Abstract
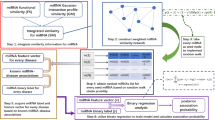
MicroRNAs (MiRNAs) have received much attention in recent years because growing evidences indicate that they play critical roles in tumor initiation and progression. Predicting underlying disease-related miRNAs from existing huge amount of biological data is a hot topic in biomedical research. Herein, we presented a novel computational model of logistic regression and random walk with restart algorithm for miRNA-disease association prediction (LRMDA) through integrating multi-source data. The model employs random walk with restart to fuse the association distribution between miRNAs and diseases and obtains highly discriminative feature from those heterogeneous data. To evaluate the performance of LRMDA, we performed 5-fold cross validation to compare it with several state-of-the-art models. As a result, our model achieves mean AUC of 0.9230 ± 0.0059. Besides, we carried out case study for predicting potential miRNAs related to Esophageal Neoplasms (EN). The achieved results indicate that 90% out of the top 50 prioritized miRNAs for EN are confirmed by biological experiments and further demonstrates the feasibility of our method. Therefore, LRMDA could potentially aid future research efforts for miRNA-disease association identification.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Victor, A.: The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431(7006), 350–355 (2004)
Chen, X., Xie, D., Wang, L., Zhao, Q., You, Z.-H., Liu, H.: BNPMDA: Bipartite Network Projection for MiRNA–Disease Association prediction. Bioinformatics 34, 3178–3186 (2018)
Wang, L., et al.: LMTRDA: using logistic model tree to predict miRNA-disease associations by fusing multi-source information of sequences and similarities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15(3), e1006865 (2019)
Kozomara, A., Birgaoanu, M., Griffiths-Jones, S.: miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1), D155–D162 (2018)
Lee, R.C., Feinbaum, R.L., Ambros, V.: The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75(5), 843 (1993)
Kozomara, A., Griffiths-Jones, S.: miRBase: annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database issue), D68–D73 (2014)
Cheng, A.M., Byrom, M.W., Jeffrey, S., Ford, L.P.: Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 33(4), 1290–1297 (2005)
Miska, E.A.: How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr. Opin. Gen. Dev. 15(5), 563–568 (2005)
Karp, X., Ambros, V.: Encountering MicroRNAs in cell fate signaling. Science 310(5752), 1288–1289 (2005)
Acunzo, M., Croce, C.M.: Downregulation of miR-15a and miR-16-1 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Chem. 62(4), 655–656 (2016)
Zhang, G., et al.: Downregulation of microRNA-181d had suppressive effect on pancreatic cancer development through inverse regulation of KNAIN2. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 39(4), 1010428317698364 (2017)
You, Z.-H., et al.: PRMDA: personalized recommendation-based MiRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 8(49), 85568 (2017)
Chen, X., et al.: A novel computational model based on super-disease and miRNA for potential miRNA–disease association prediction. Mol. BioSyst. 13(6), 1202–1212 (2017)
Chen, X., Gong, Y., Zhang, D.H., You, Z.H., Li, Z.W.: DRMDA: deep representations-based miRNA-disease association prediction. J. Cell Mol. Med. 22(1), 472–485 (2018)
Bandyopadhyay, S., Mitra, R., Maulik, U., Zhang, M.Q.: Development of the human cancer microRNA network. Silence 1(1), 6 (2010)
You, Z.H., et al.: PBMDA: a novel and effective path-based computational model for miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13(3), e1005455 (2017)
Chen, X., Huang, L.: LRSSLMDA: Laplacian Regularized Sparse Subspace Learning for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13(12), e1005912 (2017)
Jiang, Q., et al.: Prioritization of disease microRNAs through a human phenome-microRNAome network. BMC Syst. Biol. 4(s1), S2 (2010)
Shi, H., et al.: Walking the interactome to identify human miRNA-disease associations through the functional link between miRNA targets and disease genes. BMC Syst. Biol. 7, 101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-7-101
Chen, X., et al.: WBSMDA: Within and Between Score for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 21106 (2016)
