Abstract
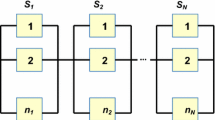
This paper addresses the issue of optimal allocation of spare modules in complex series-parallel redundant systems in order to obtain a required reliability under cost constraints. To solve this optimization problem, an analytical method based on the Lagrange multipliers technique is first applied. Then the results are improved by using other optimization methods such as an evolutionary algorithm and an original fine tuning algorithm based on the idea of hill climbing. The numerical results highlight the advantage of combining analytical approaches with fine tuning algorithms in case of very large systems. By using such a combined technique, better solutions are obtained than those given by classic heuristic search algorithms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tillman, F.A., Hwang, C.L., Kuo, W.: Optimization techniques for system reliability with redundancy. A review. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 26, 148–155 (1977)
Tillman, F.A., Hwang, C.L., Kuo, W.: Optimization of System Reliability. Marcel Dekker, New York (1980)
Shooman, M.: Reliability of Computer Systems and Networks, pp. 331–383. Wiley, New York (2002)
Misra, K.B. (ed.): Handbook of Performability Engineering, pp. 499–532. Springer, London (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84800-131-2
Chern, M.: On the computational complexity of reliability redundancy allocation in series system. Oper. Res. Lett. 11, 309–315 (1992)
Albert, A.A.: A measure of the effort required to increase reliability. Technical report No. 43, Stanford University, Applied Mathematics and Statistics Laboratory (1958)
Misra, K.B.: A simple approach for constrained redundancy optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. R-20(3), 117–120 (1971)
Agarwal, K.K., Gupta, J.S.: On minimizing the cost of reliable systems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. R-24, 205–206 (1975)
Rajendra Prasad, V., Nair, K.P.K., Aneja, Y.P.: A heuristic approach to optimal assignment of components to parallel-series network. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 40(5), 555–558 (1992)
El-Neweihi, E., Proschan, F., Sethuraman, J.: Optimal allocation of components in parallel-series and series-parallel systems. J. Appl. Probab. 23(3), 770–777 (1986)
Everett, H.: Generalized Lagrange multiplier method of solving problems of optimal allocation of resources. Oper. Res. 11, 399–417 (1963)
Misra, K.B.: Reliability optimization of a series-parallel system, part I: Lagrangian multipliers approach, part II: maximum principle approach. IEEE Trans. Reliab. R-21, 230–238 (1972)
Blischke, W.R., Prabhakar, D.N.: Reliability: Modelling, Prediction, and Optimization. Wiley, New York (2000)
Belmann, R., Dreyfus, S.: Dynamic programming and the reliability of multi-component devices. Oper. Res. 6(2), 200–206 (1958)
Coit, D.W., Smith, A.E.: Reliability optimization of series-parallel systems using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 45, 254–260 (1996)
Marseguerra, M., Zio, E.: System design optimization by genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium, Los Angeles, CA, pp. 222–227. IEEE (2000)
Agarwal, M., Gupta, R.: Genetic search for redundancy optimization in complex systems. J. Qual. Maintenance Eng. 12(4), 338–353 (2006)
Romera, R., Valdes, J.E., Zequeira, R.I.: Active redundancy allocation in systems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 53(3), 313–318 (2004)
Shooman, M.L., Marshall, C.: A mathematical formulation of reliability optimized design. In: Henry, J., Yvon, J.P. (eds.) System Modelling and Optimization. LNCIS, vol. 197, pp. 941–950. Springer, Heidelberg (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0035543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Cașcaval, P., Leon, F. (2019). Active Redundancy Allocation in Complex Systems by Using Different Optimization Methods. In: Nguyen, N., Chbeir, R., Exposito, E., Aniorté, P., Trawiński, B. (eds) Computational Collective Intelligence. ICCCI 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11683. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28377-3_52
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28377-3_52
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-28376-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-28377-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)