B., Sun, T.: Kinematic calibration of a 5-DoF parallel kinematic machine. Precis. Eng. 45, 242–261 (2016)
Renders, J.M., Rossignol, E., Becquet, M., Hanus, R.: Kinematic calibration and geometrical parameter identification for robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 7(6), 721–732 (1991)
Zhou, J., Kang, H.J.: A hybrid least-squares genetic algorithm–based algorithm for simultaneous identification of geometric and compliance errors in industrial robots. Adv. Mech. Eng. 7(6), 1687814015590289 (2015)
Jiang, Z., Zhou, W., Li, H., Mo, Y., Ni, W., Huang, Q.: A new kind of accurate calibration method for robotic kinematic parameters based on the extended Kalman and particle filter algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(4), 3337–3345 (2018)
Barati, M., Khoogar, A.R., Nasirian, M.: Estimation and calibration of robot link parameters with intelligent techniques. Iran. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 7(4), 225–234 (2011)
Xie, X., Li, Z., Wang, G.: Manipulator calibration based on PSO-RBF neural network error model. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, Malang City, Indonesia, p. 020026. AIP Publishing (2018)
Jang, J.H., Kim, S.H., Kwak, Y.K.: Calibration of geometric and non-geometric errors of an industrial robot. Robotica 19(3), 311–321 (2001)
Tao, P.Y., Yang, G.: Calibration of industrial robots with product-of-exponential (POE) model and adaptive neural networks. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, Washington, USA, pp. 1448–1454. IEEE, May 2015
Kluk, P., Misiurski, G., Morawski, R.Z.: Total least squares versus RBF neural networks in static calibration of transducers. In: IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Sensing, Processing, Networking. IMTC Proceedings, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, pp. 424–427. IEEE (1997)
Liao, W.H., Aggarwal, J.K.: Curve and surface interpolation using rational radial basis functions. In: Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Vienna, Austria, pp. 8–13. IEEE (1996)
Park, J., Sandberg, I.W.: Universal approximation using radial-basis-function networks. Neural Comput. 3(2), 246–257 (1991)
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the 2019 Research fund of University of Ulsan, Ulsan, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Le, PN., Kang, HJ. (2019). A New Hybrid Calibration Method for Robot Manipulators by Combining Model–Based Identification Technique and a Radial Basis Function–Based Error Compensation. In: Huang, DS., Huang, ZK., Hussain, A. (eds) Intelligent Computing Methodologies. ICIC 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11645. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26766-7_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26766-7_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-26765-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-26766-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)