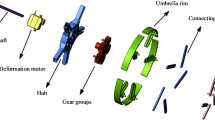
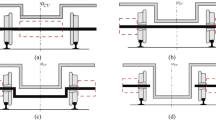
Abstract
Facing with the problem of high labor intensity, low standard of automation and low production efficiency, traditional pattern of rocket cabins transportation should be eliminated. The traditional way was still unable to cope with the mixed flow of multiple series and types of rocket cabin. Hence, it is of great significance to design an AGV with good stability, good driving performance and load capacity as the transport equipment of the rocket cabin. A heavy load Omnidirectional AGV for rocket cabin transportation is proposed. A kinematic model of the AGV was set up and analyzed by the software of ADAMS (Automatic Dynamic Analysis of Mechanical Systems). Results of the ADAMS simulation indicate that the driving mechanism of the automatic guide vehicle in this study performs well in most working conditions, and the problem of “locked up” in the transverse working conditions has also been well solved. It is of great reference significance to the research of the heavy-duty automatic guided vehicle for large segment transshipment.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campion, G., Bastin, G., D’Andrea-Novel, B.: Structural properties and classification of kinematic and dynamic models of wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 12(1), 47–62 (1996)
Zhao, D., Yi, J., Deng, X.: Structure and kinematic analysis of omni-directional mobile robots. Robot. 25(5), 394–398 (2003)
Siegwart, R., Nourbakhsh, I.R., Scaramuzza, D.: Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots. The MIT Press, Cambridge (2012)
Jaulin, L.: Mobile Robotics. ISTE Press, London (2015)
Niku, S.B.: Introduction to Robotics: Analysis, Control, Applications, 2nd edn. Willey, Hoboken (2011)
Craig, J.J.: Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control, 4th edn. Pearson Education, London (2018)
Huang, C., Yang, C., Huang, J.Y.: Path tracking of an autonomous ground vehiclewith different paylosds by hierarchical improved fuzzy dynamic sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(2), 899–914 (2018)
Kodagoda, K.R.S., Wijesoma, W.S., Teoh, E.K.: Fuzzy speed and steering control of an AGV. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 10(1), 112–120 (2002)
Lee, S., Yang, H.: Navigation of automated guided vehicles using magnet spot guidance method. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 28, 425–436 (2012)
Williams, R.L., Carter, B.E., Gallina, P., Rosati, G.: Dynamic model with slip for wheeled omnidirectional robots
Martínez-Barberá, H., Herrero-Pérez, D.: Autonomous navigation of an automated guided vehicle in industrial environments. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 26, 296–311 (2010)
Tahboub, K.A., Asada, H.H.: Dynamics analysis and control of a holonomic vehicle with a continuously variable transmission. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 124(3), 118–126 (2002)
Wilson, L., Williams, C., Yance, J., et al.: Design and modeling of a redundant omnidirectional RoboCup goalie. In: Proceedings RoboCup 2001 International Symposium, Seattle (2001)
Wang, K., Shi, W., Yang, C., Yao, W., Ya, H., Chen, X., et al.: Commercial vehicle cab suspension system vibration modes and transmission characteristics by means of ADAMS. J. Jilin Univ. (Eng. Technol. Ed.) 40(2), 330–334 (2010)
Carter, B., Good, M., Dorohoff, M., et al.: Mechanical design and modeling of an omnidirectional RoboCup player. In: RoboCup AI Conference, Seattle, W A, pp. 1–10 (2001)
Paromtchik, I.E., Rembold, U.A.: Motion generation approach for an omnidirectional vehicle. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, pp. 1213–1218 (2000)
Holmberg, R., Khatib, O.: Development and control of a holonomic mobile robot for mobile manipulation tasks. Int. J. Robot. Res. 19(11), 1066–1074 (2000)
Park, T.B., Lee, J.H., Yi, B.J., et al.: Optimal design and actuator sizing of redundantly actuated omni-directional mobile robots. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco (2002)
Moore, K.L., Flann, N.S.: A six-wheeled omnidirectional autonomous mobile robot. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 20(6), 53–66 (2000)
Schramm, D., Hiller, M., Bardini, R.: Vehicle Dynamics: Modeling and Simulation, p. 8 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Y., Xu, Zg., Liu, Sk., Wang, Qy. (2019). Design and Simulation of Heavy Load Wheeled Mobile Robot Driving Mechanism. In: Yu, H., Liu, J., Liu, L., Ju, Z., Liu, Y., Zhou, D. (eds) Intelligent Robotics and Applications. ICIRA 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11745. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27529-7_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27529-7_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-27528-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-27529-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)