Chen, X., Huang, L., Xie, D., Zhao, Q.: EGBMMDA: Extreme Gradient Boosting Machine for MiRNA-Disease Association prediction. Cell Death Dis. 9(1), 3 (2018)
Li, J.-Q., Rong, Z.-H., Chen, X., Yan, G.-Y., You, Z.-H.: MCMDA: matrix completion for MiRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 8(13), 21187–21199 (2017)
Huang, Y.-A., et al.: EPMDA: an expression-profile based computational model for microRNA-disease association prediction. Oncotarget 8(50), 87033 (2017)
Li, Y., et al.: HMDD v2.0: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(Database issue), D1070–D1074 (2014)
Wang, D., Wang, J., Lu, M., Song, F., Cui, Q.: Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinformatics 26(13), 1644–1650 (2010)
Xuan, P., et al.: Prediction of microRNAs associated with human diseases based on weighted k most similar neighbors. PLoS ONE 8(8), e70204 (2013)
Chen, X., Zhang, D.-H., You, Z.-H.: A heterogeneous label propagation approach to explore the potential associations between miRNA and disease. J. Transl. Med. 16(1), 348 (2018)
Jiang, Q., Wang, G., Jin, S., Li, Y., Wang, Y.: Predicting human microRNA-disease associations based on support vector machine. Int. J. Data Min. Bioinform. 8(3), 282–293 (2013)
Li, Z.W., et al.: Accurate prediction of protein-protein interactions by integrating potential evolutionary information embedded in PSSM profile and discriminative vector machine classifier. Oncotarget 8(14), 23638 (2017)
An, J.Y., et al.: Identification of self-interacting proteins by exploring evolutionary information embedded in PSI-BLAST-constructed position specific scoring matrix. Oncotarget 7(50), 82440–82449 (2016)
Li, Z., et al.: In silico prediction of drug-target interaction networks based on drug chemical structure and protein sequences. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 11174 (2017)
Köhler, S., Bauer, S., Horn, D., Robinson, P.N.: Walking the interactome for prioritization of candidate disease genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82(4), 949–958 (2008)
Wei, L., Wu, S., Zhang, J., Xu, Y.: Random walk based global feature for disease gene identification. In: Tan, T., Li, X., Chen, X., Zhou, J., Yang, J., Cheng, H. (eds.) CCPR 2016. CCIS, vol. 663, pp. 464–473. Springer, Singapore (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3005-5_38
Yang, Z., et al.: dbDEMC: a database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. BMC Genom. 11(Suppl 4), S5 (2010)
Jiang, Q., et al.: miR2Disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database), D98–D104 (2009)
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R.L., Torre, L.A., Jemal, A.: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68(6), 394–424 (2018)
Zhang, C., et al.: Expression profile of MicroRNAs in serum: a fingerprint for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Chem. 56(12), 1871–1879 (2010)
Shen, F., et al.: Genetic variants in miR-196a2 and miR-499 are associated with susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese Han population. Tumor Biol. 37(4), 4777–4784 (2016)
Zhao-Li, C., et al.: microRNA-92a promotes lymph node metastasis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via E-cadherin. J. Biol. Chem. 286(12), 10725–10734 (2011)
Sun, Y., Yu, X., Bai, Q.: miR-204 inhibits invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting FOXM1 in esophageal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8(10), 12775–12783 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61873270, 61732012), the Jiangsu Postdoctoral Innovation Plan (Grant No. 1701031C), and the Jiangsu Shuangchuang Talents Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, Z., Nie, R., You, Z., Zhao, Y., Ge, X., Wang, Y. (2019). LRMDA: Using Logistic Regression and Random Walk with Restart for MiRNA-Disease Association Prediction. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Huang, ZK. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11644. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26969-2_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26969-2_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-26968-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-26969-2
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)